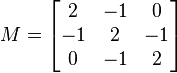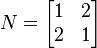Positive-definite matrix
来源:互联网 发布:java可变参数 定义 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/19 01:58
In linear algebra, a symmetric n × n real matrix M is said to be positive definite if zTMz is positive for every non-zero columnvectorz of n real numbers. Here zT denotes thetranspose ofz.
- The real symmetric matrix
- is positive definite since for any non-zero column vector z with entriesa,b and c, we have
- This result is a sum of squares, and therefore non-negative; and is zero only ifa =b = c = 0, that is, when z is zero.
- The real symmetric matrix
is not positive definite. If z is the vector
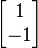 , one has
, one has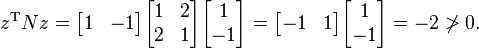
More generally, an n × n Hermitian matrix M is said to be positive definite ifz*Mz is real and positive for all non-zero complex vectors z. Herez* denotes the conjugate transpose of z.
- 摘自:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Positive_semidefinite_matrix
0 0
- Positive Semi-definite matrix
- Positive-definite matrix
- 正定矩阵(Positive-definite Matrix)
- 正定矩阵 Positive definite matrix
- 正定矩阵(Positive-definite Matrix)
- positive definite quadratic form and positive definite matrix
- Positive-definite matrix(正定矩阵)
- 正定矩阵(positive definite matrix)
- Positive-definite kernel
- 正定矩阵(definite matrix)
- Strictly Positive Matrix CodeForces
- HMM 做训练的 Sigma not positive definite (非正定的)原因及处理办法
- CF(Strictly Positive Matrix) 强连通分量
- CodeForces 402E Strictly Positive Matrix
- Definite Values
- Codeforces Round #236 (Div. 2) E. Strictly Positive Matrix
- CF DIV2 236E Strictly Positive Matrix(强连通)
- cf402EStrictly Positive Matrix【tarjan前向星模板、矩阵】
- Android编译问题小汇总
- Raw-OS源码分析之消息系统-Queue_Buffer
- 基于JQuery框架的AJAX实例代码
- [LeetCode]Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
- Android应用中实现系统“分享”接口
- Positive-definite matrix
- 《App,这样设计才好卖》
- java Process抽象类
- 模拟赛 数列的期望
- 如何找回回收站删除的图片
- plot函数参数
- VS注释与取消注释快捷键
- JSON与XML的区别比较
- iOS通过iTunes search检测版本更新,并提示用户更新!