akka actor中FSM有限状态机的设计原则
来源:互联网 发布:如何查看计算机mac地址 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 00:16
akka actor中的FSM有限状态机的设计原则参考了erlang中的FSM(http://www.erlang.org/documentation/doc-4.8.2/doc/design_principles/fsm.html)
许多应用程序可以利用FSMs来设计,Protocol stacks是其中的一个例子。
我们可以用一个关系集合来描述一个FSM,形式如下:
State(S) x Event(E) -> Actions (A), State(S')...这些关系可以被解释为如下含义:
If we are in state S and the event E occurs, we should perform the actions A and make a transition to the state S'. 如果当前状态处于S,且事件E发生了的话,我们应该执行行为A,并把状态转移到S'
如果用Erlang的gen_fsm行为来编程的话,上述转换规则可以用如下代码来表示:
StateName(Event, StateData) -> .. code for actions here ... {next_state, StateName', StateData'}下图用一个简单的FSM来描述”Plain Ordinary Telephony Service“(POTS, 一般的电话服务)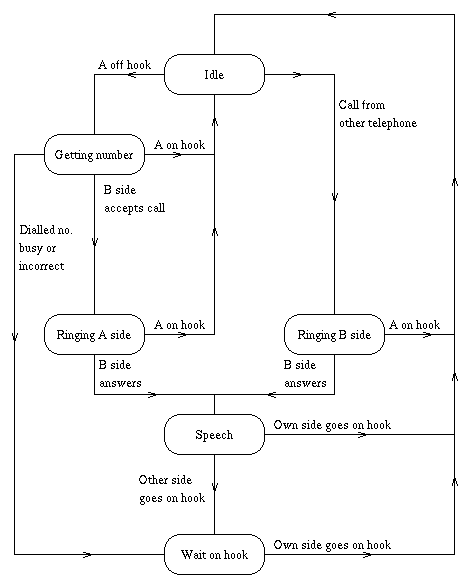
电话服务POTS FSM可以用以下gen_fsm行为来描述:
init(A) -> {ok, idle, A}.idle({off_hook, A}, A) -> {next_state, getting_number, {A,[]}};idle({seize, A}, B) when A /= B -> {next_state, ringing_b_side, {B, A});idle(_, A) -> {next_state, idle, A}.getting_number({digit, D}, {A, Seq}) -> case ... of ... -> ... {next_state, ringing_a_side, {A, B}}; ... -> ... {next_state, getting_number, {A, Seq1}}; ... -> ... {next_state, wait_on_hook, A} end;getting_number({on_hook, A}, {A,_}) -> {next_state, idle, A}.ringing_a_side({on_hook, A}, {A, B}) -> {next_state, idle, A};ringing_a_side({answered, B}, {A, B}) -> {next_state, speech, {A,B}}.ringing_b_side({on_hook, A}, {B, A}) -> {next_state, idle, B};ringing_b_side({off_hook, B}, {B, A}) -> {next_state, speech, {B, A}}.speech({on_hook, A}, {A, B}) -> {next_state, idle, A};speech({on_hook, B}, {A, B}) -> {next_state, wait_on_hook, A}.wait_on_hook({on_hook, A}, A) -> {next_state, idle, A}.上述代码只是描述了状态转移。为了增加行为,需要增加以下代码:getting_number({digit, D}, {A, Seq}) -> Seq1 = Seq ++ [D], case number_analyser:analyse(Seq1) of {user, B} -> hw:seize(B, A), {next_state, ringing_a_side, {A, B}}; get_more_digits -> {next_state, getting_number, {A, Seq1}}; invalid_number -> hw:send_nasty_tone(A, bad_number_tone), {next_state, wait_on_hook, A} end;getting_number({on_hook, A}, {A,_}) -> hw:stop_codec(A), {next_state, idle, A}.为了完成这个例子,我们需要把FSM和时间生成器程序打包成behaviour模型,然后增加FSM相关的代码,如下所示:
-module(pots).-behaviour(gen_fsm).-export([...]).start() -> gen_fsm:start(...)stop() -> gen_fsm:send_all_state_event(...)on_hook(A) -> gen_fsm:send_event(..., {off_hook, A})....一个FSM的例子:上面的POTS例子并没有包含全部的细节。下面的小例子是完整的:
-module(test1_fsm).-behaviour(gen_fsm).%% interface routines%% start us upstart() -> gen_fsm:start({local, hello}, test1_fsm, [], []).%% send a hello -- this will end up in the FSM routineshello() -> gen_fsm:send_event(hello, {hello, self()}).%% send a stop this will end up in "handle_event"stop() -> gen_fsm:send_all_state_event(hello, stopit).%% -- interface end%% This initialisation routine gets calledinit(_) -> {ok, idle, []}.%% The state machineidle({hello, A}, []) -> {next_state, one, A}.one({hello, B}, A) -> A ! {hello, B}, B ! {hello, A}, {next_state, idle, []}.%% this handles events in *any* statehandle_event(stopit, AnyState, TheStateData) -> {stop, i_shall_stop, []}. %% tell it to stop%% This is the finalisation routine - it gets called%% When we have to stopterminate(i_shall_stop, TheStateIwasIn, TheStateData) -> ok.------------------------------华丽的分割线----------------------------------------------------------------
上面主要讲的是Erlang中的FSM的使用,下面来正式介绍Akka 中的FSM。为了展示Akka FSM特质的大部分特性,我们假设一个Actor接收和存队列大量的爆发式传过来的消息,在消息爆发过后,转发或者清除消息。
to be continued...........
0 0
- akka actor中FSM有限状态机的设计原则
- FPGA--有限状态机(FSM)的设计
- Unity3D-FSM有限状态机的简单设计
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现
- Unity3D-FSM有限状态机的简单设计
- 有限状态机FSM的设计与实现
- 有限状态机(FSM)设计原理
- 有限状态机FSM的理解
- 有限状态机FSM的理解
- 对于akka中,actor模型的理解。
- 【Akka】Akka中actor的生命周期与DeathWatch监控
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现(一)
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现(一)
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现(1)
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现(二)
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现(一)
- 有限状态机(FSM)的设计与实现(二)
- 设计模式_实现简单的有限状态机(FSM)
- IIS设置静态内容缓存时间
- HTTP
- Android Service 服务(一)—— Service
- 揭秘:过亿App的前100万用户怎么来的
- java jtds 连接数据库
- akka actor中FSM有限状态机的设计原则
- SQL Server中Row_number() 和 Rank() 的用法
- 职场的你需要谨慎
- c#关键词implicit和explicit
- Using Java 6 Processors in Eclipse
- java OOP中常用的设计原则
- Python查缺补漏之一 动态实例属性、引用、转义
- cmos 导通的电压关系
- JAVA的时间处理类——Date类与Calendar类


