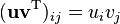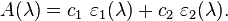化学计量学中一些重要的概念
来源:互联网 发布:域名whois反查 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/17 00:02
1.向量内积实际上是投影运算
Definition (matrix multiplication)
The outer product u ⊗ v is equivalent to a matrix multiplication uvT, provided that u is represented as a m × 1 column vector and v as a n × 1 column vector (which makes vT a row vector).[1]For instance, if m = 4 and n = 3, then
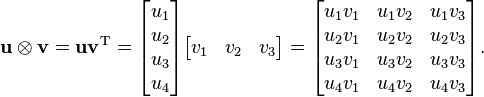
Or in index notation:
For complex vectors, it is customary to use the conjugate transpose of v (denoted vH):
Contrast with inner product[edit]
If m = n, then one can take the matrix product the other way, yielding a scalar (or 1 × 1 matrix):
which is the standard inner product for Euclidean vector spaces, better known as the dot product. The inner product is the trace of the outer product.
Rank of an outer product[edit]
If u and v are both nonzero then the outer product matrix uvT always has matrix rank 1, as can be easily seen by multiplying it with a vector x:
which is just a scalar vTx multiplied by a vector u.
("Matrix rank" should not be confused with "tensor order", or "tensor degree", which is sometimes referred to as "rank".)
4.矩阵的秩(对化学方面的意义)- 1.如果物质测量的得到的矩阵只有秩为1,则证明物质中只有一个化合物
- 重要性质:只要知道矩阵的秩是多少,就明白这里面有多少个化合物
- 2.beer-lambert law -matrix
Chemical analysis[edit]
Beer's law can be applied to the analysis of a mixture by spectrophotometry, without the need for extensive pre-processing of the sample. An example is the determination of bilirubin in blood plasma samples. The spectrum of pure bilirubin is known, so the molar attenuation coefficient is known. Measurements are made at one wavelength that is nearly unique for bilirubin and at a second wavelength in order to correct for possible interferences.The concentration is given by c = Acorrected / ε. For a more complicated example, consider a mixture in solution containing two components at concentrations c1 and c2. The absorbance at any wavelength, λ is, for unit path length, given by
Therefore, measurements at two wavelengths yields two equations in two unknowns and will suffice to determine the concentrations c1 and c2 as long as the molar absorbances of the two components, ε1 and ε2 are known at both wavelengths. This two system equation can be solved using Cramer's rule. In practice it is better to use linear least squares to determine the two concentrations from measurements made at more than two wavelengths. Mixtures containing more than two components can be analyzed in the same way, using a minimum of n wavelengths for a mixture containing n components. The law is used widely in infra-red spectroscopy and near-infrared spectroscopy for analysis of polymer degradation and oxidation (also in biological tissue). Thecarbonyl group attenuation at about 6 micrometres can be detected quite easily, and degree of oxidation of the polymer calculated.
- 5.矩阵的秩的重要意义
- (1)转置后秩不变(2)r(A)<=min(m,n),A是m*n型矩阵(3)r(kA)=r(A),k不等于0(4)r(A)=0 <=> A=0(5)r(A+B)<=r(A)+r(B)(6)r(AB)<=min(r(A),r(B))(7)r(A)+r(B)-n<=r(AB)特别的:A:m*n,B:n*s,AB=0 -> r(A)+r(B)<=n(8)P,Q为可逆矩阵, 则 r(PA)=r(A)=r(AQ)=r(PAQ)
- 化学计量学中一些重要的概念
- Struts2中一些重要概念的理解
- Storm中一些重要的概念
- CSS中一些重要概念
- AOP的一些重要概念
- 数据库的一些重要概念
- 一些重要概念的回顾
- Hbase的一些重要概念
- 计算机系统的一些重要概念
- linux文件系统中一些重要概念的分析
- OpenERP的开发中,有如下一些重要概念
- 【java】一些重要的概念理解
- 关于Extjs一些重要概念的领悟
- spark配置环境的一些重要概念
- 有关数学的一些重要概念
- 一些重要概念
- Android学习笔记2-开发过程中一些重要概念
- JMS中一些重要概念和实例展示
- 【代码】命名规范
- WebForm 获取实体类的数据,填充页面(用AJAX异步获取值,和用session传值)
- 串口通信之项目实例一
- 如何用地址栏查看网页的源代码
- css3 transform
- 化学计量学中一些重要的概念
- btrace 学习笔记
- 十八、运算符重载(二)++运算符重载、!运算符重载、赋值运算符重载、Integer和String的初步实现
- 15.2010 年中兴面试题
- cocos2dx中创建裁剪区域 实现在指定区域精灵才能出现
- 计算机网络的基础知识
- Cocos2d-x 随机数 CCRANDOM_0_1()
- 用quick制作仿PkrCruncher
- java web查询某个时间段记录