cf. #304 div.2
来源:互联网 发布:js异步 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/29 22:41
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546点击打开链接
前三题难度不大,不过时间只有2小时,看来我是得加快做题的效率呀 。
。
A soldier wants to buy w bananas in the shop. He has to pay k dollars for the first banana, 2k dollars for the second one and so on (in other words, he has to pay i·k dollars for the i-th banana).
He has n dollars. How many dollars does he have to borrow from his friend soldier to buy w bananas?
The first line contains three positive integers k, n, w (1 ≤ k, w ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ n ≤ 109), the cost of the first banana, initial number of dollars the soldier has and number of bananas he wants.
Output one integer — the amount of dollars that the soldier must borrow from his friend. If he doesn't have to borrow money, output 0.
3 17 4
13
Colonel has n badges. He wants to give one badge to every of his n soldiers. Each badge has a coolness factor, which shows how much it's owner reached. Coolness factor can be increased by one for the cost of one coin.
For every pair of soldiers one of them should get a badge with strictly higher factor than the second one. Exact values of their factors aren't important, they just need to have distinct factors.
Colonel knows, which soldier is supposed to get which badge initially, but there is a problem. Some of badges may have the same factor of coolness. Help him and calculate how much money has to be paid for making all badges have different factors of coolness.
First line of input consists of one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000).
Next line consists of n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ n), which stand for coolness factor of each badge.
Output single integer — minimum amount of coins the colonel has to pay.
41 3 1 4
1
51 2 3 2 5
2
In first sample test we can increase factor of first badge by 1.
In second sample test we can increase factors of the second and the third badge by 1.
Two bored soldiers are playing card war. Their card deck consists of exactly n cards, numbered from 1 to n, all values are different. They divide cards between them in some manner, it's possible that they have different number of cards. Then they play a "war"-like card game.
The rules are following. On each turn a fight happens. Each of them picks card from the top of his stack and puts on the table. The one whose card value is bigger wins this fight and takes both cards from the table to the bottom of his stack. More precisely, he first takes his opponent's card and puts to the bottom of his stack, and then he puts his card to the bottom of his stack. If after some turn one of the player's stack becomes empty, he loses and the other one wins.
You have to calculate how many fights will happen and who will win the game, or state that game won't end.
First line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10), the number of cards.
Second line contains integer k1 (1 ≤ k1 ≤ n - 1), the number of the first soldier's cards. Then follow k1 integers that are the values on the first soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
Third line contains integer k2 (k1 + k2 = n), the number of the second soldier's cards. Then follow k2 integers that are the values on the second soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
All card values are different.
If somebody wins in this game, print 2 integers where the first one stands for the number of fights before end of game and the second one is 1 or 2 showing which player has won.
If the game won't end and will continue forever output - 1.
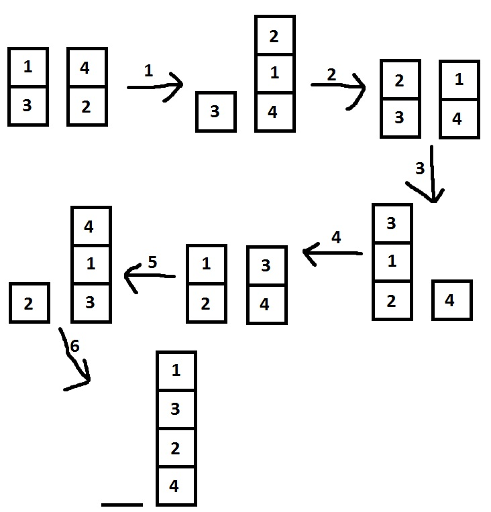
42 1 32 4 2
6 2
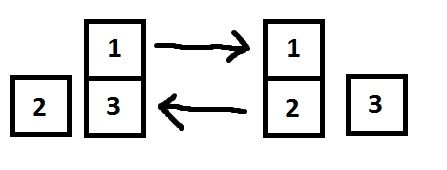
31 22 1 3
-1
First sample:
Second sample:
//A. Soldier and Bananas#include <stdio.h>#include <math.h>int main(){ int k, w; long long sum, n; scanf("%d%lld%d", &k, &n, &w); sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= w; i++) sum += k * i; if (sum > n) printf("%lld\n", sum - n); else printf("0\n");}//B. Soldier and Badges#include <stdio.h>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int cmp(int a, int b){ return a < b;}int main(){ int n, ans; ans = 0; int a[3005]; scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); sort(a, a+n, cmp); for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) if (a[i] >= a[i+1]){ while (a[i+1] <= a[i]){ a[i+1] += 1; ans += 1; } } printf("%d\n", ans);}//C.Soldier and Cards#include <stdio.h>#include <algorithm>#include <math.h>#include <queue>#include <string.h>using namespace std;typedef struct{ int s;}node;queue <node> q;queue <node> p;int vis[11][11];int main(){ int n; scanf("%d", &n); int ans = 0; node map; int k1, k2; scanf("%d", &k1); for (int i = 0; i < k1; i++){ scanf("%d", &map.s); p.push(map); } scanf("%d", &k2); for (int i = 0; i < k2; i++){ scanf("%d", &map.s); q.push(map); } while (1){ if(p.empty()){ printf("%d 2\n", ans); break; } if(q.empty()){ printf("%d 1\n", ans); break; } node tmpa = p.front(); node tmpb = q.front(); if(ans > 1000000){ printf("-1\n"); break; } vis[tmpa.s][tmpb.s] = 1; q.pop(); p.pop(); ans += 1; if (tmpa.s > tmpb.s){ p.push(tmpb); p.push(tmpa); } else{ q.push(tmpa); q.push(tmpb); } } }- cf. #304 div.2
- Soldier and Cards(CF #304 Div.2)
- Cf 99 Div.2
- Cf 103 div.2
- Cf 104 div.2
- Cf 102 Div.2
- Cf 101 Div.2
- Cf 105 Div.2
- Cf 98 Div.2
- Cf 97 Div.2
- Cf 95 Div.2
- CF #151 div 2
- cf-#189-div 2
- CF 192 DIV.2
- CF#262 (Div. 2)
- CF #308 (Div. 2)
- CF #310 (Div. 2)
- CF #309 (Div. 2)
- J2EE详细入门教程--人员登入
- 【云分析】之十四《一张图读懂2015 IaaS云服务格局》
- Floyd算法求解所有顶点间的最短路径
- 难忘的理发经历
- 更改导航栏标题
- cf. #304 div.2
- leetcode - The Skyline Problem
- 经典面试题
- 《C++语言基础》程序阅读——多态性与抽象类
- 人员登入2 ---登入页面
- GCD 深入理解(一)
- GRE词汇记忆方法:复习要放在第一要位
- ESB实现原理
- bzoj 1034 n [ZJOI2008]泡泡堂BNB 贪心 田忌赛马


