剑指Offer-第2章 面试需要的基础知识
来源:互联网 发布:手机淘宝装修日记 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/04 19:18
面试题1: 赋值运算符函数

一般的写法是如下形式:
CMyString& operator=(const CMyString& str){ if(this!=&str){ delete[] m_pData; int sz=strlen(str.m_pData); m_pData=new char[sz+1]; strcpy(m_pData,str.m_pData); } return *this; }

CMyString& operator=(const CMyString& str){ if(this!=&str){ CMyString tmp_str(str); char *p=m_pData; m_pData=tmp_str.m_pData; tmp_str.m_pData=p; } return *this; }
完整的测试实例如下:
class CMyString{ public: CMyString(char *pData=NULL){ if(pData==NULL){ m_pData=new char[1]; m_pData[0]='\0'; } else{ int sz=strlen(pData); m_pData=new char[sz+1]; strcpy(m_pData,pData); } } CMyString(const CMyString& str){ int sz=strlen(str.m_pData); m_pData=new char[sz+1]; strcpy(m_pData,str.m_pData); } ~CMyString(){ delete[] m_pData; } //经典写法,适用于初级程序员 /* CMyString& operator=(const CMyString& str){ if(this!=&str){ delete[] m_pData; int sz=strlen(str.m_pData); m_pData=new char[sz+1]; strcpy(m_pData,str.m_pData); } return *this; } */ //考虑异常安全性,高级写法 CMyString& operator=(const CMyString& str){ if(this!=&str){ CMyString tmp_str(str); char *p=m_pData; m_pData=tmp_str.m_pData; tmp_str.m_pData=p; } return *this; } void print(ostream& os)const { os<<m_pData; } private: char* m_pData;}; ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const CMyString& str){ str.print(os); return os; }void Test1(){ printf("Test1 begins:\n"); char* text = "Hello world"; CMyString str1(text); CMyString str2; str2 = str1; printf("The expected result is: %s.\n", text); printf("The actual result is: "); cout<<str2<<endl;}// 赋值给自己void Test2(){ printf("Test2 begins:\n"); char* text = "Hello world"; CMyString str1(text); str1 = str1; printf("The expected result is: %s.\n", text); printf("The actual result is: "); cout<<str1<<endl;}// 连续赋值void Test3(){ printf("Test3 begins:\n"); char* text = "Hello world"; CMyString str1(text); CMyString str2, str3; str3 = str2 = str1; printf("The expected result is: %s.\n", text); printf("The actual result is: "); cout<<str2<<endl; printf("The expected result is: %s.\n", text); printf("The actual result is: "); cout<<str3<<endl;}int main(){ Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); return 0;}
面试题2: 实现singleton模式
![]()
//这是基本的形式class singleton_{ public: static singleton_* get_instance(){ if(_instance==0) _instance=new singleton_; return _instance; } private: singleton_(){} ~singleton_(){} static singleton_* _instance;};singleton_* singleton_::_instance=0;//下面的方法可以应用在多线程中,主要是利用锁的帮助class locker{ public: locker(){ pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL); } ~locker(){ pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); } void lock(){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); } void unlock(){ pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } private: pthread_mutex_t mutex;};class singleton{ public: static singleton* get_instance(); private: singleton(){} ~singleton(){} private: static singleton* _instance; static locker llock;};singleton* singleton::_instance=0;locker singleton::llock;singleton* singleton::get_instance(){ if(_instance==0){ llock.lock(); printf("locked\n"); if(_instance==0) _instance=new singleton; llock.unlock(); printf("unlocked\n"); } return _instance;}int main(){ int pid; for(int i=0;i<2;i++){ pid=fork(); if(pid<0) printf("error\n"); else if(pid==0){ singleton* slt=singleton::get_instance(); printf("child:%x\n",slt); } else{ singleton* slt=singleton::get_instance(); printf("parent:%x\n",slt); } }}
参考: http://blog.csdn.net/joanlynnlove/article/details/7462254
面试题3: 二维数组中的查找


代码如下:
bool FindInPartiallySortedMatrix(int *matrix,int row,int col,int number){ if(matrix==0||row<0||col<0) return false; int i=0,j=col-1; while(i<row&&j>=0){ int t=matrix[i*col+j]; if(t==number) return true; else if(t>number) --j; else i++; } return false;}// ====================测试代码====================void Test(char* testName, int* matrix, int rows, int columns, int number, bool expected){ if(testName != NULL) printf("%s begins: ", testName); bool result = FindInPartiallySortedMatrix(matrix, rows, columns, number); if(result == expected) printf("Passed.\n"); else printf("Failed.\n");}// 1 2 8 9// 2 4 9 12// 4 7 10 13// 6 8 11 15// 要查找的数在数组中void Test1(){ int matrix[][4] = {{1, 2, 8, 9}, {2, 4, 9, 12}, {4, 7, 10, 13}, {6, 8, 11, 15}}; Test("Test1", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 7, true);}// 1 2 8 9// 2 4 9 12// 4 7 10 13// 6 8 11 15// 要查找的数不在数组中void Test2(){ int matrix[][4] = {{1, 2, 8, 9}, {2, 4, 9, 12}, {4, 7, 10, 13}, {6, 8, 11, 15}}; Test("Test2", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 5, false);}// 1 2 8 9// 2 4 9 12// 4 7 10 13// 6 8 11 15// 要查找的数是数组中最小的数字void Test3(){ int matrix[][4] = {{1, 2, 8, 9}, {2, 4, 9, 12}, {4, 7, 10, 13}, {6, 8, 11, 15}}; Test("Test3", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 1, true);}// 1 2 8 9// 2 4 9 12// 4 7 10 13// 6 8 11 15// 要查找的数是数组中最大的数字void Test4(){ int matrix[][4] = {{1, 2, 8, 9}, {2, 4, 9, 12}, {4, 7, 10, 13}, {6, 8, 11, 15}}; Test("Test4", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 15, true);}// 1 2 8 9// 2 4 9 12// 4 7 10 13// 6 8 11 15// 要查找的数比数组中最小的数字还小void Test5(){ int matrix[][4] = {{1, 2, 8, 9}, {2, 4, 9, 12}, {4, 7, 10, 13}, {6, 8, 11, 15}}; Test("Test5", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 0, false);}// 1 2 8 9// 2 4 9 12// 4 7 10 13// 6 8 11 15// 要查找的数比数组中最大的数字还大void Test6(){ int matrix[][4] = {{1, 2, 8, 9}, {2, 4, 9, 12}, {4, 7, 10, 13}, {6, 8, 11, 15}}; Test("Test6", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 16, false);}// 鲁棒性测试,输入空指针void Test7(){ Test("Test7", NULL, 0, 0, 16, false);}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); return 0;}
面试题4: 替换空格

这儿的关键问题是替换后字符串的长度变大了, 所以主要的问题是如何在低复杂度情况下完成复制.
代码如下:
void replace_blank(char *str,int capacity){ if(str==0||capacity<0) return ; int blk_cnt=0; int len=0; while(str[len]!='\0') { if(str[len]==' ') blk_cnt++; len++; } if(len+1+blk_cnt*2>capacity) return ; char *p1,*p2; p1=str+len+1; p2=str+len+1+blk_cnt*2; while(p1>=str&&p2>=p1){ if(*p1==' '){ p1--; *p2--='0'; *p2--='2'; *p2--='%'; } else *p2--=*p1--; }}void Test(char* testName, char string[], int length, char expected[]){ if(testName != NULL) printf("%s begins: ", testName); replace_blank(string, length); if(expected == NULL && string == NULL) printf("passed.\n"); else if(expected == NULL && string != NULL) printf("failed.\n"); else if(strcmp(string, expected) == 0) printf("passed.\n"); else printf("failed.\n");}// 空格在句子中间void Test1(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = "hello world"; Test("Test1", string, length, "hello%20world");}// 空格在句子开头void Test2(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = " helloworld"; Test("Test2", string, length, "%20helloworld");}// 空格在句子末尾void Test3(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = "helloworld "; Test("Test3", string, length, "helloworld%20");}// 连续有两个空格void Test4(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = "hello world"; Test("Test4", string, length, "hello%20%20world");}// 传入NULLvoid Test5(){ Test("Test5", NULL, 0, NULL);}// 传入内容为空的字符串void Test6(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = ""; Test("Test6", string, length, "");}//传入内容为一个空格的字符串void Test7(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = " "; Test("Test7", string, length, "%20");}// 传入的字符串没有空格void Test8(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = "helloworld"; Test("Test8", string, length, "helloworld");}// 传入的字符串全是空格void Test9(){ const int length = 100; char string[length] = " "; Test("Test9", string, length, "%20%20%20");}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); Test8(); Test9(); return 0;}
面试题5: 从尾到头打印链表

本题目中需要用到链表的定义:
struct ListNode{ int m_nValue; ListNode* m_pNext;};ListNode* CreateListNode(int value){ ListNode* pNode = new ListNode(); pNode->m_nValue = value; pNode->m_pNext = NULL; return pNode;}void ConnectListNodes(ListNode* pCurrent, ListNode* pNext){ if(pCurrent == NULL) { printf("Error to connect two nodes.\n"); exit(1); } pCurrent->m_pNext = pNext;}void PrintListNode(ListNode* pNode){ if(pNode == NULL) { printf("The node is NULL\n"); } else { printf("The key in node is %d.\n", pNode->m_nValue); }}void PrintList(ListNode* pHead){ printf("PrintList starts.\n"); ListNode* pNode = pHead; while(pNode != NULL) { printf("%d\t", pNode->m_nValue); pNode = pNode->m_pNext; } printf("\nPrintList ends.\n");}void DestroyList(ListNode* pHead){ ListNode* pNode = pHead; while(pNode != NULL) { pHead = pHead->m_pNext; delete pNode; pNode = pHead; }}void AddToTail(ListNode** pHead, int value){ ListNode* pNew = new ListNode(); pNew->m_nValue = value; pNew->m_pNext = NULL; if(*pHead == NULL) { *pHead = pNew; } else { ListNode* pNode = *pHead; while(pNode->m_pNext != NULL) pNode = pNode->m_pNext; pNode->m_pNext = pNew; }}void RemoveNode(ListNode** pHead, int value){ if(pHead == NULL || *pHead == NULL) return; ListNode* pToBeDeleted = NULL; if((*pHead)->m_nValue == value) { pToBeDeleted = *pHead; *pHead = (*pHead)->m_pNext; } else { ListNode* pNode = *pHead; while(pNode->m_pNext != NULL && pNode->m_pNext->m_nValue != value) pNode = pNode->m_pNext; if(pNode->m_pNext != NULL && pNode->m_pNext->m_nValue == value) { pToBeDeleted = pNode->m_pNext; pNode->m_pNext = pNode->m_pNext->m_pNext; } } if(pToBeDeleted != NULL) { delete pToBeDeleted; pToBeDeleted = NULL; }}
本题的代码如下:
void PrintListReversingly_Iteratively(ListNode* pHead){ if(pHead==0) return ; stack<ListNode*> st; ListNode* p=pHead; while(p!=0){ st.push(p); p=p->m_pNext; } while(!st.empty()){ p=st.top();st.pop(); cout<<p->m_nValue<<' '; } cout<<endl;}void PrintListReversingly_Recursively(ListNode* pHead){ if(pHead==0) return; PrintListReversingly_Recursively(pHead->m_pNext); cout<<pHead->m_nValue<<' ';}void Test(ListNode* pHead){ PrintList(pHead); PrintListReversingly_Iteratively(pHead); printf("\n"); PrintListReversingly_Recursively(pHead);}// 1->2->3->4->5void Test1(){ printf("\nTest1 begins.\n"); ListNode* pNode1 = CreateListNode(1); ListNode* pNode2 = CreateListNode(2); ListNode* pNode3 = CreateListNode(3); ListNode* pNode4 = CreateListNode(4); ListNode* pNode5 = CreateListNode(5); ConnectListNodes(pNode1, pNode2); ConnectListNodes(pNode2, pNode3); ConnectListNodes(pNode3, pNode4); ConnectListNodes(pNode4, pNode5); Test(pNode1); DestroyList(pNode1);}// 只有一个结点的链表: 1void Test2(){ printf("\nTest2 begins.\n"); ListNode* pNode1 = CreateListNode(1); Test(pNode1); DestroyList(pNode1);}// 空链表void Test3(){ printf("\nTest3 begins.\n"); Test(NULL);}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); return 0;}
面试题6: 重建二叉树

二叉树相关的定义:
struct BinaryTreeNode { int m_nValue; BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft; BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight; };BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value){ BinaryTreeNode* pNode = new BinaryTreeNode(); pNode->m_nValue = value; pNode->m_pLeft = NULL; pNode->m_pRight = NULL; return pNode;}void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight){ if(pParent != NULL) { pParent->m_pLeft = pLeft; pParent->m_pRight = pRight; }}void PrintTreeNode(BinaryTreeNode* pNode){ if(pNode != NULL) { printf("value of this node is: %d\n", pNode->m_nValue); if(pNode->m_pLeft != NULL) printf("value of its left child is: %d.\n", pNode->m_pLeft->m_nValue); else printf("left child is null.\n"); if(pNode->m_pRight != NULL) printf("value of its right child is: %d.\n", pNode->m_pRight->m_nValue); else printf("right child is null.\n"); } else { printf("this node is null.\n"); } printf("\n");}void PrintTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot){ PrintTreeNode(pRoot); if(pRoot != NULL) { if(pRoot->m_pLeft != NULL) PrintTree(pRoot->m_pLeft); if(pRoot->m_pRight != NULL) PrintTree(pRoot->m_pRight); }}void DestroyTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot){ if(pRoot != NULL) { BinaryTreeNode* pLeft = pRoot->m_pLeft; BinaryTreeNode* pRight = pRoot->m_pRight; delete pRoot; pRoot = NULL; DestroyTree(pLeft); DestroyTree(pRight); }}
本题的代码如下:
BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder, int* endPreorder, int* startInorder, int* endInorder);BinaryTreeNode* Construct(int* preorder, int* inorder, int length){ if(preorder==0||inorder==0||length<0) return 0; return ConstructCore(preorder,preorder+length-1,inorder,inorder+length-1);}BinaryTreeNode* ConstructCore(int* startPreorder, int* endPreorder, int* startInorder, int* endInorder){ //判断输入是否合法 if(startPreorder>endPreorder||startInorder>endInorder) return 0; int rootValue=startPreorder[0]; BinaryTreeNode* root=new BinaryTreeNode; root->m_nValue=rootValue; root->m_pLeft=root->m_pRight=0; if(startPreorder==endPreorder){ if(startInorder==endInorder&&*startPreorder==*startInorder) return root; else throw exception(); } int *rootInorder=startInorder; while(rootInorder<=endInorder&&*rootInorder!=rootValue) ++rootInorder; if(rootInorder>endInorder||rootInorder==endInorder&&*rootInorder!=rootValue) throw std::exception(); int len=rootInorder-startInorder; //对len的检查和开头的判断检查的效果是一样的。// if(len>0) root->m_pLeft=ConstructCore(startPreorder+1,startPreorder+len,startInorder,rootInorder-1);// if(len<endPreorder-startPreorder) root->m_pRight=ConstructCore(startPreorder+len+1,endPreorder,rootInorder+1,endInorder); return root;}// ====================测试代码====================void Test(char* testName, int* preorder, int* inorder, int length){ if(testName != NULL) printf("%s begins:\n", testName); printf("The preorder sequence is: "); for(int i = 0; i < length; ++ i) printf("%d ", preorder[i]); printf("\n"); printf("The inorder sequence is: "); for(int i = 0; i < length; ++ i) printf("%d ", inorder[i]); printf("\n"); try { BinaryTreeNode* root = Construct(preorder, inorder, length); PrintTree(root); DestroyTree(root); } catch(std::exception& exception) { printf("Invalid Input.\n"); }}// 普通二叉树// 1// / \// 2 3 // / / \// 4 5 6// \ /// 7 8void Test1(){ const int length = 8; int preorder[length] = {1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8}; int inorder[length] = {4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6}; Test("Test1", preorder, inorder, length);}// 所有结点都没有右子结点// 1// / // 2 // / // 3 // /// 4// /// 5void Test2(){ const int length = 5; int preorder[length] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int inorder[length] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; Test("Test2", preorder, inorder, length);}// 所有结点都没有左子结点// 1// \ // 2 // \ // 3 // \// 4// \// 5void Test3(){ const int length = 5; int preorder[length] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int inorder[length] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; Test("Test3", preorder, inorder, length);}// 树中只有一个结点void Test4(){ const int length = 1; int preorder[length] = {1}; int inorder[length] = {1}; Test("Test4", preorder, inorder, length);}// 完全二叉树// 1// / \// 2 3 // / \ / \// 4 5 6 7void Test5(){ const int length = 7; int preorder[length] = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7}; int inorder[length] = {4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7}; Test("Test5", preorder, inorder, length);}// 输入空指针void Test6(){ Test("Test6", NULL, NULL, 0);}// 输入的两个序列不匹配void Test7(){ const int length = 7; int preorder[length] = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7}; int inorder[length] = {4, 2, 8, 1, 6, 3, 7}; Test("Test7: for unmatched input", preorder, inorder, length);}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); return 0;}
面试题7: 用两个栈实现队列操作

template <typename T> class CQueue{public: CQueue(void); ~CQueue(void); // 在队列末尾添加一个结点 void appendTail(const T& node); // 删除队列的头结点 T deleteHead();private: stack<T> stack1; stack<T> stack2;};template <typename T> CQueue<T>::CQueue(void){}template <typename T> CQueue<T>::~CQueue(void){}template<typename T> void CQueue<T>::appendTail(const T& element){ stack1.push(element);} template<typename T> T CQueue<T>::deleteHead(){ if(stack2.size()<= 0) { while(stack1.size()>0) { T& data = stack1.top(); stack1.pop(); stack2.push(data); } } if(stack2.size() == 0) throw exception(); T head = stack2.top(); stack2.pop(); return head;}void Test(char actual, char expected){ if(actual == expected) printf("Test passed.\n"); else printf("Test failed.\n");}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ CQueue<char> queue; queue.appendTail('a'); queue.appendTail('b'); queue.appendTail('c'); char head = queue.deleteHead(); Test(head, 'a'); head = queue.deleteHead(); Test(head, 'b'); queue.appendTail('d'); head = queue.deleteHead(); Test(head, 'c'); queue.appendTail('e'); head = queue.deleteHead(); Test(head, 'd'); head = queue.deleteHead(); Test(head, 'e'); return 0;}
面试题8: 旋转数组的最小数字

很多题目会用到快排的思想, 快排中最核心的地方就是利用一个数将数组分为两部分, 实现方法如下:
方法1: 从两边往中间遍历
int Partition(int *a,int low,int high){ if(a== NULL || low>high) throw new std::exception(); int pivot=a[low]; int i=low,j=high+1; while(1){ do i++; while(a[i]<pivot); do j--; while(a[j]>pivot); if(i>=j) break; swap(a[i],a[j]); } swap(a[low],a[j]); return j;}
方法2: 从一边往另一边遍历,比较巧
int RandomInRange(int minl,int maxl){ return rand()%(maxl-minl+1)+minl;}int Partition_(int data[],int start, int end){ if(data == NULL || start >end ) throw new std::exception(); int index = RandomInRange(start, end); swap(data[index], data[end]); int small = start - 1; for(index = start; index < end; ++ index) { if(data[index] < data[end]) { ++ small; if(small != index) swap(data[index], data[small]); } } ++ small; swap(data[small], data[end]); return small;}

代码如下:
int MinInOrder(int* numbers, int index1, int index2);int Min(int *arr,int len){ if(arr==0||len<=0) throw exception(); int i=0,j=len-1; int mid=i; while(arr[i]>=arr[j]){ //如果前后指针指向相邻的两个数,那么后面的那个数就是我们所要查找的。 if(j-i==1){ mid=j; break; } mid=(i+j)/2; //如果三个数相同,只能采取线性查找了。 if(arr[i]==arr[j]&& arr[mid]==arr[i]) return MinInOrder(arr,i,j); //缩小查找范围 if(arr[mid]>=arr[i]) i=mid; else if(arr[mid]<=arr[j]) j=mid; } return arr[mid];}//线性查找int MinInOrder(int *a,int l,int r){ int res=a[l]; for(int i=l;i<r;i++) if(res>a[i]) res=a[i]; return res;}// ====================测试代码====================void Test(int* numbers, int length, int expected){ int result = 0; try { result = Min(numbers, length); for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i) printf("%d ", numbers[i]); if(result == expected) printf("\tpassed\n"); else printf("\tfailed\n"); } catch (...) { if(numbers == NULL) printf("Test passed.\n"); else printf("Test failed.\n"); }}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ // 典型输入,单调升序的数组的一个旋转 int array1[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2}; Test(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int), 1); // 有重复数字,并且重复的数字刚好的最小的数字 int array2[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 1, 2}; Test(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int), 1); // 有重复数字,但重复的数字不是第一个数字和最后一个数字 int array3[] = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 2}; Test(array3, sizeof(array3) / sizeof(int), 1); // 有重复的数字,并且重复的数字刚好是第一个数字和最后一个数字 int array4[] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}; Test(array4, sizeof(array4) / sizeof(int), 0); // 单调升序数组,旋转0个元素,也就是单调升序数组本身 int array5[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; Test(array5, sizeof(array5) / sizeof(int), 1); // 数组中只有一个数字 int array6[] = {2}; Test(array6, sizeof(array6) / sizeof(int), 2); // 输入NULL Test(NULL, 0, 0); return 0;}
面试题9: 斐波那契数列

这儿总结一下所有求解斐波那契数列的方法:
方法1:
经典的递归方式.
方法2:
迭代的方式
方法3:
比较巧的方法, 根据递推表达式得到一个矩阵的表示形式:
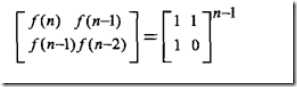
三种方法的代码如下:
int Fibonacci1(int n){ if(n==0) return 0; if(n==1) return 1; return Fibonacci1(n-1)+Fibonacci1(n-2);}int Fibonacci2(int n){ if(n==0) return 0; if(n==1) return 1; int fn,fn_1,fn_2; fn_1=1,fn_2=0; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ fn=fn_1+fn_2; fn_2=fn_1; fn_1=fn; } return fn;}struct Matrix2By2{ Matrix2By2 ( long long m00 = 0, long long m01 = 0, long long m10 = 0, long long m11 = 0 ) :m_00(m00), m_01(m01), m_10(m10), m_11(m11) { } long long m_00; long long m_01; long long m_10; long long m_11;};Matrix2By2 MatrixMultiply( const Matrix2By2& matrix1, const Matrix2By2& matrix2){ return Matrix2By2( matrix1.m_00 * matrix2.m_00 + matrix1.m_01 * matrix2.m_10, matrix1.m_00 * matrix2.m_01 + matrix1.m_01 * matrix2.m_11, matrix1.m_10 * matrix2.m_00 + matrix1.m_11 * matrix2.m_10, matrix1.m_10 * matrix2.m_01 + matrix1.m_11 * matrix2.m_11);}Matrix2By2 MatrixPower(unsigned int n){ assert(n > 0); Matrix2By2 matrix; if(n == 1) { matrix = Matrix2By2(1, 1, 1, 0); } else if(n % 2 == 0) { matrix = MatrixPower(n / 2); matrix = MatrixMultiply(matrix, matrix); } else if(n % 2 == 1) { matrix = MatrixPower((n - 1) / 2); matrix = MatrixMultiply(matrix, matrix); matrix = MatrixMultiply(matrix, Matrix2By2(1, 1, 1, 0)); } return matrix;}long long Fibonacci3(unsigned int n){ int result[2] = {0, 1}; if(n < 2) return result[n]; Matrix2By2 PowerNMinus2 = MatrixPower(n - 1); return PowerNMinus2.m_00;}// ====================测试代码====================void Test(int n, int expected){ if(Fibonacci1(n) == expected) printf("Test for %d in solution1 passed.\n", n); else printf("Test for %d in solution1 failed.\n", n); if(Fibonacci2(n) == expected) printf("Test for %d in solution2 passed.\n", n); else printf("Test for %d in solution2 failed.\n", n); if(Fibonacci3(n) == expected) printf("Test for %d in solution3 passed.\n", n); else printf("Test for %d in solution3 failed.\n", n);}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ Test(0, 0); Test(1, 1); Test(2, 1); Test(3, 2); Test(4, 3); Test(5, 5); Test(6, 8); Test(7, 13); Test(8, 21); Test(9, 34); Test(10, 55); Test(40, 102334155); return 0;}



面试题10: 二进制中1的个数

很多的解法.
方法1:
不断的除以2或右移. 判断其中1的个数.
存在的问题是, 对于负数就不行了.
方法2:
将1不断左移, 然后与原数进行按位与操作.
方法3:
利用n&(n-1)的技巧
方法2和3的代码如下:
int NumberOf1_Solution1(int n){ int count = 0; unsigned int flag = 1; while(flag) { if(n & flag) count ++; flag = flag << 1; } return count;}int NumberOf1_Solution2(int n){ int count = 0; while (n) { ++ count; n = (n - 1) & n; } return count;}void Test(int number, unsigned int expected){ int actual = NumberOf1_Solution1(number); if(actual == expected) printf("Solution1: Test for %p passed.\n", number); else printf("Solution1: Test for %p failed.\n", number); actual = NumberOf1_Solution2(number); if(actual == expected) printf("Solution2: Test for %p passed.\n", number); else printf("Solution2: Test for %p failed.\n", number); printf("\n");}int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ // 输入0,期待的输出是0 Test(0, 0); // 输入1,期待的输出是1 Test(1, 1); // 输入10,期待的输出是2 Test(10, 2); // 输入0x7FFFFFFF,期待的输出是31 Test(0x7FFFFFFF, 31); // 输入0xFFFFFFFF(负数),期待的输出是32 Test(0xFFFFFFFF, 32); // 输入0x80000000(负数),期待的输出是1 Test(0x80000000, 1); return 0;}


0 0
- 剑指Offer-第2章 面试需要的基础知识
- 剑指offer——C++面试需要的基础知识
- 剑指offer——C++面试需要的基础知识
- 剑指offer:面试的基础知识(二)
- 剑指offer:面试的基础知识(一)
- 剑指offer:面试的基础知识(三)
- 面试-需要掌握的基础知识
- 剑指offer读书总结-->面试所需的基础知识
- 剑指offer 第二章 基础知识
- 剑指offer面试题目63(二叉搜索树的第k个结点)
- 《剑指offer》-第2章(2)
- 《剑指offer》第2章总结
- 《剑指offer》读书笔记(第2章)
- 《剑指offer》-第2章(1)
- 第2章 Docker 的基础知识
- 第2章 Cache的基础知识
- 剑指offer:面试的三个环节
- 《剑指offer》之面试的流程
- tomcat结合nginx使用小结
- Android.mk集成第三方jar与so的方法
- echarts 根据实际数据改变仪表盘颜色
- C++Primer第五版 4.11.1节练习
- javah 使用方法 jni
- 剑指Offer-第2章 面试需要的基础知识
- wxWidgets下显示下载进度条
- AFNetworking 上传文件
- VS2010搜索对话框函数的方法
- Mac OS X: 系统nvram启动参数
- (转帖)HashMap的读写并发 脏读 脏数据
- java解析xml的几种方式 SAX解析
- 嵌入式中 volatile 用法
- 通过管道执行cmd命令



