【Codeforces Round 335 (Div 2) D】【构造 脑洞】Lazy Student 图的最小生成树告诉边权和选取情况让你还原图
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝怎么改差评为好评 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 01:58
#include<stdio.h>#include<iostream>#include<string.h>#include<string>#include<ctype.h>#include<math.h>#include<set>#include<map>#include<vector>#include<queue>#include<bitset>#include<algorithm>#include<time.h>using namespace std;void fre(){freopen("c://test//input.in","r",stdin);freopen("c://test//output.out","w",stdout);}#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)#define ls o<<1#define rs o<<1|1typedef long long LL;typedef unsigned long long UL;typedef unsigned int UI;template <class T1,class T2>inline void gmax(T1 &a,T2 b){if(b>a)a=b;}template <class T1,class T2>inline void gmin(T1 &a,T2 b){if(b<a)a=b;}const int N=1e5+10,M=0,Z=1e9+7,ms63=1061109567;int n,m;struct A{int v;int u;int o;bool operator < (const A& b)const{if(v!=b.v)return v<b.v;return u>b.u;}}a[N];int b[N],c[N];bool check(){int ed=1;int x=1;int y=3;for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){if(a[i].u==1){b[a[i].o]=ed;c[a[i].o]=++ed;}else{if(y>ed)return 0;b[a[i].o]=x;c[a[i].o]=y;if(--x==0){++y;x=y-2;}}}return 1;}int main(){while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)scanf("%d%d",&a[i].v,&a[i].u),a[i].o=i;sort(a+1,a+m+1);if(check()){for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)printf("%d %d\n",b[i],c[i]);}else puts("-1");}return 0;}/*【题意】这题也是十分有趣的。给你一个图,图上有n(1e5)个结点,m(1e5范围且n-1<=m<=C(n,2))。保证图联通。我们现在,依次告诉你这m条边的——(长度,是否为最小生成树上选取的边)让你构造一个图,还原这m条边的可能连接关系。或者判定这样的图不存在并输出-1【类型】构造 脑洞 最小生成树【分析】这题还是要借助最小生成树的相关知识的。最小生成树是每次选边权最小的边,然后如果不存在环,就选取。于是,我们要按照(边权>,选取>不选取)的关键字排序。对于当前的边,其边权肯定大于等于之前的边权。如果这条边需要选取,我们可以直接以链式关系选取。如果这条边不需要选取,我们需要构建一个环,使得之前环上的所有边(已选取)都小于等于这个边的权值。如果这条边不选取,而又找不到这个环,那么就false。注意不能有重边和自环。【时间复杂度&&优化】O(nlogn)【数据】4 61 11 12 11 01 01 0*/ 1 0
- 【Codeforces Round 335 (Div 2) D】【构造 脑洞】Lazy Student 图的最小生成树告诉边权和选取情况让你还原图
- Codeforces Round 335 (Div 2) D. Lazy Student【构造 脑洞 最小生成树】
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2) 606D Lazy Student(最小生成树+stl)
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2) D. Lazy Student
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2)D. Lazy Student
- codeforces 606D. Lazy Student(#335 逆最小生成树)
- Codeforces 606 D Lazy Student【逆最小生成树+思维】好题
- CF - 605B.Lazy Student,构造最小生成树
- 【Codeforces Round #430 (Div. 2) D】 D. Vitya and Strange Lesson ("带lazy" 的字典树)
- 605B. Lazy Student(codeforces Round 335)
- Codeforces Round #309 (Div. 2) D 构造
- CF 335 div.1-B/div.2-D/605 B Lazy Student
- 【Codeforces Round 375 (Div 2) F】【构造 贪心】st-Spanning Tree 树的特殊最小生成树使得S度不超SD,T度不超TD
- Codeforces Round #306 (Div. 2) D - Regular Bridge 构造
- Codeforces Round #340 (Div. 2)(D)构造
- Codeforces Round #410 (Div.2) D.Mike and distrubition-构造
- Codeforces Round #446 (Div. 2) D. Gluttony (构造 贪心)
- Codeforces Round #306 (Div. 2) D. Regular Bridge (构造)
- android布局详解
- 【Codeforces Round 335 (Div 2) C】【贪心 脑洞 有趣排序】Sorting Railway Cars 全排列排序可以提前后提后的最小操作数
- jQuery插件开发详细教程
- android 窗口管理
- 设计模式之解释器模式
- 【Codeforces Round 335 (Div 2) D】【构造 脑洞】Lazy Student 图的最小生成树告诉边权和选取情况让你还原图
- [MD学习]使用ActionBar+DrawableLayout+Palette打造侧滑UI
- jni开发注意事项
- Shell教程(二):变量、特殊变量
- iOS9适配 之 关于info.plist 第三方登录 添加URL Schemes白名单
- 云应用百宝云交互界面专题分析
- ajax跨域请求
- servlet3.0异步处理
- 用sigsetjmp和siglongjmp 解决从信号处理程序返回后信号仍被屏蔽问题
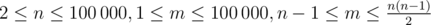 ) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph.
) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph.

