ID3算法
来源:互联网 发布:php 邮件内容html输出 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 16:55
摘要
决策树是对数据进行分类,以此达到预测的目的。该决策树方法先根据训练集数据形成决策树,如果该树不能对所有对象给出正确的分类,那么选择一些例外加入到训练集数据中,重复该过程一直到形成正确的决策集。决策树代表着决策集的树形结构。
先上问题吧,我们统计了14天的气象数据(指标包括outlook,temperature,humidity,windy),并已知这些天气是否打球(play)。如果给出新一天的气象指标数据:sunny,cool,high,TRUE,判断一下会不会去打球。
outlooktemperaturehumiditywindyplaysunnyhothighfalsenosunnyhothightruenoovercasthothighfalseyesrainymildhighfalseyesrainycoolnormalfalseyesrainycoolnormaltruenoovercastcoolnormaltrueyessunnymildhighfalsenosunnycoolnormalfalseyesrainymildnormalfalseyessunnymildnormaltrueyesovercastmildhightrueyesovercasthotnormalfalseyesrainymildhightrueno
现在我们使用ID3归纳决策树的方法来求解该问题。
预备知识:信息熵
熵是无序性(或不确定性)的度量指标。假如事件A的全概率划分是(A1,A2,...,An),每部分发生的概率是(p1,p2,...,pn),那信息熵定义为:

通常以2为底数,所以信息熵的单位是bit。
补充两个对数去处公式:
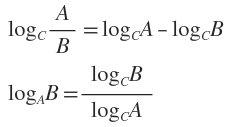
ID3算法
构造树的基本想法是随着树深度的增加,节点的熵迅速地降低。熵降低的速度越快越好,这样我们有望得到一棵高度最矮的决策树。
在没有给定任何天气信息时,根据历史数据,我们只知道新的一天打球的概率是9/14,不打的概率是5/14。此时的熵为:
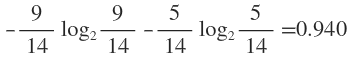
属性有4个:outlook,temperature,humidity,windy。我们首先要决定哪个属性作树的根节点。
对每项指标分别统计:在不同的取值下打球和不打球的次数。
下面我们计算当已知变量outlook的值时,信息熵为多少。
outlook=sunny时,2/5的概率打球,3/5的概率不打球。entropy=0.971
outlook=overcast时,entropy=0
outlook=rainy时,entropy=0.971
而根据历史统计数据,outlook取值为sunny、overcast、rainy的概率分别是5/14、4/14、5/14,所以当已知变量outlook的值时,信息熵为:5/14 × 0.971 + 4/14 × 0 + 5/14 × 0.971 = 0.693
这样的话系统熵就从0.940下降到了0.693,信息增溢gain(outlook)为0.940-0.693=0.247
同样可以计算出gain(temperature)=0.029,gain(humidity)=0.152,gain(windy)=0.048。
gain(outlook)最大(即outlook在第一步使系统的信息熵下降得最快),所以决策树的根节点就取outlook。
接下来要确定N1取temperature、humidity还是windy?在已知outlook=sunny的情况,根据历史数据,我们作出类似table 2的一张表,分别计算gain(temperature)、gain(humidity)和gain(windy),选最大者为N1。
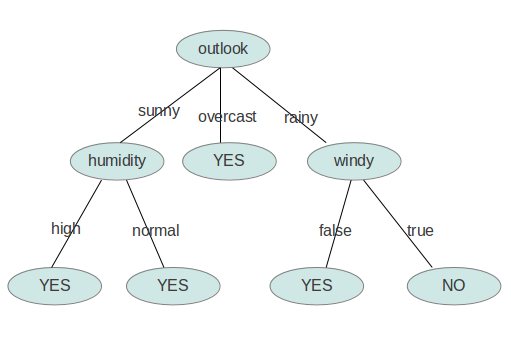
依此类推,构造决策树。当系统的信息熵降为0时,就没有必要再往下构造决策树了,此时叶子节点都是纯的--这是理想情况。最坏的情况下,决策树的高度为属性(决策变量)的个数,叶子节点不纯(这意味着我们要以一定的概率来作出决策)。
Java实现
最终的决策树保存在了XML中,使用了Dom4J,注意如果要让Dom4J支持按XPath选择节点,还得引入包jaxen.jar。程序代码要求输入文件满足ARFF格式,并且属性都是标称变量。
实验用的数据文件:
@relation weather.symbolic @attribute outlook {sunny, overcast, rainy} @attribute temperature {hot, mild, cool} @attribute humidity {high, normal} @attribute windy {TRUE, FALSE} @attribute play {yes, no} @data sunny,hot,high,FALSE,no sunny,hot,high,TRUE,no overcast,hot,high,FALSE,yes rainy,mild,high,FALSE,yes rainy,cool,normal,FALSE,yes rainy,cool,normal,TRUE,no overcast,cool,normal,TRUE,yes sunny,mild,high,FALSE,no sunny,cool,normal,FALSE,yes rainy,mild,normal,FALSE,yes sunny,mild,normal,TRUE,yes overcast,mild,high,TRUE,yes overcast,hot,normal,FALSE,yes rainy,mild,high,TRUE,no程序代码:
package com.dfsj;import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import org.dom4j.Document; import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper; import org.dom4j.Element; import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat; import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter; public class ID3 { private ArrayList<String> attribute = new ArrayList<String>(); // 存储属性的名称 private ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> attributevalue = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(); // 存储每个属性的取值 private ArrayList<String[]> data = new ArrayList<String[]>();; // 原始数据 int decatt; // 决策变量在属性集中的索引 public static final String patternString = "@attribute(.*)[{](.*?)[}]"; Document xmldoc; Element root; public ID3() { xmldoc = DocumentHelper.createDocument(); root = xmldoc.addElement("root"); root.addElement("DecisionTree").addAttribute("value", "null"); } public static void main(String[] args) { ID3 inst = new ID3(); inst.readARFF(new File("/home/orisun/test/weather.nominal.arff")); inst.setDec("play"); LinkedList<Integer> ll=new LinkedList<Integer>(); for(int i=0;i<inst.attribute.size();i++){ if(i!=inst.decatt) ll.add(i); } ArrayList<Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i=0;i<inst.data.size();i++){ al.add(i); } inst.buildDT("DecisionTree", "null", al, ll); inst.writeXML("/home/orisun/test/dt.xml"); return; } //读取arff文件,给attribute、attributevalue、data赋值 public void readARFF(File file) { try { FileReader fr = new FileReader(file); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); String line; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString); while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(line); if (matcher.find()) { attribute.add(matcher.group(1).trim()); String[] values = matcher.group(2).split(","); ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>(values.length); for (String value : values) { al.add(value.trim()); } attributevalue.add(al); } else if (line.startsWith("@data")) { while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { if(line=="") continue; String[] row = line.split(","); data.add(row); } } else { continue; } } br.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } //设置决策变量 public void setDec(int n) { if (n < 0 || n >= attribute.size()) { System.err.println("决策变量指定错误。"); System.exit(2); } decatt = n; } public void setDec(String name) { int n = attribute.indexOf(name); setDec(n); } //给一个样本(数组中是各种情况的计数),计算它的熵 public double getEntropy(int[] arr) { double entropy = 0.0; int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); sum += arr[i]; } entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); entropy /= sum; return entropy; } //给一个样本数组及样本的算术和,计算它的熵 public double getEntropy(int[] arr, int sum) { double entropy = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); } entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); entropy /= sum; return entropy; } public boolean infoPure(ArrayList<Integer> subset) { String value = data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt]; for (int i = 1; i < subset.size(); i++) { String next=data.get(subset.get(i))[decatt]; //equals表示对象内容相同,==表示两个对象指向的是同一片内存 if (!value.equals(next)) return false; } return true; } // 给定原始数据的子集(subset中存储行号),当以第index个属性为节点时计算它的信息熵 public double calNodeEntropy(ArrayList<Integer> subset, int index) { int sum = subset.size(); double entropy = 0.0; int[][] info = new int[attributevalue.get(index).size()][]; for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) info[i] = new int[attributevalue.get(decatt).size()]; int[] count = new int[attributevalue.get(index).size()]; for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) { int n = subset.get(i); String nodevalue = data.get(n)[index]; int nodeind = attributevalue.get(index).indexOf(nodevalue); count[nodeind]++; String decvalue = data.get(n)[decatt]; int decind = attributevalue.get(decatt).indexOf(decvalue); info[nodeind][decind]++; } for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) { entropy += getEntropy(info[i]) * count[i] / sum; } return entropy; } // 构建决策树 public void buildDT(String name, String value, ArrayList<Integer> subset, LinkedList<Integer> selatt) { Element ele = null; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<Element> list = root.selectNodes("//"+name); Iterator<Element> iter=list.iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()){ ele=iter.next(); if(ele.attributeValue("value").equals(value)) break; } if (infoPure(subset)) { ele.setText(data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt]); return; } int minIndex = -1; double minEntropy = Double.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < selatt.size(); i++) { if (i == decatt) continue; double entropy = calNodeEntropy(subset, selatt.get(i)); if (entropy < minEntropy) { minIndex = selatt.get(i); minEntropy = entropy; } } String nodeName = attribute.get(minIndex); selatt.remove(new Integer(minIndex)); ArrayList<String> attvalues = attributevalue.get(minIndex); for (String val : attvalues) { ele.addElement(nodeName).addAttribute("value", val); ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < subset.size(); i++) { if (data.get(subset.get(i))[minIndex].equals(val)) { al.add(subset.get(i)); } } buildDT(nodeName, val, al, selatt); } } // 把xml写入文件 public void writeXML(String filename) { try { File file = new File(filename); if (!file.exists()) file.createNewFile(); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file); OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint(); // 美化格式 XMLWriter output = new XMLWriter(fw, format); output.write(xmldoc); output.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } }最终生成的文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <root> <DecisionTree value="null"> <outlook value="sunny"> <humidity value="high">no</humidity> <humidity value="normal">yes</humidity> </outlook> <outlook value="overcast">yes</outlook> <outlook value="rainy"> <windy value="TRUE">no</windy> <windy value="FALSE">yes</windy> </outlook> </DecisionTree> </root>
用图形象地表示就是:
- id3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- ID3算法
- STL的红与黑--rb_tree红黑树
- iOS CAReplicatorLayer简单笔记
- Educational Codeforces Round 2 D.Area of Two Circles' Intersection(计算几何)
- spring data 接口之 CrudRepository
- C++对象模型
- ID3算法
- spring data 接口之 PagingAndSortingRepository
- Ubuntu安装libgtk-x11-2.0
- Syntax error, parameterized types are only available if source level is 1.5 or greater
- linux的软链接
- ‘聪明的搜索算法’ A*算法
- 多个div放置在同一行
- iOS空页面 DZNEmptyDataSet
- CentOs关闭防火墙


