hdu-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(DFS+最小生成树)
来源:互联网 发布:python编码汉字互转 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/18 09:50
题目链接:点击打开链接
Minimal Ratio Tree
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 3909 Accepted Submission(s): 1203
Problem Description
For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated according to the following equation.
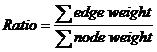
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
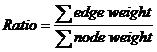
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
Input
Input contains multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains two integers n (2<=n<=15) and m (2<=m<=n), which stands for the number of nodes in the graph and the number of nodes in the minimal ratio tree. Two zeros end the input. The next line contains n numbers which stand for the weight of each node. The following n lines contain a diagonally symmetrical n×n connectivity matrix with each element shows the weight of the edge connecting one node with another. Of course, the diagonal will be all 0, since there is no edge connecting a node with itself.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
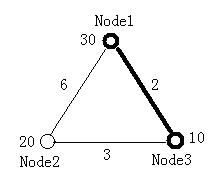
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.

Output
For each test case output one line contains a sequence of the m nodes which constructs the minimal ratio tree. Nodes should be arranged in ascending order. If there are several such sequences, pick the one which has the smallest node number; if there's a tie, look at the second smallest node number, etc. Please note that the nodes are numbered from 1 .
Sample Input
3 230 20 100 6 26 0 32 3 02 21 10 22 00 0
Sample Output
1 31 2
题意:有n个点。接着输入n个点的权值,再输入图,代表了各条边的权值,题目说明了主对角线全为0,因此不用特别处理i==j的情况。
思路:n只有15, 想到用DFS全遍历,当然,裸DFS会TLE,于是只要加点剪枝就可以了。 31msAC。
这里剪枝的条件是1:第一个数+m<=n为什么呢? 假设n是5,m是3,那么第一个数至多是3吧(3,4,5),大于3就不行了
2:我们可以让序列严格递增,这样可以减少很少遍历,(同样几个数字,不剪枝会改变顺序出现很多次)
于是问题就简单了,题目要求m个点,每次我们遍历出符合条件的m个点时,其实m个点的权值就确定了,那么要让边和/点的权值结果最小,自然就是让边和最小了。
所以此时只要在这m个点求一次最小生成树得到最短长度就能得到一个题目要求的"最小比例树"了,然后再在所有符合条件的结果中取最小的,就是最终答案了~
代码:
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>#include <cmath>using namespace std;#define N 20#define INF 1<<30#define eps 1e-8int n,m;double minn;int ma[N][N];int p[N],ans[N];int f[N],flag[N];int d[N],flag1[N];int prim(){ int ret=0;///最小生成树大小 memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag)); for(int i=1;i<m;i++) d[i]=ma[f[0]][f[i]]; flag[0]=1; for(int i=1;i<m;i++) { int v=-1; for(int j=0;j<m;j++) if(!flag[j]&&(v==-1||(d[v]>d[j]))) v=j; if(v==-1) return -1; ret+=d[v]; flag[v]=1; for(int j=0;j<m;j++) if(!flag[j]&&d[j]>ma[f[v]][f[j]]) d[j]=ma[f[v]][f[j]]; } return ret;}void dfs(int k){ if(k==m) { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) sum+=p[f[i]]; double ret=prim(); if(fabs(ret+1)<eps) return; if(minn-(ret/sum)>eps) { minn=ret/sum; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) ans[i]=f[i]; } return; } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(k==0&&i+m>n) return; if(k>0&&i<f[k-1]) continue; if(!flag1[i]) { flag1[i]=1; f[k]=i; dfs(k+1); flag1[i]=0; } }}int main(){ while(~scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)&&n) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&p[i]); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<n;j++) scanf("%d",&ma[i][j]); memset(flag1,0,sizeof(flag1)); minn=INF; dfs(0); for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]+1); printf("%d\n",ans[m-1]+1); } return 0;} 0 0
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs+最小生成树)
- hdu-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(DFS+最小生成树)
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs枚举 + 最小生成树)~~~
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (dfs+Prim最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs+最小生成树-Prim)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs+最小生成树-Prim)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(DFS+Kruskal最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(数据结构-最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(图论-最小生成树)
- HDU-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(最小生成树[Prim])
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(最小生成树)
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (DFS枚举+最小生成树Prim)
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree dfs枚举组合情况+最小生成树★
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree dfs枚举组合情况+最小生成树★
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(枚举+最小生成树)
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree【深搜+最小生成树】
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 最小生成树kruskal
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(枚举组合+最小生成树)
- 图片跟随鼠标移动(jquery)
- OpenGl 学习笔记 01
- AndroidStudio--Terminal的使用
- Android匹配Uri工具类UriMatcher
- html初探
- hdu-2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(DFS+最小生成树)
- 学习OpenCV——Surf(特征点篇)&flann快速最近邻搜索算法
- Partition-方案一. 通过 Export/import 方法
- django 购物系统 - 添加至购物车表单
- eclipse/intellij idea 远程调试hadoop 2.6.0
- android获取屏幕的宽高
- AFNetworking 3.0迁移指南
- 直接插入排序
- 是否可以从一个静态(static)方法内部发出对非静态(non-static)方法的调用?


