DispatcherServlet 源码阅读(1)
来源:互联网 发布:龙舌兰推荐 知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/24 05:10
有时间还是应该多看看源码。
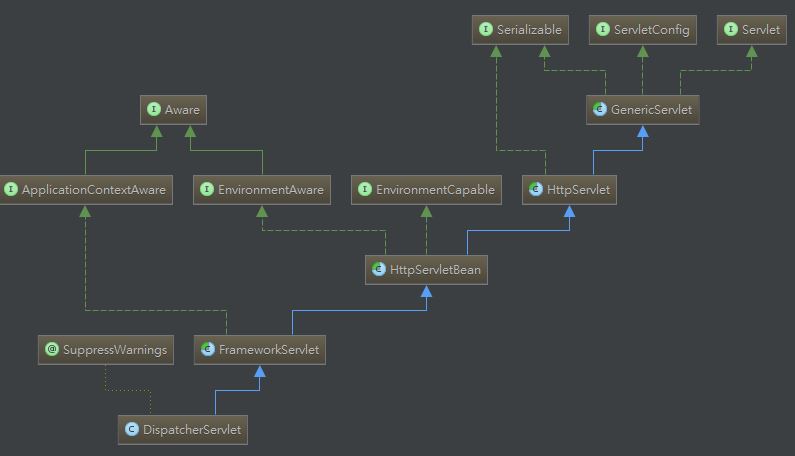
DispatcherServlet 是一个实实在在的 Servlet,所以 Spring MVC 引入后不会改变 Servlet 容器的行为,仍然是解析 web.xml 部署文件,只需要在里面配置这个 Servlet 即可。
比如下面配置 dispatcher Servlet 处理所有的请求,也体现了 DispatcherServlet 是前端控制器(Front Controller)。contextConfigLocation 上下文参数用于配置路径的指定,如果没有的话就使用默认的值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> /WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet.xml classpath:service-context.xml </param-value> </context-param></web-app>DispatcherServlet 初始化
DispatcherServlet 的父类 HttpServletBean 覆盖了 HttpServlet 的 init 方法,实现该 servlet 的初始化。
/** * Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and * invoke subclass initialization. * @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required * properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails. */ @Override public final void init() throws ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } // Set bean properties from init parameters. try { PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); throw ex; } // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); } }正如注释所说 initServletBean() 留由子类实现,体现了模板方法模式,当上述bean属性设置完成后,进入这里 FrameworkServlet#init() 创建 Servlet 的上下文 WebApplicationContext,initWebApplicationContext 首先会获得该 Web 应用的 root WebApplicationContext (通常是由 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 加载的),然后根据这个根上下文得到我们这个 Servlet 的 WebApplicationContext。initFrameworkServlet 方法是空的,而且子类 DispatcherServlet 也没有覆盖。
/** * Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties * have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext. */ @Override protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } } /** * Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet. * <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation * of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses. * @return the WebApplicationContext instance * @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext) * @see #setContextClass * @see #setContextConfigLocation */ protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. onRefresh(wac); } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); } } return wac; }DispatcherServlet 处理请求流程
FrameworkServlet 中覆盖了 HttpServlet 的 doGet(),doPost()等方法,而 doGet(),doPost()等又直接调用方法 processRequest 来处理请求,代码如下。
/** * Delegate GET requests to processRequest/doService. * <p>Will also be invoked by HttpServlet's default implementation of {@code doHead}, * with a {@code NoBodyResponse} that just captures the content length. * @see #doService * @see #doHead */ @Override protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } /** * Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}. * @see #doService */ @Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }然后我们进入 processRequest 方法,实际的请求处理是调用其抽象方法 doService。
/** * Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome. * <p>The actual event handling is performed by the abstract * {@link #doService} template method. */ protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (failureCause != null) { this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause); } else { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing"); } else { this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request"); } } } publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } } /** * Subclasses must implement this method to do the work of request handling, * receiving a centralized callback for GET, POST, PUT and DELETE. * <p>The contract is essentially the same as that for the commonly overridden * {@code doGet} or {@code doPost} methods of HttpServlet. * <p>This class intercepts calls to ensure that exception handling and * event publication takes place. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doGet * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doPost */ protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;然后在 DispatcherServlet 中具体实现请求的处理分发,先是把一些资源放到请求属性中,然后调用 doDispatch 实现请求分发到控制器的 handler。doDispatch 中首先会判断是否是文件传输流的请求(利用MultipartResolver),如果是的话就会转为 MultipartHttpServletRequest。接下来 getHandler(processedRequest) 根据请求获得对应的handler,最后调用 handle() 处理请求,会反射到在控制器中实现的方法。
/** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */ @Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } } /** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Error err) { triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }HandlerAdapter接口的handle方法抽象的是一个handler如何处理一个请求,该接口实现有下面几个。
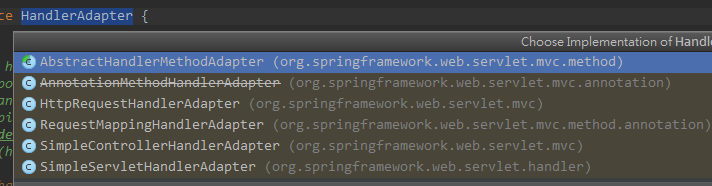
AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter 基于HTTP请求的路径,方法,请求参数,使用 RequestMapping 注解来映handler,从 Spring 3.2建议使用RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。这里看看AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter是如何实现handle方法的, 使用了反射,最后通过 invokeHandlerMethod 执行了对应的handler方法。
@Override public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handler); Boolean annotatedWithSessionAttributes = this.sessionAnnotatedClassesCache.get(clazz); if (annotatedWithSessionAttributes == null) { annotatedWithSessionAttributes = (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(clazz, SessionAttributes.class) != null); this.sessionAnnotatedClassesCache.put(clazz, annotatedWithSessionAttributes); } if (annotatedWithSessionAttributes) { checkAndPrepare(request, response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers, true); } else { checkAndPrepare(request, response, true); } // Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required. if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { return invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handler); } } } return invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handler); } protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ServletHandlerMethodResolver methodResolver = getMethodResolver(handler); Method handlerMethod = methodResolver.resolveHandlerMethod(request); ServletHandlerMethodInvoker methodInvoker = new ServletHandlerMethodInvoker(methodResolver); ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); ExtendedModelMap implicitModel = new BindingAwareModelMap(); Object result = methodInvoker.invokeHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, handler, webRequest, implicitModel); ModelAndView mav = methodInvoker.getModelAndView(handlerMethod, handler.getClass(), result, implicitModel, webRequest); methodInvoker.updateModelAttributes(handler, (mav != null ? mav.getModel() : null), implicitModel, webRequest); return mav; }小结
不要满足于得心应手的事,要不断的做触及能力之上的东西,才会成长。
- DispatcherServlet 源码阅读(1)
- spring源码分析(1) 之 DispatcherServlet:
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(一)
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(二)
- SpringMVC源码(二)DispatcherServlet
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(三)
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(五)
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(六)
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(七)
- DispatcherServlet 源码分析(八)
- SpringMVC深度探险(1,2,3,4)Spring源码阅读:Spring MVC 初始化 - 螺 丝 钉 / DispatcherServlet的初始化主线
- SpringMVC核心控制器DispatcherServlet类结构源码阅读
- SpringMVC源码分析(一)之DispatcherServlet
- VODemo源码阅读(1)
- struts1源码阅读(1)
- struts1源码阅读(1)
- Spring 源码阅读(1)
- sqlalchemy源码阅读(1)
- VMWare Workstation 10.0.4 install guest tool on RHEL7
- Java基础算法(鸡兔同笼、古诗文倒序、递归入门程序、递归解决淘汰问题)
- 增强for循环不止是语法上的优雅
- 聚类算法评价指标:Purity、NMI、MI、entropy、precision、recall、F值、RI值
- MySQL读书笔记-安装初始化操作
- DispatcherServlet 源码阅读(1)
- 一种赋值方式
- Word Pattern
- 【C++】STL常用容器总结之一:容器与迭代器
- java算法(一)——排序算法(下)之 合并排序
- 自定义VC作为iOS程序的RootVC
- Pods-frameworks.sh: No such file or directory、Pods-resources.sh: No such file or directory
- android webview设置内容的字体大小
- liunxqu安装nginx