webpack入门与解析(一)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝网站制作 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/11 04:49
1.初始化
npm init -y
这个命令会创建一个默认的package.json。它包含了项目的一些配置参数,通过它可以进行初始安装。详细参数:https://docs.npmjs.com/files/package.json。
不要y参数的话,会在命令框中设置各项参数,但觉得没啥必要。
2.安装webpack
npm install webpack --save-dev
3.目录结构
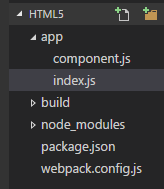
export default function () { var element = document.createElement('h1'); element.innerHTML = 'Hello world'; return element;}
component.js 是输出一个内容为h1元素。export default 是ES6语法,表示指定默认输出。import的时候不用带大括号。
import component from './component';document.body.appendChild(component());index.js 的作用就是引用Component模块,并在页面上输出一个h1元素。但完成这个还需要一个插件,因为目前我们还没有index.html文件。
npm install html-webpack-plugin --save-dev
4.设置 webpack 配置文件
const path = require('path');const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');const PATHS = { app: path.join(__dirname, 'app'), build: path.join(__dirname, 'build'),};module.exports = { entry: { app: PATHS.app, }, output: { path: PATHS.build, filename: '[name].js', }, plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ title: 'Webpack demo', }), ],};第一次看到这个配置文件是有点懵,主要是exports,分三个部分,一个入口,一个输出,一个插件。入口指向了app文件夹。默认会把包含"index.js"的文件作为入口。输出指定了build地址和一个文件名;[name]这儿表示占位符,可以看成webpack提供的一个变量。这个具体后面再看。而HtmlWebpackPlugin会生成一个默认的html文件。
5.打包
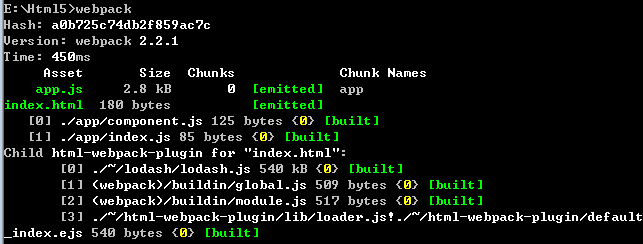
这个输出包含了Hash(每次打包值都不同),Version,Time(耗时)。以及输出的文件信息。 这时打开build文件夹,发现多了一个app.js和index.html文件,双击index.html:
{ "name": "Html5", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "build": "webpack" }, "keywords": [], "author": "", "license": "ISC", "devDependencies": { "html-webpack-plugin": "^2.28.0", "webpack": "^2.2.1" }}
指定build。在cmd中执行npm run build 得到同样的结果
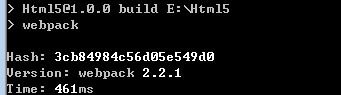
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Webpack demo</title> </head> <body> <script type="text/javascript" src="app.js"></script></body></html>
默认引用了app.js。
6、解析
app.js


/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap/******/ // The module cache/******/ var installedModules = {};/******/ // The require function/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {/******/ // Check if module is in cache/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId])/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {/******/ i: moduleId,/******/ l: false,/******/ exports: {}/******/ };/******/ // Execute the module function/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);/******/ // Flag the module as loaded/******/ module.l = true;/******/ // Return the exports of the module/******/ return module.exports;/******/ }/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;/******/ // expose the module cache/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;/******/ // identity function for calling harmony imports with the correct context/******/ __webpack_require__.i = function(value) { return value; };/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {/******/ configurable: false,/******/ enumerable: true,/******/ get: getter/******/ });/******/ }/******/ };/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);/******/ return getter;/******/ };/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };/******/ // __webpack_public_path__/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";/******/ // Load entry module and return exports/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 1);/******/ })/************************************************************************//******/ ([/* 0 *//***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {"use strict";/* harmony default export */ __webpack_exports__["a"] = function () { var element = document.createElement('h1'); element.innerHTML = 'Hello world'; return element;};/***/ }),/* 1 *//***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {"use strict";Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });/* harmony import */ var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__ = __webpack_require__(0);document.body.appendChild(__webpack_require__.i(__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__["a" /* default */])());/***/ })/******/ ]);
而app.js内容比较多了。整体是一个匿名函数。
(function(module) {})([(function (){}), function() {}])
app文件夹中的两个js文件成了这儿的两个模块。函数最开始是从__webpack_require__开始
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 1);这里指定从模块1执行(赋值语句的返回值为其值)。而模块1的调用是通过__webpack_require__的这句执行的。
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);通过call调用模块的主要作用是为了把参数传过去。
(function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {"use strict";Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });/* harmony import */ var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__ = __webpack_require__(0);document.body.appendChild(__webpack_require__.i(__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__["a" /* default */])());/***/ })
__webpack_require__ 每加载一个模块都会先去模块缓存中找,没有就新建一个module对象:
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} };
模块1中加载了模块0,
var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__ = __webpack_require__(0);
__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__ 返回的是这个模块0的exports部分。而之前Component.js的默认方法定义成了
__webpack_exports__["a"] = function () {var element = document.createElement('h1');element.innerHTML = 'Hello world';return element;}
所以再模块1的定义通过"a“来获取这个方法:
document.body.appendChild(__webpack_require__.i(__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__component__["a" /* default */])());
这样就完整了,但这里使用了__webpack_require__.i 将原值返回。
/******/ // identity function for calling harmony imports with the correct context/******/ __webpack_require__.i = function(value) { return value; };
不太明白这个i函数有什么作用。这个注释也不太明白,路过的大神希望可以指点下。
小结:
webpack通过一个立即执行的匿名函数将各个开发模块作为参数初始化,每个js文件(module)对应一个编号,每个js中export的方法或者对象有各自指定的关键字。通过这种方式将所有的模块和接口方法管理起来。然后先加载最后的一个模块(应该是引用别的模块的模块),这样进而去触发别的模块的加载,使整个js运行起来。到这基本了解了webpack的功能和部分原理,但略显复杂,且没有感受到有多大的好处。继续探索。
- webpack入门与解析(一)
- webpack入门与解析(一)
- webpack入门与解析(一)
- webpack入门与解析(一)
- webpack入门与解析(一)
- 【webpack】-- 入门与解析
- 【webpack】-- 入门与解析
- webpack基础入门(一)
- webpack入门(一)
- 【webpack】-- 自动刷新与解析
- 【webpack】-- 自动刷新与解析
- webpack入门(一)——webpack 介绍
- webpack 打包 + es6 + react入门(一)webpack打包
- webpack入门(一)——webpack 介绍
- (一)webpack入门——webpack的安装
- Webpack 入门(一):安装 / 打包 / 命令行
- 入门学习webpack打包工具(一)
- Webpack入门
- Linux内核源码分析方法
- attribute和property
- Problem B. gCube Google APAC 2016 University Test Round A
- 文章标题android自制多媒体视频播放器和图片压缩技术(字节数组转成Bitmap)
- 蓝桥杯省赛题 四平方和
- webpack入门与解析(一)
- lintcode133最长单词(字符串处理easy)
- Ubuntu 使用cron 设置定时启动任务
- Java Web程序结构
- 局部最小值位置练习
- PAT甲级练习1044. Shopping in Mars (25)
- 软件运行与内存的关系
- 终于理解list_entry和list_for_each_entry
- apache2.4虚拟机配置


