5种创建型模式之:原型模式(Prototype)
来源:互联网 发布:神马软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/07 09:28
定义:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
类型:创建类模式
类图:
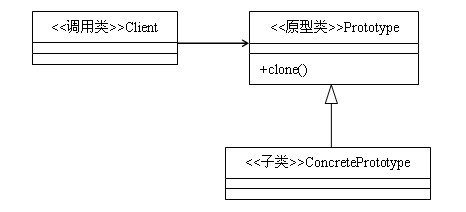
原型模式主要用于对象的复制,它的核心是就是类图中的原型类Prototype。Prototype类需要具备以下两个条件:
- 实现Cloneable接口。在java语言有一个Cloneable接口,它的作用只有一个,就是在运行时通知虚拟机可以安全地在实现了此接口的类上使用clone方法。在java虚拟机中,只有实现了这个接口的类才可以被拷贝,否则在运行时会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常。
- 重写Object类中的clone方法。Java中,所有类的父类都是Object类,Object类中有一个clone方法,作用是返回对象的一个拷贝,但是其作用域protected类型的,一般的类无法调用,因此,Prototype类需要将clone方法的作用域修改为public类型。
原型模式是一种比较简单的模式,也非常容易理解,实现一个接口,重写一个方法即完成了原型模式。在实际应用中,原型模式很少单独出现。经常与其他模式混用,他的原型类Prototype也常用抽象类来替代。
运用场景
资源优化场景
类初始化需要消化非常多的资源,这个资源包括数据、硬件资源等。
性能和安全要求的场景
通过new产生一个对象需要非常繁琐的数据准备或访问权限,则可以使用原型模式。
一个对象多个修改者的场景
一个对象需要提供给其他对象访问,而且各个调用者可能都需要修改其值时,可以考虑使用原型模式拷贝多个对象供调用者使用。
在实际项目中,原型模式很少单独出现,一般是和工厂方法模式一起出现,通过clone的方法创建一个对象,然后由工厂方法提供给调用者。原型模式已经与Java融为浑然一体,大家可以随手拿来使用。
实现代码:
原型模式的优点及适用场景
使用原型模式创建对象比直接new一个对象在性能上要好的多,因为Object类的clone方法是一个本地方法,它直接操作内存中的二进制流,特别是复制大对象时,性能的差别非常明显。
使用原型模式的另一个好处是简化对象的创建,使得创建对象就像我们在编辑文档时的复制粘贴一样简单。
因为以上优点,所以在需要重复地创建相似对象时可以考虑使用原型模式。比如需要在一个循环体内创建对象,假如对象创建过程比较复杂或者循环次数很多的话,使用原型模式不但可以简化创建过程,而且可以使系统的整体性能提高很多。
原型模式的注意事项
- 使用原型模式复制对象不会调用类的构造方法。因为对象的复制是通过调用Object类的clone方法来完成的,它直接在内存中复制数据,因此不会调用到类的构造方法。不但构造方法中的代码不会执行,甚至连访问权限都对原型模式无效。还记得单例模式吗?单例模式中,只要将构造方法的访问权限设置为private型,就可以实现单例。但是clone方法直接无视构造方法的权限,所以,单例模式与原型模式是冲突的,在使用时要特别注意。
- 深拷贝与浅拷贝。Object类的clone方法只会拷贝对象中的基本的数据类型,对于数组、容器对象、引用对象等都不会拷贝,这就是浅拷贝。如果要实现深拷贝,必须将原型模式中的数组、容器对象、引用对象等另行拷贝。例如:
由于ArrayList不是基本类型,所以成员变量list,不会被拷贝,需要我们自己实现深拷贝,幸运的是Java提供的大部分的容器类都实现了Cloneable接口。所以实现深拷贝并不是特别困难。
PS:深拷贝与浅拷贝问题中,会发生深拷贝的有java中的8中基本类型以及他们的封装类型,另外还有String类型。其余的都是浅拷贝。
浅拷贝: 对值类型的成员变量进行值的复制,对引用类型的成员变量只复制引用,不复制引用的对象.
深拷贝: 对值类型的成员变量进行值的复制,对引用类型的成员变量也进行引用对象的复制.
类图:

实例一:浅拷贝
public class Prototype implements Cloneable {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testPrototype();
}
private static void testPrototype(){
Prototype pro = new Prototype();
pro.setName("original object");
Prototype pro1 = (Prototype)pro.clone();
pro.setName("changed object1");
System.out.println("original object:" + pro.getName());
System.out.println("cloned object:" + pro1.getName());
}
}
结果:
original object:changed object1
cloned object:original object
实例二: 浅拷贝
public class Prototype{
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class NewPrototype implements Cloneable {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
private Prototype prototype;
public Prototype getPrototype() {
return prototype;
}
public void setPrototype(Prototype prototype) {
this.prototype = prototype;
}
public Object clone(){
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
testPrototype();
}
private static void testPrototype(){
Prototype pro = new Prototype();
pro.setName("original object");
NewPrototype newObj = new NewPrototype();
newObj.setId("test1");
newObj.setPrototype(pro);
NewPrototype copyObj = (NewPrototype)newObj.clone();
copyObj.setId("testCopy");
copyObj.getPrototype().setName("changed object");
System.out.println("original object id:" + newObj.getId());
System.out.println("original object name:" + newObj.getPrototype().getName());
System.out.println("cloned object id:" + copyObj.getId());
System.out.println("cloned object name:" + copyObj.getPrototype().getName());
}
}
结果:
original object id:test1
original object name:changed object
cloned object id:testCopy
cloned object name:changed object
实例三: 深拷贝
public class Prototype implements Cloneable {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
public class NewPrototype implements Cloneable {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
private Prototype prototype;
public Prototype getPrototype() {
return prototype;
}
public void setPrototype(Prototype prototype) {
this.prototype = prototype;
}
public Object clone(){
NewPrototype ret = null;
try {
ret = (NewPrototype)super.clone();
ret.prototype = (Prototype)this.prototype.clone();
return ret;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
public class TestMain {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
testDeepCopy();
}
private static void testDeepCopy(){
Prototype pro = new Prototype();
pro.setName("original object");
NewPrototype newObj = new NewPrototype();
newObj.setId("test1");
newObj.setPrototype(pro);
NewPrototype copyObj = (NewPrototype)newObj.clone();
copyObj.setId("testCopy");
copyObj.getPrototype().setName("changed object");
System.out.println("original object id:" + newObj.getId());
System.out.println("original object name:" + newObj.getPrototype().getName());
System.out.println("cloned object id:" + copyObj.getId());
System.out.println("cloned object name:" + copyObj.getPrototype().getName());
}
}
结果:
original object id:test1
original object name:original object
cloned object id:testCopy
cloned object name:changed object
实例四: 利用串行化来做深复制
把对象写道流里的过程是串行化(Serilization)过程;把对象从流中读出来是并行化(Deserialization)过程. 写在流里的是对象的一个拷贝,然后再从流里读出来重建对象.
public class PrototypeSe implements Serializable {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class NewPrototypeSe implements Serializable {
private String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
private PrototypeSe prototype;
public PrototypeSe getPrototype() {
return prototype;
}
public void setPrototype(PrototypeSe prototype) {
this.prototype = prototype;
}
public Object deepClone(){
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(this);
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(bo.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
return oi.readObject();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
public class TestDeepClone {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
PrototypeSe po = new PrototypeSe();
po.setName("test1");
NewPrototypeSe se = new NewPrototypeSe();
se.setPrototype(po);
NewPrototypeSe deepClone = (NewPrototypeSe)se.deepClone();
deepClone.getPrototype().setName("test2");
System.out.println("original name:" + se.getPrototype().getName());
System.out.println("cloned name:" + deepClone.getPrototype().getName());
}
}
结果:
original name:test1
cloned name:test2
- 5种创建型模式之:原型模式(Prototype)
- 创建型模式之原型(ProtoType)模式
- 创建型模式之原型模式(prototype)
- 创建型模式之原型模式PROTOTYPE
- 创建模式之Prototype(原型)
- 创建模式之Prototype(原型)
- Prototype原型(创建型模式)
- Prototype原型(创建型模式)
- 创建型-原型模式(prototype)
- (创建模式)设计模式之Prototype(原型)
- 六、创建模式之原型(Prototype)模式
- 设计模式笔记--创建型模式之四--原型prototype
- 创建型模式之原型模式(ProtoType)
- 设计模式之Prototype(原型模式)对象创建型
- 设计模式(创建型)之原型模式(Prototype Pattern)
- 【设计模式】创建型模式之原型Prototype
- 设计模式之对象创建型 — prototype 原型模式
- Prototype - 原型创建模式
- SAP HANA SLT在表中隐藏字段并传入HANA的方法
- HDU 2078复习时间
- Python3的列表list和元组tuple初学总结(未完)
- 常用排序算法,java描述
- 18.输入和输出函数
- 5种创建型模式之:原型模式(Prototype)
- 三大框架面试题
- Python入门教程(一)Python简介
- java
- iOS多线程网络之GCD进阶
- Spring依赖注入之@Inject,@Autowired,@Resource
- 1046. Shortest Distance (20)
- 经典Java面试题 ——Spring AOP
- Python入门教程(二)Python环境搭建


