仿知乎悬浮功能按钮FloatingActionButton
来源:互联网 发布:大数据涂子沛主要观点 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/22 15:44
前段时间在看属性动画,恰巧这个按钮的效果可以用属性动画实现,所以就来实践实践。效果基本出来了,大家可以自己去完善。
首先看一下效果图:

我们看到点击FloatingActionButton后会展开一些item,然后会有一个蒙板效果,这都是这个View的功能。那么这整个View肯定是个ViewGroup,我们一部分一部分来看。
首先是这个最小的Tag: 
这个Tag带文字,可以是一个TextView,但为了美观,我们使用CardView,CardView是一个FrameLayout,我们要让它具有显示文字的功能,就继承CardView自定义一个ViewGroup。
public class TagView extends CardView内部维护一个TextView,在其构造函数中我们实例化一个TextView用来显示文字,并在外部调用setTagText的时候把TextView添加到这个CardView中。
public class TagView extends CardView { private TextView mTextView; public TagView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public TagView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public TagView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); mTextView = new TextView(context); mTextView.setSingleLine(true); } protected void setTextSize(float size){ mTextView.setTextSize(size); } protected void setTextColor(int color){ mTextView.setTextColor(color); } //给内部的TextView添加文字 protected void setTagText(String text){ mTextView.setText(text); addTag(); } //添加进这个layout中 private void addTag(){ LayoutParams layoutParams = new LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT , ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, Gravity.CENTER); int l = dp2px(8); int t = dp2px(8); int r = dp2px(8); int b = dp2px(8); layoutParams.setMargins(l, t, r, b); //addView会引起所有View的layout addView(mTextView, layoutParams); } private int dp2px(int value){ return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP , value, getResources().getDisplayMetrics()); }}接下来我们看这个item,它是一个tag和一个fab的组合:
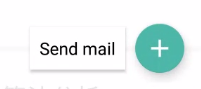
tag使用刚才我们自定义的TagView,fab就用系统的FloatingActionButton,这里显然需要一个ViewGroup来组合这两个子View,可以使用LinearLayout,这里我们就直接使用ViewGroup。
public class TagFabLayout extends ViewGroup我们为这个ViewGroup设置自定义属性,是为了给tag设置text:
<declare-styleable name="FabTagLayout"> <attr name="tagText" format="string" /> </declare-styleable>在构造器中获取自定义属性,初始化TagView并添加到该ViewGroup中:
public TagFabLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); getAttributes(context, attrs); settingTagView(context); } private void getAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attributeSet){ TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attributeSet , R.styleable.FabTagLayout); mTagText = typedArray.getString(R.styleable.FabTagLayout_tagText); typedArray.recycle(); } private void settingTagView(Context context){ mTagView = new TagView(context); mTagView.setTagText(mTagText); addView(mTagView); }在onMeasure对该ViewGroup进行测量,这里我直接把宽高设置成wrap_content的了,match_parent和精确值感觉没有必要。TagView和FloatingActionButton横向排列,中间和两边留一点空隙。
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int width = 0; int height = 0; int count = getChildCount(); for(int i=0; i<count; i++){ View view = getChildAt(i); measureChild(view, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); width += view.getMeasuredWidth(); height = Math.max(height, view.getMeasuredHeight()); } width += dp2px(8 + 8 + 8); height += dp2px(8 + 8); //直接将该ViewGroup设定为wrap_content的 setMeasuredDimension(width, height); }在onLayout中横向布局,tag在左,fab在右。
@Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { //为子View布局 View tagView = getChildAt(0); View fabView = getChildAt(1); int tagWidth = tagView.getMeasuredWidth(); int tagHeight = tagView.getMeasuredHeight(); int fabWidth = fabView.getMeasuredWidth(); int fabHeight = fabView.getMeasuredHeight(); int tl = dp2px(8); int tt = (getMeasuredHeight() - tagHeight) / 2; int tr = tl + tagWidth; int tb = tt + tagHeight; int fl = tr + dp2px(8); int ft = (getMeasuredHeight() - fabHeight) / 2; int fr = fl + fabWidth; int fb = ft + fabHeight; fabView.layout(fl, ft, fr, fb); tagView.layout(tl, tt, tr, tb); bindEvents(tagView, fabView); }还要为这两个子View注册OnClickListener,这是点击事件传递的源头。
private void bindEvents(View tagView, View fabView){ tagView.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { if(mOnTagClickListener != null){ mOnTagClickListener.onTagClick(); } } }); fabView.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (mOnFabClickListener != null){ mOnFabClickListener.onFabClick(); } } }); }现在item的ViewGroup有了,我们还需要一个蒙板,一个主fab,那么我们来看最终的ViewGroup。 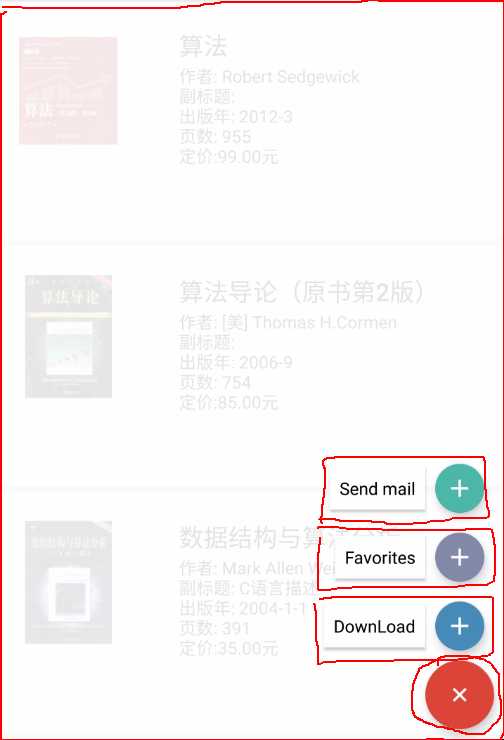
思路也很清楚,蒙板是match_parent的,主fab在右下角(当然我们可以自己设置,也可以对外提供接口来设置位置),三个item(也就是TagFabLayout)在主fab的上面。至于动画效果,在点击事件中触发。
public class MultiFloatingActionButton extends ViewGroup这里我们还需要自定义一些属性,比如蒙板的颜色、主Fab的颜色、主Fab的图案(当然,你把主Fab直接写在xml中就可以直接定义这些属性)、动画的duaration、动画的模式等。
<attr name="animationMode"> <enum name="fade" value="0"/> <enum name="scale" value="1"/> <enum name="bounce" value="2"/> </attr> <attr name="position"> <enum name="left_bottom" value="0"/> <enum name="right_bottom" value="1"/> </attr> <declare-styleable name="MultiFloatingActionButton"> <attr name="backgroundColor" format="color"/> <attr name="switchFabIcon" format="reference"/> <attr name="switchFabColor" format="color"/> <attr name="animationDuration" format="integer"/> <attr name="animationMode"/> <attr name="position"/> </declare-styleable>在构造器中我们同样是获取并初始化属性:
public MultiFloatingActionButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //获取属性值 getAttributes(context, attrs); //添加一个背景View和一个FloatingActionButton setBaseViews(context); }private void getAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attrs){ TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton); mBackgroundColor = typedArray.getColor( R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton_backgroundColor, Color.TRANSPARENT); mFabIcon = typedArray.getDrawable(R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton_switchFabIcon); mFabColor = typedArray.getColorStateList(R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton_switchFabColor); mAnimationDuration = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton_animationDuration, 150); mAnimationMode = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton_animationMode, ANIM_SCALE); mPosition = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.MultiFloatingActionButton_position, POS_RIGHT_BOTTOM); typedArray.recycle(); }接着我们初始化、添加蒙板和主fab。
private void setBaseViews(Context context){ mBackgroundView = new View(context); mBackgroundView.setBackgroundColor(mBackgroundColor); mBackgroundView.setAlpha(0); addView(mBackgroundView); mFloatingActionButton = new FloatingActionButton(context); mFloatingActionButton.setBackgroundTintList(mFabColor); mFloatingActionButton.setImageDrawable(mFabIcon); addView(mFloatingActionButton); }在onMeasure中,我们并不会对这个ViewGroup进行wrap_content的支持,因为基本上都是match_parent的吧,也不会有精确值,而且这个ViewGroup应该是在顶层的。我们看下onLayout方法,在这个方法中,我们对所有子View进行布局。
@Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { if(changed){ //布局背景和主Fab layoutFloatingActionButton(); layoutBackgroundView(); layoutItems(); } }首先布局主Fab,它在右下角,然后添加点击事件,点击这个主Fab后,会涉及到旋转主Fab,改变蒙板透明度,打开或关闭items等操作,这些等下再说。
private void layoutFloatingActionButton(){ int width = mFloatingActionButton.getMeasuredWidth(); int height = mFloatingActionButton.getMeasuredHeight(); int fl = 0; int ft = 0; int fr = 0; int fb = 0; switch (mPosition){ case POS_LEFT_BOTTOM: case POS_RIGHT_BOTTOM: fl = getMeasuredWidth() - width - dp2px(8); ft = getMeasuredHeight() - height - dp2px(8); fr = fl + width; fb = ft + height; break; } mFloatingActionButton.layout(fl, ft, fr, fb); bindFloatingEvent();}private void bindFloatingEvent(){ mFloatingActionButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { rotateFloatingButton(); changeBackground(); changeStatus(); if (isMenuOpen) { openMenu(); } else { closeMenu(); } } }); }然后布局背景:
private void layoutBackgroundView(){ mBackgroundView.layout(0, 0 , getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight()); }接着布局items,并为items添加点击事件。每个item都是TagFabLayout,可以为它setOnTagClickListener和setOnFabClickListener,以便我们点击这两块区域的时候都要能响应,并且我们让这两个回调函数中做同样的事情:旋转主Fab、改变背景、关闭items(因为能点击一定是展开状态)。此时还要在这个ViewGroup中设置一个接口OnFabItemClickListener,用于将点击的位置传递出去,例如Activity实现了这个接口,就可以在onTagClick和onFabClick方法中调用mOnFabItemClickListener.onFabItemClick()方法。说一下这里的布局,是累积向上的,注意坐标的计算。
private void layoutItems(){ int count = getChildCount(); for(int i=2; i<count; i++) { TagFabLayout child = (TagFabLayout) getChildAt(i); child.setVisibility(INVISIBLE); //获取自身测量宽高,这里说一下,由于TagFabLayout我们默认形成wrap_content,所以这里测量到的是wrap_content的最终大小 int width = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int height = child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 获取主Fab测量宽高 int fabHeight = mFloatingActionButton.getMeasuredHeight(); int cl = 0; int ct = 0; switch (mPosition) { case POS_LEFT_BOTTOM: case POS_RIGHT_BOTTOM: cl = getMeasuredWidth() - width - dp2px(8); ct = getMeasuredHeight() - fabHeight - (i - 1) * height - dp2px(8); } child.layout(cl, ct, cl + width, ct + height); bindMenuEvents(child, i); prepareAnim(child); }}private void bindMenuEvents(final TagFabLayout child, final int pos){ child.setOnTagClickListener(new TagFabLayout.OnTagClickListener() { @Override public void onTagClick() { rotateFloatingButton(); changeBackground(); changeStatus(); closeMenu(); if(mOnFabItemClickListener != null){ mOnFabItemClickListener.onFabItemClick(child, pos); } } }); child.setOnFabClickListener(new TagFabLayout.OnFabClickListener() { @Override public void onFabClick() { rotateFloatingButton(); changeBackground(); changeStatus(); closeMenu(); if (mOnFabItemClickListener != null){ mOnFabItemClickListener.onFabItemClick(child, pos); } } });}现在所有的布局和点击事件都已经绑定好了,我们来看下rotateFloatingButton()、 changeBackground() 、 openMenu() 、closeMenu()这几个和属性动画相关的函数。
其实也很简单,rotateFloatingButton()对mFloatingActionButton的rotation这个属性进行改变,以菜单是否打开为判断条件。
private void rotateFloatingButton(){ ObjectAnimator animator = isMenuOpen ? ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mFloatingActionButton , "rotation", 45F, 0f) : ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mFloatingActionButton, "rotation", 0f, 45f); animator.setDuration(150); animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator()); animator.start(); }changeBackground()改变mBackgroundView的alpha这个属性,也是以菜单是否打开为判断条件。
private void changeBackground(){ ObjectAnimator animator = isMenuOpen ? ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBackgroundView, "alpha", 0.9f, 0f) : ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBackgroundView, "alpha", 0f, 0.9f); animator.setDuration(150); animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator()); animator.start(); }openMenu() 中根据不同的模式来实现打开的效果,看一下scaleToShow(),这里同时对scaleX、scaleY、alpha这3个属性进行动画,来达到放大显示的效果。
private void openMenu(){ switch (mAnimationMode){ case ANIM_BOUNCE: bounceToShow(); break; case ANIM_SCALE: scaleToShow(); } }private void scaleToShow(){ for(int i = 2; i<getChildCount(); i++){ View view = getChildAt(i); view.setVisibility(VISIBLE); view.setAlpha(0); ObjectAnimator scaleX = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "scaleX", 0f, 1f); ObjectAnimator scaleY = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "scaleY", 0f, 1f); ObjectAnimator alpha = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "alpha", 0f, 1f); AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet(); set.playTogether(scaleX, scaleY, alpha); set.setDuration(mAnimationDuration); set.start(); }}差不多达到我们要求的效果了,但是还有一个小地方需要注意一下,在menu展开的时候,如果我们点击menu以外的区域,即蒙板上的区域,此时ViewGroup是不会拦截任何Touch事件,如果在这个FloatingActionButton下面有可以被点击响应的View,比如ListView,就会在蒙板显示的情况下进行响应,正确的逻辑应该是关闭menu。

那么我们需要在onInterceptTouchEvent中处理事件的拦截,这里判断的方法是:如果menu是打开的,我们在DOWN事件中判断x,y是否落在了a或b区域,如下图
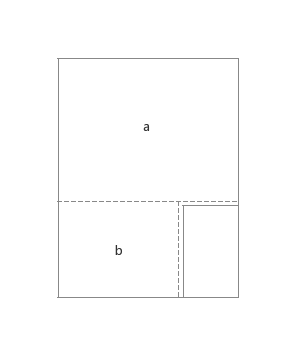
如果是的话,该ViewGroup应该拦截这个事件,交由自身的onTouchEvent处理。
@Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { boolean intercepted = false; int x = (int)ev.getX(); int y = (int)ev.getY(); if(isMenuOpen){ switch (ev.getAction()){ case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: if(judgeIfTouchBackground(x, y)){ intercepted = true; } intercepted = false; break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: intercepted = false; break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: intercepted = false; break; } } return intercepted; } private boolean judgeIfTouchBackground(int x, int y){ Rect a = new Rect(); Rect b = new Rect(); a.set(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight() - getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1).getTop()); b.set(0, getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1).getTop(), getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1).getLeft(), getHeight()); if(a.contains(x, y) || b.contains(x, y)){ return true; } return false; }在onTouchEvent中做关闭menu等操作。
@Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { if(isMenuOpen){ closeMenu(); changeBackground(); rotateFloatingButton(); changeStatus(); return true; } return super.onTouchEvent(event); }再看一下,效果不错。

由于我做的小app中涉及到切换夜间模式,这个ViewGroup的背景色应该随着主题改变,设置该View的背景色为
app:backgroundColor="?attr/myBackground"重写ViewGroup的 setBackgroundColor方法,这里所谓的背景色其实就是蒙板的颜色。
public void setBackgroundColor(int color){ mBackgroundColor = color; mBackgroundView.setBackgroundColor(color);}
基本功能到这里全部完成了,问题还有很多,比如没有提供根据不同的position进行布局、没有提供根据不同mode设置menu开闭的效果,但是后续我还会继续改进和完善^ ^。欢迎交流。如果大家需要源码,可以去我源码里的customview里面自取。在这里
- 仿知乎悬浮功能按钮FloatingActionButton
- 悬浮按钮FloatingActionButton控件
- 浅谈FloatingActionButton(悬浮按钮)
- MaterialDesign之FloatingActionButton(悬浮按钮)
- 悬浮按钮点击回到顶部FloatingActionButton
- Android编程:悬浮菜单按钮FloatingActionButton实例
- FloatingActionButton(悬浮按钮)
- Android FloatingActionButton(FAB) 悬浮按钮
- Android 5.0新控件——FloatingActionButton(悬浮按钮)
- Android 悬浮按钮 FloatingActionButton 和交互提示 SnackBar
- Android 5.0新控件 FloatingActionButton | 悬浮按钮 介绍及使用详情
- FloatingActionButton 浮动按钮
- FloatingActionButton展开按钮
- 仿知乎FloatingActionButton浮动按钮动画效果实现(一)
- 仿知乎FloatingActionButton浮动按钮动画效果实现(二)
- 仿知乎FloatingActionButton浮动按钮动画效果实现(三)
- 悬浮按钮
- 悬浮按钮
- Jquey调试代码
- Android开发技巧——FlingViewPager与RecyclerPagerAdapter
- 两个整数交换
- java spring框架学习
- https
- 仿知乎悬浮功能按钮FloatingActionButton
- Centos下的vim的配置
- 虚拟机连接Xshell
- 练习3.24
- mongodb权威指南-基础
- 拦截器与过滤器的区别以及他们的配置
- HTTP协议请求方法简述及get和post方法区别
- C#与C++数据类型比较及结构体转换
- mvc mvvm mvp


