Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
来源:互联网 发布:旋风象棋软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 12:49
本文转载至:http://ifeve.com/pipe/
Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。
这里是Pipe原理的图示:
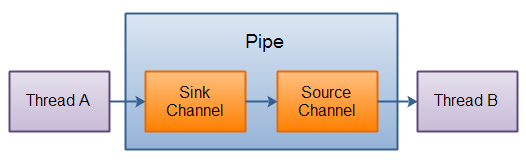
创建管道
通过Pipe.open()方法打开管道。例如:
1Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();向管道写数据
要向管道写数据,需要访问sink通道。像这样:
1Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();通过调用SinkChannel的write()方法,将数据写入SinkChannel,像这样:
01String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis();02ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);03buf.clear();04buf.put(newData.getBytes());05 06buf.flip();07 08while(buf.hasRemaining()) {09 sinkChannel.write(buf);10}从管道读取数据
从读取管道的数据,需要访问source通道,像这样:
1Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();调用source通道的read()方法来读取数据,像这样:
1ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);2 3int bytesRead = sourceChannel.read(buf);read()方法返回的int值会告诉我们多少字节被读进了缓冲区。
java 示例代码:
package com.zzg.nio.pip;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;import java.nio.channels.Pipe;public class PipChannelUtil {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stub// 创建管道Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();// 向管道写数据Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis();ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);buf.clear();buf.put(newData.getBytes());buf.flip();while (buf.hasRemaining()) {sinkChannel.write(buf);}// 可以往source Channel读数据Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();buf.clear();System.out.println("buffer 大小:" + buf);int bytesRead = sourceChannel.read(buf);// read()方法返回的int值会告诉我们多少字节被读进了缓冲区System.out.println("buffer 大小:" + buf);}} 0 0
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- C语言复习笔记 11
- 看第三方是遇到的 英语 集锦
- iOS NSDate用法
- java设计模式--观察者模式 Observer
- C# Tostring 格式化输出字符串全解
- Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
- JSP中#,%,$取值符号的说明
- Java源文件判断
- Hibernate学习笔记(第四天)
- OpenGL.error.NullFunctionError: Attempt to call an undefined function (ubuntu14(32位) python opengl )
- 【PM】互联网项目管理的特点总结
- 数据库模型设计——主键的设计
- 观察者模式(Observer Pattern)
- 软件流程规范---java代码规范


