task_struct结构体
来源:互联网 发布:对万方数据库的评价 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/22 14:18
文章转载至[http://blog.csdn.net/npy_lp/article/details/7292563](http://blog.csdn.net/npy_lp/article/details/7292563)
内核源码:linux-2.6.38.8.tar.bz2
目标平台:ARM体系结构
进程是处于执行期的程序以及它所管理的资源(如打开的文件、挂起的信号、进程状态、地址空间等等)的总称。注意,程序并不是进程,实际上两个或多个进程不仅有可能执行同一程序,而且还有可能共享地址空间等资源。
Linux内核通过一个被称为进程描述符的task_struct结构体来管理进程,这个结构体包含了一个进程所需的所有信息。它定义在linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/sched.h文件中。
本文将尽力就task_struct结构体所有成员的用法进行简要说明。
1、进程状态
- volatile long state;
- int exit_state;

volatile long state; int exit_state;
state成员的可能取值如下:
- #define TASK_RUNNING 0
- #define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 1
- #define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 2
- #define __TASK_STOPPED 4
- #define __TASK_TRACED 8
- /* in tsk->exit_state */
- #define EXIT_ZOMBIE 16
- #define EXIT_DEAD 32
- /* in tsk->state again */
- #define TASK_DEAD 64
- #define TASK_WAKEKILL 128
- #define TASK_WAKING 256

#define TASK_RUNNING 0
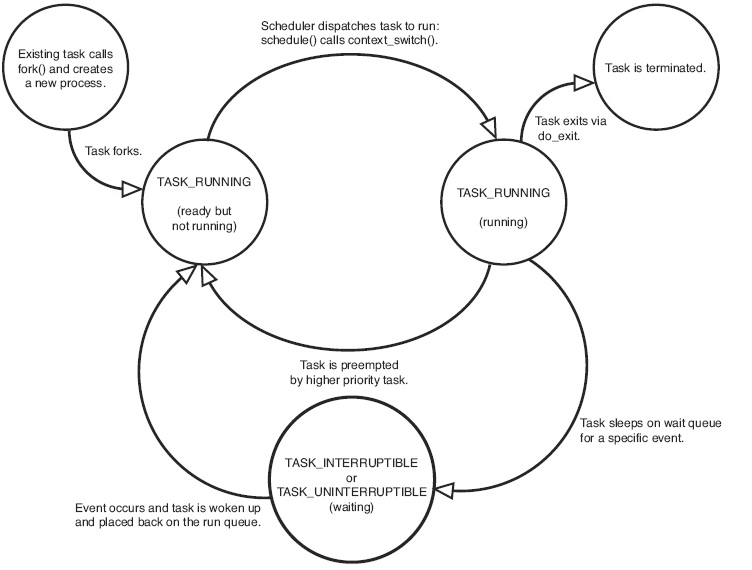
系统中的每个进程都必然处于以上所列进程状态中的一种。
TASK_RUNNING表示进程要么正在执行,要么正要准备执行。
TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE表示进程被阻塞(睡眠),直到某个条件变为真。条件一旦达成,进程的状态就被设置为TASK_RUNNING。
TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE的意义与TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE类似,除了不能通过接受一个信号来唤醒以外。
__TASK_STOPPED表示进程被停止执行。
__TASK_TRACED表示进程被debugger等进程监视。
EXIT_ZOMBIE表示进程的执行被终止,但是其父进程还没有使用wait()等系统调用来获知它的终止信息。
EXIT_DEAD表示进程的最终状态。
EXIT_ZOMBIE和EXIT_DEAD也可以存放在exit_state成员中。进程状态的切换过程和原因大致如下图(图片来自《Linux Kernel Development》):
2、进程标识符(PID)
- pid_t pid;
- pid_t tgid;

pid_t pid; pid_t tgid;
在CONFIG_BASE_SMALL配置为0的情况下,PID的取值范围是0到32767,即系统中的进程数最大为32768个。
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/threads.h */
- #define PID_MAX_DEFAULT (CONFIG_BASE_SMALL ? 0x1000 : 0x8000)

/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/threads.h */#define PID_MAX_DEFAULT (CONFIG_BASE_SMALL ? 0x1000 : 0x8000)
在Linux系统中,一个线程组中的所有线程使用和该线程组的领头线程(该组中的第一个轻量级进程)相同的PID,并被存放在tgid成员中。只有线程组的领头线程的pid成员才会被设置为与tgid相同的值。注意,getpid()系统调用返回的是当前进程的tgid值而不是pid值。
3、进程内核栈
- void *stack;

void *stack;
进程通过alloc_thread_info函数分配它的内核栈,通过free_thread_info函数释放所分配的内核栈。
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/fork.c */
- static inline struct thread_info *alloc_thread_info(struct task_struct *tsk)
- {
- #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_STACK_USAGE
- gfp_t mask = GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_ZERO;
- #else
- gfp_t mask = GFP_KERNEL;
- #endif
- return (struct thread_info *)__get_free_pages(mask, THREAD_SIZE_ORDER);
- }
- static inline void free_thread_info(struct thread_info *ti)
- {
- free_pages((unsigned long)ti, THREAD_SIZE_ORDER);
- }

/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/fork.c */ static inline struct thread_info *alloc_thread_info(struct task_struct *tsk){#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_STACK_USAGE gfp_t mask = GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_ZERO;#else gfp_t mask = GFP_KERNEL;#endif return (struct thread_info *)__get_free_pages(mask, THREAD_SIZE_ORDER);}static inline void free_thread_info(struct thread_info *ti){ free_pages((unsigned long)ti, THREAD_SIZE_ORDER);}其中,THREAD_SIZE_ORDER宏在linux-2.6.38.8/arch/arm/include/asm/thread_info.h文件中被定义为1,也就是说alloc_thread_info函数通过调用__get_free_pages函数分配2个页的内存(它的首地址是8192字节对齐的)。
Linux内核通过thread_union联合体来表示进程的内核栈,其中THREAD_SIZE宏的大小为8192。
- union thread_union {
- struct thread_info thread_info;
- unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
- };

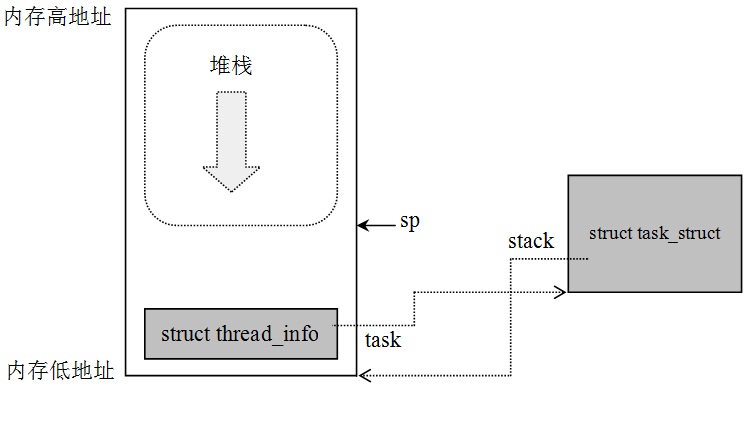
union thread_union { struct thread_info thread_info; unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];};当进程从用户态切换到内核态时,进程的内核栈总是空的,所以ARM的sp寄存器指向这个栈的顶端。因此,内核能够轻易地通过sp寄存器获得当前正在CPU上运行的进程。
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/arch/arm/include/asm/current.h */
- static inline struct task_struct *get_current(void)
- {
- return current_thread_info()->task;
- }
- #define current (get_current())
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/arch/arm/include/asm/thread_info.h */
- static inline struct thread_info *current_thread_info(void)
- {
- register unsigned long sp asm (“sp”);
- return (struct thread_info *)(sp & ~(THREAD_SIZE - 1));
- }

/* linux-2.6.38.8/arch/arm/include/asm/current.h */static inline struct task_struct *get_current(void){ return current_thread_info()->task;}#define current (get_current())/* linux-2.6.38.8/arch/arm/include/asm/thread_info.h */ static inline struct thread_info *current_thread_info(void){ register unsigned long sp asm ("sp"); return (struct thread_info *)(sp & ~(THREAD_SIZE - 1));}进程内核栈与进程描述符的关系如下图:
4、标记
- unsigned int flags; /* per process flags, defined below */

unsigned int flags; /* per process flags, defined below */
flags成员的可能取值如下:
- #define PF_KSOFTIRQD 0x00000001 /* I am ksoftirqd */
- #define PF_STARTING 0x00000002 /* being created */
- #define PF_EXITING 0x00000004 /* getting shut down */
- #define PF_EXITPIDONE 0x00000008 /* pi exit done on shut down */
- #define PF_VCPU 0x00000010 /* I’m a virtual CPU */
- #define PF_WQ_WORKER 0x00000020 /* I’m a workqueue worker */
- #define PF_FORKNOEXEC 0x00000040 /* forked but didn’t exec */
- #define PF_MCE_PROCESS 0x00000080 /* process policy on mce errors */
- #define PF_SUPERPRIV 0x00000100 /* used super-user privileges */
- #define PF_DUMPCORE 0x00000200 /* dumped core */
- #define PF_SIGNALED 0x00000400 /* killed by a signal */
- #define PF_MEMALLOC 0x00000800 /* Allocating memory */
- #define PF_USED_MATH 0x00002000 /* if unset the fpu must be initialized before use */
- #define PF_FREEZING 0x00004000 /* freeze in progress. do not account to load */
- #define PF_NOFREEZE 0x00008000 /* this thread should not be frozen */
- #define PF_FROZEN 0x00010000 /* frozen for system suspend */
- #define PF_FSTRANS 0x00020000 /* inside a filesystem transaction */
- #define PF_KSWAPD 0x00040000 /* I am kswapd */
- #define PF_OOM_ORIGIN 0x00080000 /* Allocating much memory to others */
- #define PF_LESS_THROTTLE 0x00100000 /* Throttle me less: I clean memory */
- #define PF_KTHREAD 0x00200000 /* I am a kernel thread */
- #define PF_RANDOMIZE 0x00400000 /* randomize virtual address space */
- #define PF_SWAPWRITE 0x00800000 /* Allowed to write to swap */
- #define PF_SPREAD_PAGE 0x01000000 /* Spread page cache over cpuset */
- #define PF_SPREAD_SLAB 0x02000000 /* Spread some slab caches over cpuset */
- #define PF_THREAD_BOUND 0x04000000 /* Thread bound to specific cpu */
- #define PF_MCE_EARLY 0x08000000 /* Early kill for mce process policy */
- #define PF_MEMPOLICY 0x10000000 /* Non-default NUMA mempolicy */
- #define PF_MUTEX_TESTER 0x20000000 /* Thread belongs to the rt mutex tester */
- #define PF_FREEZER_SKIP 0x40000000 /* Freezer should not count it as freezable */
- #define PF_FREEZER_NOSIG 0x80000000 /* Freezer won’t send signals to it */

#define PF_KSOFTIRQD 0x00000001 /* I am ksoftirqd */#define PF_STARTING 0x00000002 /* being created */#define PF_EXITING 0x00000004 /* getting shut down */#define PF_EXITPIDONE 0x00000008 /* pi exit done on shut down */#define PF_VCPU 0x00000010 /* I'm a virtual CPU */#define PF_WQ_WORKER 0x00000020 /* I'm a workqueue worker */#define PF_FORKNOEXEC 0x00000040 /* forked but didn't exec */#define PF_MCE_PROCESS 0x00000080 /* process policy on mce errors */#define PF_SUPERPRIV 0x00000100 /* used super-user privileges */#define PF_DUMPCORE 0x00000200 /* dumped core */#define PF_SIGNALED 0x00000400 /* killed by a signal */#define PF_MEMALLOC 0x00000800 /* Allocating memory */#define PF_USED_MATH 0x00002000 /* if unset the fpu must be initialized before use */#define PF_FREEZING 0x00004000 /* freeze in progress. do not account to load */#define PF_NOFREEZE 0x00008000 /* this thread should not be frozen */#define PF_FROZEN 0x00010000 /* frozen for system suspend */#define PF_FSTRANS 0x00020000 /* inside a filesystem transaction */#define PF_KSWAPD 0x00040000 /* I am kswapd */#define PF_OOM_ORIGIN 0x00080000 /* Allocating much memory to others */#define PF_LESS_THROTTLE 0x00100000 /* Throttle me less: I clean memory */#define PF_KTHREAD 0x00200000 /* I am a kernel thread */#define PF_RANDOMIZE 0x00400000 /* randomize virtual address space */#define PF_SWAPWRITE 0x00800000 /* Allowed to write to swap */#define PF_SPREAD_PAGE 0x01000000 /* Spread page cache over cpuset */#define PF_SPREAD_SLAB 0x02000000 /* Spread some slab caches over cpuset */#define PF_THREAD_BOUND 0x04000000 /* Thread bound to specific cpu */#define PF_MCE_EARLY 0x08000000 /* Early kill for mce process policy */#define PF_MEMPOLICY 0x10000000 /* Non-default NUMA mempolicy */#define PF_MUTEX_TESTER 0x20000000 /* Thread belongs to the rt mutex tester */#define PF_FREEZER_SKIP 0x40000000 /* Freezer should not count it as freezable */#define PF_FREEZER_NOSIG 0x80000000 /* Freezer won't send signals to it */
5、表示进程亲属关系的成员
- struct task_struct *real_parent; /* real parent process */
- struct task_struct *parent; /* recipient of SIGCHLD, wait4() reports */
- struct list_head children; /* list of my children */
- struct list_head sibling; /* linkage in my parent’s children list */
- struct task_struct *group_leader; /* threadgroup leader */

struct task_struct *real_parent; /* real parent process */ struct task_struct *parent; /* recipient of SIGCHLD, wait4() reports */ struct list_head children; /* list of my children */ struct list_head sibling; /* linkage in my parent's children list */ struct task_struct *group_leader; /* threadgroup leader */
在Linux系统中,所有进程之间都有着直接或间接地联系,每个进程都有其父进程,也可能有零个或多个子进程。拥有同一父进程的所有进程具有兄弟关系。
real_parent指向其父进程,如果创建它的父进程不再存在,则指向PID为1的init进程。
parent指向其父进程,当它终止时,必须向它的父进程发送信号。它的值通常与real_parent相同。
children表示链表的头部,链表中的所有元素都是它的子进程。
sibling用于把当前进程插入到兄弟链表中。
group_leader指向其所在进程组的领头进程。
6、ptrace系统调用
- unsigned int ptrace;
- struct list_head ptraced;
- struct list_head ptrace_entry;
- unsigned long ptrace_message;
- siginfo_t *last_siginfo; /* For ptrace use. */
- ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_HW_BREAKPOINT
- atomic_t ptrace_bp_refcnt;
- endif

unsigned int ptrace; struct list_head ptraced; struct list_head ptrace_entry; unsigned long ptrace_message; siginfo_t *last_siginfo; /* For ptrace use. */#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_HW_BREAKPOINT atomic_t ptrace_bp_refcnt;#endif
成员ptrace被设置为0时表示不需要被跟踪,它的可能取值如下:
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/ptrace.h */
- #define PT_PTRACED 0x00000001
- #define PT_DTRACE 0x00000002 /* delayed trace (used on m68k, i386) */
- #define PT_TRACESYSGOOD 0x00000004
- #define PT_PTRACE_CAP 0x00000008 /* ptracer can follow suid-exec */
- #define PT_TRACE_FORK 0x00000010
- #define PT_TRACE_VFORK 0x00000020
- #define PT_TRACE_CLONE 0x00000040
- #define PT_TRACE_EXEC 0x00000080
- #define PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE 0x00000100
- #define PT_TRACE_EXIT 0x00000200

/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/ptrace.h */#define PT_PTRACED 0x00000001#define PT_DTRACE 0x00000002 /* delayed trace (used on m68k, i386) */#define PT_TRACESYSGOOD 0x00000004#define PT_PTRACE_CAP 0x00000008 /* ptracer can follow suid-exec */#define PT_TRACE_FORK 0x00000010#define PT_TRACE_VFORK 0x00000020#define PT_TRACE_CLONE 0x00000040#define PT_TRACE_EXEC 0x00000080#define PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE 0x00000100#define PT_TRACE_EXIT 0x00000200
7、Performance Event
- #ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTS
- struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp[perf_nr_task_contexts];
- struct mutex perf_event_mutex;
- struct list_head perf_event_list;
- #endif

#ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTS struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp[perf_nr_task_contexts]; struct mutex perf_event_mutex; struct list_head perf_event_list;#endif
Performance Event是一款随 Linux 内核代码一同发布和维护的性能诊断工具。这些成员用于帮助PerformanceEvent分析进程的性能问题。
关于Performance Event工具的介绍可参考文章http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-perf1/index.html?ca=drs-#major1和http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-perf2/index.html?ca=drs-#major1。
8、进程调度
- int prio, static_prio, normal_prio;
- unsigned int rt_priority;
- const struct sched_class *sched_class;
- struct sched_entity se;
- struct sched_rt_entity rt;
- unsigned int policy;
- cpumask_t cpus_allowed;

int prio, static_prio, normal_prio; unsigned int rt_priority; const struct sched_class *sched_class; struct sched_entity se; struct sched_rt_entity rt; unsigned int policy; cpumask_t cpus_allowed;
实时优先级范围是0到MAX_RT_PRIO-1(即99),而普通进程的静态优先级范围是从MAX_RT_PRIO到MAX_PRIO-1(即100到139)。值越大静态优先级越低。
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/sched.h */
- #define MAX_USER_RT_PRIO 100
- #define MAX_RT_PRIO MAX_USER_RT_PRIO
- #define MAX_PRIO (MAX_RT_PRIO + 40)
- #define DEFAULT_PRIO (MAX_RT_PRIO + 20)

/* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/sched.h */#define MAX_USER_RT_PRIO 100#define MAX_RT_PRIO MAX_USER_RT_PRIO#define MAX_PRIO (MAX_RT_PRIO + 40)#define DEFAULT_PRIO (MAX_RT_PRIO + 20)
static_prio用于保存静态优先级,可以通过nice系统调用来进行修改。
rt_priority用于保存实时优先级。
normal_prio的值取决于静态优先级和调度策略。
prio用于保存动态优先级。
policy表示进程的调度策略,目前主要有以下五种:
- #define SCHED_NORMAL 0
- #define SCHED_FIFO 1
- #define SCHED_RR 2
- #define SCHED_BATCH 3
- /* SCHED_ISO: reserved but not implemented yet */
- #define SCHED_IDLE 5

#define SCHED_NORMAL 0#define SCHED_FIFO 1#define SCHED_RR 2#define SCHED_BATCH 3/* SCHED_ISO: reserved but not implemented yet */#define SCHED_IDLE 5
SCHED_NORMAL用于普通进程,通过CFS调度器实现。SCHED_BATCH用于非交互的处理器消耗型进程。SCHED_IDLE是在系统负载很低时使用。
SCHED_FIFO(先入先出调度算法)和SCHED_RR(轮流调度算法)都是实时调度策略。
sched_class结构体表示调度类,目前内核中有实现以下四种:
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_fair.c */
- static const struct sched_class fair_sched_class;
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_rt.c */
- static const struct sched_class rt_sched_class;
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_idletask.c */
- static const struct sched_class idle_sched_class;
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_stoptask.c */
- static const struct sched_class stop_sched_class;

/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_fair.c */ static const struct sched_class fair_sched_class;/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_rt.c */static const struct sched_class rt_sched_class;/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_idletask.c */static const struct sched_class idle_sched_class;/* linux-2.6.38.8/kernel/sched_stoptask.c */static const struct sched_class stop_sched_class;
se和rt都是调用实体,一个用于普通进程,一个用于实时进程,每个进程都有其中之一的实体。
cpus_allowed用于控制进程可以在哪里处理器上运行。
- task_struct结构体
- task_struct结构体
- 【linux】task_struct结构体
- 浅析task_struct结构体
- 浅析task_struct结构体
- task_struct结构体详解
- task_struct结构体字段
- task_struct结构体注释
- task_struct结构体
- 进程task_struct结构体
- Task_struct结构体
- task_struct结构体
- task_struct结构体
- 浅析task_struct结构体
- linux的task_struct结构体
- Linux中的task_struct结构体
- task_struct结构体成员详解
- linux PCB task_struct结构体
- 元件引脚直径与PCB焊盘孔径对应关系
- 深度学习之理解神经网络的四个公式
- 【链表】实现LRU缓存策略LRU Cache
- Python学习笔记 --- Python命名规范
- PHP OpenSSL&Mcrypt实现AES加密
- task_struct结构体
- FA-期间重新打开
- 设计模式之原型模式
- gles小注意
- ubuntu 安装搜狗输入法 [防坑版]
- angular 如果给date初始化值,model一定得是Date类型,否则会报错
- BPCU的含义
- 使用JADX进行安卓反编译的心得
- [Google Guava] 缓存


