线段树学习
来源:互联网 发布:cf一直网络出现异常 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/29 12:45
HH神的线段树出神入化,所以跟着HH学习线段树。
风格:
maxn是题目给的最大区间,而节点数要开4倍,确切的说……
lson和rson辨别表示结点的左孩子和右孩子。
PushUp(int rt)是把当前结点的信息更新到父节点
PushDown(int rt)是把当前结点的信息更新给孩子结点。
rt表示当前子树的根(root),也就是当前所在的结点。
思想:
对于每个非叶节点所标示的结点 [a,b],其做孩子表示的区间是[a,(a+b)/2],其右孩子表示[(a+b)/2,b].
构造:
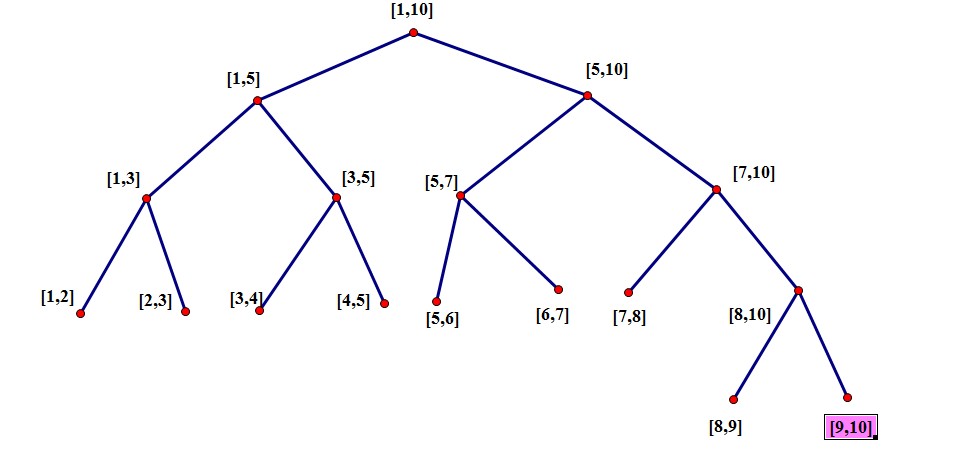
离散化和线段树:
题目:x轴上有若干个线段,求线段覆盖的总长度。
普通解法:设置坐标范围[min,max],初始化为0,然后每一段分别染色为1,最后统计1的个数,适用于线段数目少,区间范围小。
离散化的解法:离散化就是一一映射的关系,即将一个大坐标和小坐标进行一一映射,适用于线段数目少,区间范围大。
例如:[10000,22000],[30300,55000],[44000,60000],[55000,60000].
第一步:排序 10000 22000 30300 44000 55000 60000
第二部:编号 1 2 3 4 5 6
第三部:用编号来代替原数,即小数代大数 。
[10000,22000]~[1,2]
[30300,55000]~[3,5]
[44000,60000]~[4,6]
[55000,60000]~[5,6]
然后再用小数进行普通解法的步骤,最后代换回去。
线段树的解法:线段树通过建立线段,将原来染色O(n)的复杂度减小到 log(n),适用于线段数目多,区间范围小的情况。
离散化的线段树:适用于线段数目多,区间范围大的情况。
构造:
动态数据结构:
struct node{
node* left;
node* right;
……
}
静态全局数组模拟(完全二叉树):
struct node{
int left;
int right;
……
}Tree[MAXN]
例如:

线段树与点树:
线段树的每一个结点表示一个点,成为点树,比如说用于求第k小数的线段树。
点树结构体:
struct node{
int l, r;
int c;//用于存放次结点的值,默认为0
}T[3*MAXN];
创建:
创建顺序为先序遍历,即先构造根节点,再构造左孩子,再构造右孩子。
void construct(int l, int r, int k){ T[k].l = l; T[k].r = r; T[k].c = 0; if(l == r) return ; int m = (l + r) >> 1; construct(l, m, k << 1); construct(m + 1, r, (k << 1) + 1); return ;} 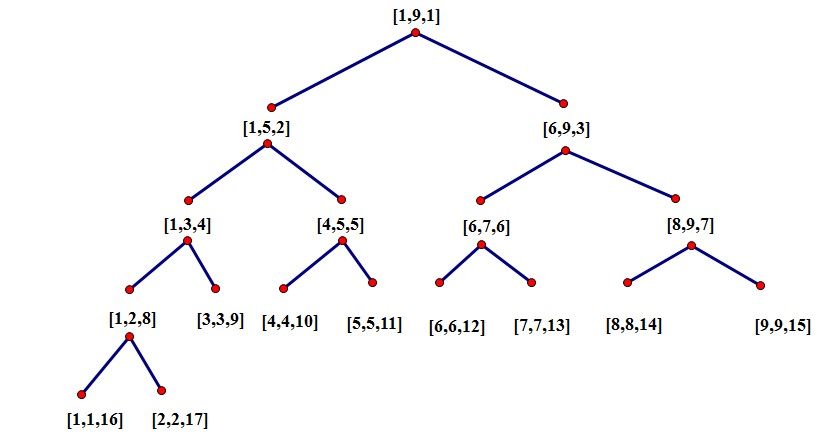
[A,B,C]:A表示左值,B表示右值,C表示在静态数组中的位置,由此可知,n个点的话大约共有2*n个结点,因此开3*n的结构体一定是够的。
更新值:
void insert(int d, int k){ //如果找到了就c值+1返回。 if(T[k].l == T[k].r && d == T[k].l){ T[k].c += 1; return ; } int m = (T[k].l + T[k].r) >> 1; if(d <= m) insert(d, k << 1); else insert(d, (k << 1) + 1); //更新每一个c,向上更新 T[k].c = T[k << 1].c + T[(k << 1) + 1].c;}查找值:
//k表示树根,d表示要查找的值void search(int d, int k, int& ans){ if(T[k].l == T[k].r){ ans = T[k].l; ans = T[k].l; } int m = (T[k].l + T[k].r) >> 1; //不懂 if(d > T[(k << 1)].c) search(d - T[k << 1].c, (k << 1) + 1, ans); else search(d, k << 1, ans);}search函数的用法不太懂。
例题解:
(待更新)
四类题型:
1.单点更新 只更新叶子结点,然后把信息用PushUp(int r)这个函数更新上来。
hdu1166:敌兵布阵
线段树功能:update:单点替换 query:区间最值
poj2828
树状数组:
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <string>#include <cstring>using namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;const int maxn = 200000;int C[maxn + 100];int B[maxn + 100];int n;PII arr[maxn + 100];int lowbit(int k) { return k & (-k); }void init() { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) C[i] = lowbit(i); memset(B, -1, n + 10);}void update(int i) { while(i <= n) { C[i]--; i += lowbit(i); }}int query(int i) { int ret = 0; while(i > 0) { ret += C[i]; i -= lowbit(i); } return ret;}void debug() { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << i << " " << query(i) << endl;}void fun(int a, int v) { int l = 1, r = n; while(l < r) { int m = (l + r) >> 1; if(query(m) >= a) r = m; else l = m + 1; } //cout << "here " << l << endl; update(l); //cout << "here2 " << endl; //debug(); B[l] = v; //return l;}int main() { while(~scanf("%d", &n)) { init(); int a, b; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); a++; arr[i].first = a; arr[i].second = b; } for(int i = n; i > 0; i--) fun(arr[i].first, arr[i].second); //debug2(); //bool flag = false; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { i == 1 ? printf("%d", B[i]) : printf(" %d", B[i]); //if(B[i] != -1 && !flag) { printf("%d", B[i]); flag = true; } //else if(B[i] != -1) printf(" %d", B[i]); } puts(""); } return 0;}poj-3468
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <iostream>using namespace std;#define lson l, m, rt<<1#define rson m+1, r, rt<<1|1typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 111111;LL col[maxn<<2];LL sum[maxn<<2];void PushUp(LL rt) { sum[rt] = sum[rt<<1] + sum[rt<<1|1];}//pushdown的作用是如果此点可以更新。//也就是更新到下一层//如果是底层,那么是不用pushdown的。void PushDown(LL rt, LL m) { if(col[rt]) { //col[rt<<1] = col[rt<<1|1] = col[rt]; col[rt<<1] += col[rt]; col[rt<<1|1] += col[rt]; sum[rt<<1] += col[rt] * (m - (m>>1)); sum[rt<<1|1] += col[rt] * (m>>1); col[rt] = 0; }}void build(LL l, LL r, LL rt) { col[rt] = 0; //cout << l << " " << r << endl; if(l == r) { scanf("%I64d", &sum[rt]); //cout << rt << " " << sum[rt] << endl; return ; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; build(lson); build(rson); PushUp(rt);}LL query(LL L, LL R, LL l, LL r, LL rt) { LL ret = 0; if(L <= l && r <= R) { //if(col[rt]) return sum[rt] + (r - l + 1) * col[rt]; return sum[rt]; } PushDown(rt, r - l + 1); int m = (l + r) >> 1; if(L <= m) ret += query(L, R, lson); if(R > m) ret += query(L, R, rson); return ret;}void update(LL L, LL R, LL c, LL l, LL r, LL rt) { if(L <= l && r <= R) { sum[rt] += c * (r - l + 1); col[rt] += c;//子节点没有更新 return ; } PushDown(rt, r - l + 1); int m = (l + r) >> 1; if(L <= m) update(L, R, c, lson); if(R > m) update(L, R, c, rson); PushUp(rt);}void debug(int n) { for(int i = 1; i <= (n*3); i++) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; for(int i = 1; i <= (n*3); i++) { cout << col[i] << " "; } cout << endl << endl; for(int i = 1; i <= (n*3); i++) { cout << i << " "; } cout << endl; for(int i = 1; i <= (n*3); i++) { cout << sum[i] << " "; } cout << endl;}int main() { LL N, Q; while(~scanf("%I64d%I64d", &N, &Q)) { //cout << "N = " << N << endl; memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum)); memset(col, 0, sizeof(col)); build(1, N, 1); //debug(N); for(int i = 0; i < Q; i++) { char ch[3]; LL a, b, c; scanf("%s", ch); if(ch[0] == 'Q') { scanf("%I64d%I64d", &a, &b); printf("%I64d\n", query(a, b, 1, N, 1)); } else { scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d", &a, &b, &c); update(a, b, c, 1, N, 1); } //debug(N); } } return 0;}- 学习线段树
- 线段树学习入门
- 留待学习线段树
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习
- 线段树 学习资料
- 学习笔记 线段树
- 线段树学习小结
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习记录
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习
- 线段树学习笔记
- 线段树学习笔记
- 学习笔记 --- 线段树
- openvpn注销证书
- 判断flash是否加载完成
- STL中std::map用法详解
- Stanford 算法入门 week 2 Assignment QuickSort
- 黑马程序员_学习日记八_集合三
- 线段树学习
- setLayoutParams
- Eclipse开发快捷键
- poj 2301 Beat the Spread!
- poj 2001
- 在Ubuntu 12.04 下解决CRT显示器刷新率问题
- 不要让英语成为你的短板
- div去除浮动
- VB的SizeOfCode 有一点点的Bug


