最大流问题
来源:互联网 发布:2016淘宝客推广 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/19 12:40
转载于 http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/07/26/2117636.html
最近又复习了下最大流问题,每次看这部分的内容都会有新的收获。可以说最大流问题的资料网上一搜一大把,根本没有必要自己写;但是大部分资料上的专业术语太多了,初学很难理解,至少我当年学这部分的时候前几次就没有看懂。所以我准备备份一点个人的理解。
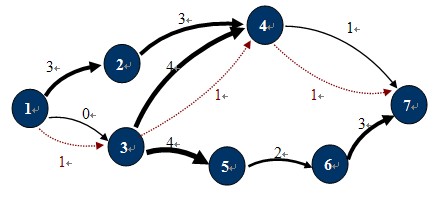 图-1
图-1
如图-1所示,在这个运输网络中,源点S和汇点T分别是1,7,各边的容量为C(u,v)。图中红色虚线所示就是一个可行流。标准图示法如图-2所示:
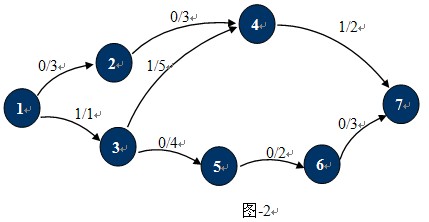
其中p(u,v) / c(u,v)分别表示该边的实际流量与最大容量。
关于最大流
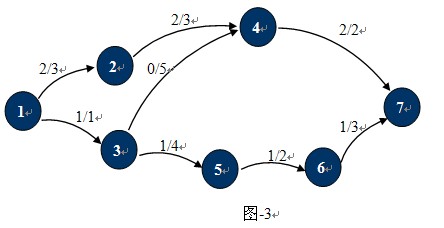
熟悉了什么是网络流,最大流也就很好理解了。就是对于任意的u∈V-{s},使得p(s,u)的和达到最大。上面的运输网络中,最大流如图-3所示:MaxFlow=p(1,2)+p(1,3)=2+1=3。
在介绍最大流问题之前,先介绍几个概念:残余网络,增广路径,反向弧,最大流定理以及求最大流的Ford-Fulkerson方法。
残余网络 增广路径 反向弧
观察下图-4,这种状态下它的残余网络如图-5所示:
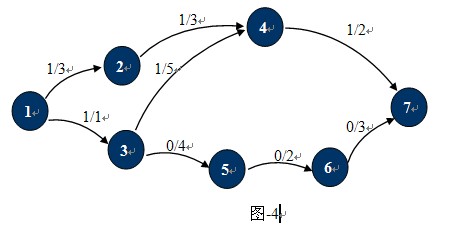
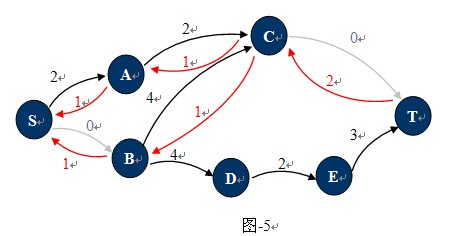
也许现在你已经知道什么是残余网络了,对于已经找到一条从S 到T的路径的网络中,只要在这条路径上,把C(u,v)的值更新为C(u,v)-P(u,v),并且添加反向弧C(v,u)。对应的增广路径Path为残留网络上从S到T的一条简单路径。图-4中1,2,4,7就是一条增广路径,当然还有1,3,4,7。
此外在未做任何操作之前,原始的有向图也是一个残余网络,它仅仅是未做任何更新而已。
最大流定理
如果残留网络上找不到增广路径,则当前流为最大流;反之,如果当前流不为最大流,则一定有增广路径。
Ford-Fulkerson方法
介绍完上面的概念之后,便可以用Ford-Fulkerson方法求最大流了。为什么叫Ford-Fulkerson方法而不是算法,原因在于可以用多种方式实现这一方法,方式并不唯一。下面介绍一种基于广度优先搜索(BFS)来计算增广路径P的算法:Edmonds-Karp算法。
算法流程如下:
设队列Q:存储当前未访问的节点,队首节点出队后,成为已检查的标点;
Path数组:存储当前已访问过的节点的增广路径;
Flow数组:存储一次BFS遍历之后流的可改进量;
Repeat:
Path清空;
源点S进入Path和Q,Path[S]<-0,Flow[S]<-+∞;
While Q非空 and 汇点T未访问 do
Begin
队首顶点u出对;
For每一条从u出发的弧(u,v) do
If v未访问 and 弧(u,v) 的流量可改进;
Then Flow[v]<-min(Flow[u],c[u][v]) and v入队 and Path[v]<-u;
End while
If(汇点T已访问)
Then 从汇点T沿着Path构造残余网络;
Until 汇点T未被访问
应用实例
这是一道最大流的入门题,题目如下:
http://acm.pku.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problem?id=1273
Description
Every time it rains on Farmer John's fields, a pond forms over Bessie's favorite clover patch. This means that the clover is covered by water for awhile and takes quite a long time to regrow. Thus, Farmer John has built a set of drainage ditches so that Bessie's clover patch is never covered in water. Instead, the water is drained to a nearby stream. Being an ace engineer, Farmer John has also installed regulators at the beginning of each ditch, so he can control at what rate water flows into that ditch.
Farmer John knows not only how many gallons of water each ditch can transport per minute but also the exact layout of the ditches, which feed out of the pond and into each other and stream in a potentially complex network.
Given all this information, determine the maximum rate at which water can be transported out of the pond and into the stream. For any given ditch, water flows in only one direction, but there might be a way that water can flow in a circle.
Input
The input includes several cases. For each case, the first line contains two space-separated integers, N (0 <= N <= 200) and M (2 <= M <= 200). N is the number of ditches that Farmer John has dug. M is the number of intersections points for those ditches. Intersection 1 is the pond. Intersection point M is the stream. Each of the following N lines contains three integers, Si, Ei, and Ci. Si and Ei (1 <= Si, Ei <= M) designate the intersections between which this ditch flows. Water will flow through this ditch from Si to Ei. Ci (0 <= Ci <= 10,000,000) is the maximum rate at which water will flow through the ditch.
Output
For each case, output a single integer, the maximum rate at which water may emptied from the pond.
Sample Input
5 4
1 2 40
1 4 20
2 4 20
2 3 30
3 4 10
Sample Output
50
2 #include <queue>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 const int N = 210;
6 const int INF = 0x7FFFFFFF;
7 int n,m,map[N][N],path[N],flow[N],start,end;
8 queue<int> q;
9
10 int bfs(){
11 int i,t;
12 while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
13 memset(path,-1,sizeof(path));
14 path[start]=0,flow[start]=INF;
15 q.push(start);
16 while(!q.empty()){
17 t=q.front();
18 q.pop();
19 if(t==end) break;
20 for(i=1;i<=m;i++){
21 if(i!=start && path[i]==-1 && map[t][i]){
22 flow[i]=flow[t]<map[t][i]?flow[t]:map[t][i];
23 q.push(i);
24 path[i]=t;
25 }
26 }
27 }
28 if(path[end]==-1) return -1;
29 return flow[m]; //一次遍历之后的流量增量
30 }
31 int Edmonds_Karp(){
32 int max_flow=0,step,now,pre;
33 while((step=bfs())!=-1){ //找不到增路径时退出
34 max_flow+=step;
35 now=end;
36 while(now!=start){
37 pre=path[now];
38 map[pre][now]-=step; //更新正向边的实际容量
39 map[now][pre]+=step; //添加反向边
40 now=pre;
41 }
42 }
43 return max_flow;
44 }
45 int main(){
46 int i,u,v,cost;
47 while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)!=EOF){
48 memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
49 for(i=0;i<n;i++){
50 scanf("%d %d %d",&u,&v,&cost);
51 map[u][v]+=cost; //not just only one input
52 }
53 start=1,end=m;
54 printf("%d\n",Edmonds_Karp());
55 }
56 return 0;
57 }
58
Description
All data concerning customers planning to visit the farm on that particular day are available to Mirko early in the morning so that he can make a sales-plan in order to maximize the number of pigs sold.
More precisely, the procedure is as following: the customer arives, opens all pig-houses to which he has the key, Mirko sells a certain number of pigs from all the unlocked pig-houses to him, and, if Mirko wants, he can redistribute the remaining pigs across the unlocked pig-houses.
An unlimited number of pigs can be placed in every pig-house.
Write a program that will find the maximum number of pigs that he can sell on that day.
Input
The next line contains M integeres, for each pig-house initial number of pigs. The number of pigs in each pig-house is greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 1000.
The next N lines contains records about the customers in the following form ( record about the i-th customer is written in the (i+2)-th line):
A K1 K2 ... KA B It means that this customer has key to the pig-houses marked with the numbers K1, K2, ..., KA (sorted nondecreasingly ) and that he wants to buy B pigs. Numbers A and B can be equal to 0.
Output
Sample Input
3 33 1 102 1 2 22 1 3 31 2 6
Sample Output
7
二、分析
这道题的见图有些复杂,不过看到猪圈有1000个,而顾客有100个,可以发现不可能以猪圈为顶点。新设两个顶点,一个s,一个t,当第一个顾客有个一个猪圈的钥匙时,就有一条从s到该顾客的边,容量为猪圈中猪的数量,以后另外有顾客有这个猪圈的钥匙是,则有一条从前一个顾客到这个顾客的边,容量为无穷大,同时每个顾客都有到t的边,容量为顾客的需求量。求最大流,使用Relabel-To-Front算法,具体算法:最大流问题
三、代码
#include<iostream>#include<list>using namespace std;#define MAXM 1001#define MAXN 101int s, t;int n, m;int pig[MAXM], record[MAXM];int c[MAXN+2][MAXN+2];int f[MAXN+2][MAXN+2];int e[MAXN+2];int h[MAXN+2];list<int> l;list<int>::iterator lit;list<int> neb[MAXN+2];list<int>::iterator nit[MAXN+2];void push(int u, int v){ int d = min(e[u], c[u][v] - f[u][v]); f[u][v] += d; f[v][u] = -f[u][v]; e[u] -= d; e[v] += d;}void relabel(int u){ int mh = INT_MAX; for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++) { if(c[u][i] > f[u][i]) mh = min(mh, h[i]); } h[u] = mh + 1;}void discharge(int u){ while(e[u] > 0) { if(nit[u] == neb[u].end()) { relabel(u); nit[u] = neb[u].begin(); continue; } int v = *nit[u]; if(c[u][v] > f[u][v] && h[u] == h[v]+1) push(u, v); else nit[u]++; }}void init_preflow(){ memset(h, 0, sizeof(h)); memset(e, 0, sizeof(e)); h[s] = n+2; for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++) { if(c[s][i] == 0) continue; f[s][i] = c[s][i]; f[i][s] = -f[s][i]; e[i] = c[s][i]; e[s] -= c[s][i]; }}void relabel_to_front(){ init_preflow(); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { l.push_back(i); nit[i] = neb[i].begin(); } lit = l.begin(); while(lit != l.end()) { int u = *lit; int old = h[u]; discharge(u); if(h[u] > old) { l.erase(lit); l.push_front(u); lit = l.begin(); } lit++; }}int main(){ memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); memset(f, 0, sizeof(f)); memset(record, -1, sizeof(record)); scanf("%d%d", &m, &n); s = 0; t = n+1; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) scanf("%d", &pig[i]); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { int a, k, b; scanf("%d", &a); for(int j=0; j<a; j++) { scanf("%d", &k); if(record[k] == -1) { if(c[s][i] == 0) { c[s][i] = pig[k]; neb[s].push_back(i); neb[i].push_back(s); } else c[s][i] += pig[k]; record[k] = i; } else { c[record[k]][i] = INT_MAX; neb[record[k]].push_back(i); neb[i].push_back(record[k]); } } scanf("%d", &b); c[i][t] = b; neb[i].push_back(t); neb[t].push_back(i); } relabel_to_front(); printf("%d\n", e[t]);}- 网络最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 网络最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- 最大流问题
- Java IO流学习总结
- Decimal to Binary
- 9i10g11g编程艺术——索引
- Java调用C和C++函数时的JNI使用区别
- 我的U盘终于中招啦:U盘快捷方式病毒
- 最大流问题
- 使用GCD
- VC程序中打开一个另一个程序并关闭
- struts2学习笔记-----拦截器
- 混合高斯模型
- 视图类动态创建视图窗口
- 从最大似然到EM算法浅解
- surfer 8 scripter 学习笔记(2)Application对象
- 如何把string的元素逆序


