HDU 2814 Interesting Fibonacci 循环节
来源:互联网 发布:乐高幻影忍者玩具淘宝 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/29 12:17
Interesting Fibonacci
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 704 Accepted Submission(s): 130
Problem Description
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers are a sequence of numbers named after Leonardo of Pisa, known as Fibonacci (a contraction of filius Bonaccio, "son of Bonaccio"). Fibonacci's 1202 book Liber Abaci introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics, although the sequence had been previously described in Indian mathematics.
The first number of the sequence is 0, the second number is 1, and each subsequent number is equal to the sum of the previous two numbers of the sequence itself, yielding the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, etc. In mathematical terms, it is defined by the following recurrence relation:
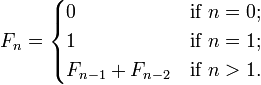
That is, after two starting values, each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. The first Fibonacci numbers (sequence A000045 in OEIS), also denoted as F[n];
F[n] can be calculate exactly by the following two expressions:
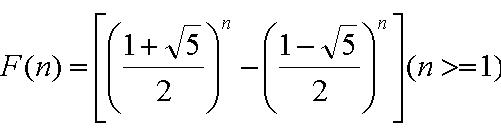
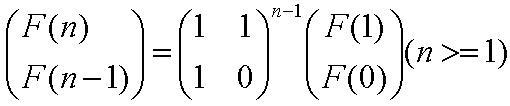
A Fibonacci spiral created by drawing arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling; this one uses squares of sizes 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, and 34;
So you can see how interesting the Fibonacci number is.
Now AekdyCoin denote a function G(n)
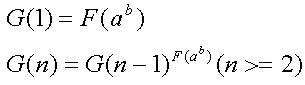
Now your task is quite easy, just help AekdyCoin to calculate the value of G (n) mod C
The first number of the sequence is 0, the second number is 1, and each subsequent number is equal to the sum of the previous two numbers of the sequence itself, yielding the sequence 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, etc. In mathematical terms, it is defined by the following recurrence relation:
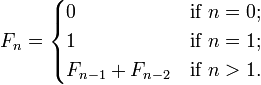
That is, after two starting values, each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. The first Fibonacci numbers (sequence A000045 in OEIS), also denoted as F[n];
F[n] can be calculate exactly by the following two expressions:
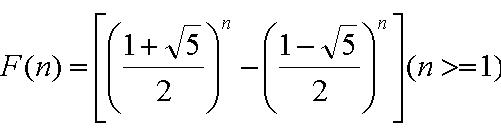
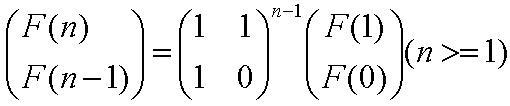
A Fibonacci spiral created by drawing arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling; this one uses squares of sizes 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, and 34;
So you can see how interesting the Fibonacci number is.
Now AekdyCoin denote a function G(n)
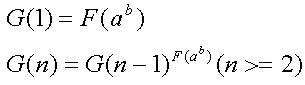
Now your task is quite easy, just help AekdyCoin to calculate the value of G (n) mod C
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T is given in the first line of the input. Each test case begins with a line containing A, B, N, C (10<=A, B<2^64, 2<=N<2^64, 1<=C<=300)
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the test case number( beginning with 1) followed by a integer which is the value of G(N) mod C
Sample Input
117 18446744073709551615 1998 139
Sample Output
Case 1: 120
Author
AekdyCoin
Source
HDU 1st “Old-Vegetable-Birds Cup” Programming Open Contest
#include <cstdlib>#include <cctype>#include <cstring>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <string>#include <iostream>#include <sstream>#include <map>#include <set>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <fstream>#include <numeric>#include <iomanip>#include <bitset>#include <list>#include <stdexcept>#include <functional>#include <utility>#include <ctime>using namespace std;typedef unsigned long long ull;ull a,b,n,c;ull f[9999];int find_loop(int c) //循环节{ int loop; f[0]=0;f[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<2005;i++) { f[i]=(f[i-1]%c+f[i-2]%c)%c; if(f[i]==1&&f[i-1]==0) { loop=i; break; } } return loop-1;}int phi(int n) //欧拉函数{ int rea=n,i; for(i=2;i*i<=n;i++) { if(n%i==0) { rea=rea-rea/i; while(n%i==0) n/=i; } } if(n>1) rea=rea-rea/n; return rea;}ull quickpow(ull a,ull b,ull c)//快速幂{ ull ans=1; a=a%c; while(b>0) { if(b&1) ans=(ans*a)%c; b=b/2; a=(a*a)%c; } return ans;}int main(){ int t; int cas=1; ull t1,t2,temp1,temp2; cin>>t; while(t--) { scanf("%I64u%I64u%I64u%I64u",&a,&b,&n,&c); printf("Case %d: ",cas++); int p=phi(c); int loop1=find_loop(c); t1=quickpow(a,b,loop1); temp1=f[t1]%c; int loop2=find_loop(p); t2=quickpow(a,b,loop2); temp2=f[t2]%p; temp2=quickpow(temp2,n-1,p); temp2+=p; printf("%d\n",quickpow(temp1,temp2,c)); }} 0 0
- HDU 2814 Interesting Fibonacci 循环节
- HDU 2814 - Interesting Fibonacci (Fibonacci性质 + 循环节)
- hdu-2814-Interesting Fibonacci-斐波那契循环节
- hdu 2814 Interesting Fibonacci
- hdu 2814 Interesting Fibonacci
- hdu 2814 Interesting Fibonacci
- hdu 2814 Interesting Fibonacci
- hdu 1021 Fibonacci Again(矩阵连乘 || 循环节)
- Uva 11582(Fibonacci循环节)
- hdu 5451 Best Solver (特征方程求通项+广义Fibonacci数列找循环节)
- hdu 5451 Best Solver 快速矩阵乘法 Fibonacci数列的循环节
- HDU 3195 Interesting Numbers
- HDU 5785 Interesting
- 广义Fibonacci数列找循环节
- 广义Fibonacci数列找循环节
- 广义Fibonacci数列找循环节
- 求Fibonacci数列的循环节
- HDU1021 Fibonacci Again 循环节||取模
- DRM进入HTML 5标准 两害相权取其轻?
- 入职一月感受
- Android特效 五种Toast详解
- Square(DFS)
- sgu 414 Orthogonal Circles 圆的正交
- HDU 2814 Interesting Fibonacci 循环节
- CentOs使用yum方式安装wine 并安装Source Insight
- poj3211 Washing Clothes
- 胜利大逃亡
- 自定义ClassLoader
- org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException: could not insert
- windows驱动数字签名
- 解决mysql自动断掉连接的问题
- 关系型数据库与NOSQL



