利用树的先序和后序遍历打印os中的目录树
来源:互联网 发布:程序员能干到多少岁 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/18 11:34
【0】README
0.1)本代码均为原创,旨在将树的遍历应用一下下以加深印象而已;(回答了学习树的遍历到底有什么用的问题?)你对比下linux 中的文件树 和我的打印结果就明理了;

0.2)我们采用的是 儿子兄弟表示法 来 表示树的整体节点构造;
0.3)儿子兄弟表示法介绍
0.3.1)如下图所示: 向下的箭头(左指针)指向第一个儿子节点, 从左到右的箭头(右指针)指向下一个兄弟节点;(间接说明了树的节点有两个指针)
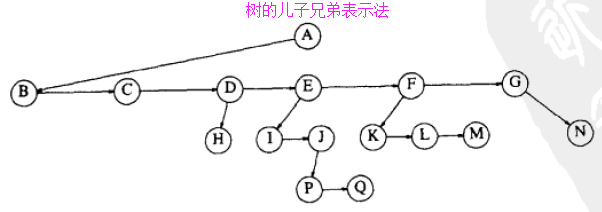

0.3.2)树节点定义代码如下:
struct Tree;typedef struct Tree *Tree;// we adopt child-sibling notationstruct Tree{ ElementType value; Tree firstChild; Tree nextSibling;};0.4)哥子第一次 使用着 丑到逼爆 的 编辑器,也是醉了,主要是markdown 对于源代码文件显示不够清晰, oh m g;
【1】任务来了
我们想要列出目录中所有文件的名字, 我们的输出格式将是:深度为 depth 的文件的名字将被 depth 次跳格缩进后打印出来;
【2】给出先序遍历+后序遍历目录树的实现代码
2.1)先序遍历步骤:
step1)访问根节点;
step2)先序遍历以儿子为根的子树;
step3)先序遍历以兄弟为根的子树;
download source code:https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/blob/master/chapter4/p68_preorder_common_tree.c
source code at a glance:
#include <stdio.h>#include <malloc.h>#define ElementType char#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str) struct Tree;typedef struct Tree *Tree;Tree createTree();Tree makeEmpty(Tree t);Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree t);// we adopt child-sibling notationstruct Tree{ElementType value;Tree firstChild;Tree nextSibling;};// create a tree with root nodeTree createTree(){Tree t;t = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree)); if(!t) { Error("out of space, from func createTree"); return NULL; } t->firstChild = NULL;t->nextSibling = NULL;t->value = '/';return t;}// make the tree empty Tree makeEmpty(Tree t){if(t){makeEmpty(t->firstChild);makeEmpty(t->nextSibling);free(t);}return NULL;}//Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree parent){Tree child;Tree newSibling;if(!parent){Error("for parent tree node is empty , you cannot insert one into the parent node, from func insert"); return NULL;}newSibling = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));if(!newSibling) { Error("out of space, from func insert"); return NULL; }newSibling->value = e;newSibling->nextSibling = NULL;newSibling->firstChild = NULL;// building the node with value e overchild = parent->firstChild;if(!child) {parent->firstChild = newSibling;return parent;}while(child->nextSibling)child = child->nextSibling; // find the last child of parent nodechild->nextSibling = newSibling;return parent;}// find the tree root node with value equaling to eTree find(ElementType e, Tree root){Tree temp;if(root == NULL)return NULL;if(root->value == e)return root;temp = find(e, root->firstChild);if(temp) return temp;elsereturn find(e, root->nextSibling);}// analog print directories and files name in the tree, which involves preorder traversal.void printPreorder(int depth, Tree root){int i;if(root) {for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)printf(" ");printf("%c\n", root->value);printPreorder(depth + 1, root->firstChild);printPreorder(depth, root->nextSibling);} }int main(){Tree tree;tree = createTree();printf("\n test for insert 'A' 'B' into the parent '/' and 'C' 'D' into the parent 'A' \n");insert('A', tree);insert('B', find('/', tree));insert('C', find('A', tree));insert('D', find('A', tree));printPreorder(1, tree);printf("\n test for insert 'E' 'F' into the parent '/' \n");insert('E', find('/', tree));insert('F', find('/', tree));printPreorder(1, tree);printf("\n test for insert 'G' 'H' into the parent 'E' and 'I' into the parent 'H' and even 'J' 'K' into the parent 'I' \n");insert('G', find('E', tree));insert('H', find('E', tree));insert('I', find('H', tree));insert('J', find('I', tree));insert('K', find('I', tree));printPreorder(1, tree);return 0;}打印结果如下:

2.2)后序遍历步骤:(不同于二叉树的后序)
step1)后序遍历以儿子为根的子树;
step2)访问根节点;
step3)后序遍历以兄弟为根的子树;
download source code:https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/blob/master/chapter4/p69_postorder_commone_tree.c
source code at a glance:
#include <stdio.h>#include <malloc.h>#define ElementType char#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str) struct Tree;typedef struct Tree *Tree;Tree createTree();Tree makeEmpty(Tree t);Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree t);// we adopt child-sibling notationstruct Tree{ElementType value;Tree firstChild;Tree nextSibling;};// create a tree with root nodeTree createTree(){Tree t;t = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree)); if(!t) { Error("out of space, from func createTree"); return NULL; } t->firstChild = NULL;t->nextSibling = NULL;t->value = '/';return t;}// make the tree empty Tree makeEmpty(Tree t){if(t){makeEmpty(t->firstChild);makeEmpty(t->nextSibling);free(t);}return NULL;}//Tree insert(ElementType e, Tree parent){Tree child;Tree newSibling;if(!parent){Error("for parent tree node is empty , you cannot insert one into the parent node, from func insert"); return NULL;}newSibling = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct Tree));if(!newSibling) { Error("out of space, from func insert"); return NULL; }newSibling->value = e;newSibling->nextSibling = NULL;newSibling->firstChild = NULL;// building the node with value e overchild = parent->firstChild;if(!child) {parent->firstChild = newSibling;return parent;}while(child->nextSibling)child = child->nextSibling; // find the last child of parent nodechild->nextSibling = newSibling;return parent;}// find the tree root node with value equaling to eTree find(ElementType e, Tree root){Tree temp;if(root == NULL)return NULL;if(root->value == e)return root;temp = find(e, root->firstChild);if(temp) return temp;elsereturn find(e, root->nextSibling);}// analog print directories and files name in the tree, which involves postorder traversal. void printPostorder(int depth, Tree root){int i;if(root) {printPostorder(depth + 1, root->firstChild);for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)printf(" ");printf("%c\n", root->value);printPostorder(depth, root->nextSibling);} }int main(){Tree tree;tree = createTree();printf("\n ====== test for postordering the common tree presented by child_sibling structure ====== \n");printf("\n test for insert 'A' 'B' into the parent '/' and 'C' 'D' into the parent 'A' \n");insert('A', tree);insert('B', find('/', tree));insert('C', find('A', tree));insert('D', find('A', tree));printPostorder(1, tree);printf("\n test for insert 'E' 'F' into the parent '/' \n");insert('E', find('/', tree));insert('F', find('/', tree));printPostorder(1, tree);printf("\n test for insert 'G' 'H' into the parent 'E' and 'I' into the parent 'H' and even 'J' 'K' into the parent 'I' \n");insert('G', find('E', tree));insert('H', find('E', tree));insert('I', find('H', tree));insert('J', find('I', tree));insert('K', find('I', tree));printPostorder(1, tree);return 0;} 打印结果如下:

0 0
- 利用树的先序和后序遍历打印os中的目录树
- 二叉树中的先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历关系
- 【数据结构_树_Tree_0983】利用二叉树中序和后序遍历确定二叉树的先序遍历
- 利用先序遍历创建二叉树的后序遍历序列(0979)
- 二叉树树的先序遍历,中序遍历和后序遍历
- 根据中序遍历和后序遍历求二叉树的先序遍历
- 利用先序和中序非递归恢复二叉树,并后序遍历输出
- 利用栈实现的二叉树的先、中、后序遍历
- 二叉树 的先序 中序、后序遍历、层次遍历以及树状打印等操作
- 利用二叉树中序及先序遍历确定该二叉树的后序序列(0984)
- 给出二叉树的先序和中序遍历,递归求解后序遍历
- 二叉树的先序、中序、后序递归遍历和非递归遍历
- 只给出先序遍历和后序遍历不能唯一确定二叉树的例子
- 树--递归实现先、中、后遍历,层序遍历和树的深度
- 由树的先序和中序遍历生成树的层序遍历后序遍历
- 已知一棵二叉树的中序遍历和后序遍历,求二叉树的先序遍历
- 已知一棵二叉树的中序遍历和后序遍历,求二叉树的先序遍历
- 给定二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历,输出它的后序遍历序列
- 小爬虫,线程,进程?
- 离线博客试用
- session request application page 之间的区别
- 5-11 分段计算居民水费
- lintcode-合并k个排序链表-104
- 利用树的先序和后序遍历打印os中的目录树
- win7 64位安卓开发环境的配置
- vim常用参数讲解
- Android功能之第三方AndroidResideMenu侧滑菜单
- 杭电acm--1076
- tomcat安装与集成
- MySQL学习笔记12:数据类型
- [POJ 1050] To the Max DP+最大子矩阵和
- UVA 题目1099 - Sharing Chocolate(状态压缩DP+记忆化搜索)


