多路平衡树—BTree(B树)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝层级和排名关系 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/07 18:43
B树属于多叉树,也称多路平衡树。有些地方也将B树称为'B-树',这里‘-’不表示减号。
■B树的主要性质:
(1)根节点至少有两个孩子。
(2)每个非根节点为[[M/2], M]个孩子,这里[M/2]表示向上取整。
(3)每个非根节点都有[[M/2], M-1]个关键字,并且以升序排列。
(4)K[i]和k[i+1]之间的孩子节点的值介于k[i]与k[i+1]之间。(5)所有叶子节点都在同一层。
■下面是一个简单的3阶B树:
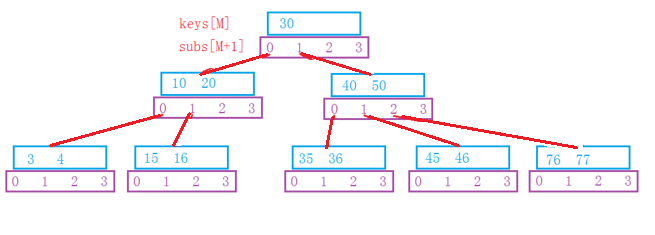
如果想给B树中,插入一个关键字,并且关键字的数目超过,且就需要对树进行调整。那就需要寻找关键字的中位数,那怎样快速的寻找关键字呢?
▲思路一:
将所有的关键字进行排序,然后将中位数寻找出来。
▲思路二:
利用快速排序的思想,选一个key值,如果左边个数等于右边个数,则中位数找到,如果没有,就在个数多的一边找出中间位置的关键字作为key值,直到key的左 = 右,则找到关键字,这样的效率更高。
■下面是插入关键字示例:
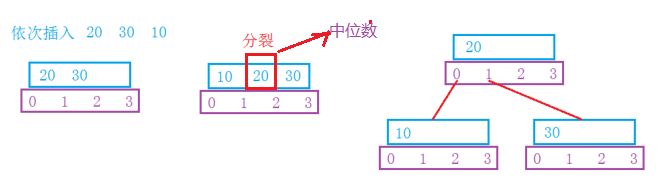
■下面是具体的实现代码:
#pragma once//实现B树(实际就是多叉树)/*性质:(1)根节点至少要2个节点 (2)每个非根节点为[(M/2), M]个孩子 (3)满足左孩子值小于根节点,右孩子值大于根节点 (4)并且每个非根节点有[(M/2)-1, M-1]个关键字,并且以升序排列 (5)key[i]和key[i+1]之间的孩子节点值介于key[i]和key[i+1]之间 (6)所有节点都在同一层*///实现k形式的结构//如果要实现K,V结构,就需要创建一个结构体,包括K,Vtemplate <class K, int M = 3> //实现M为缺省的,值最好取计数,能够更加方便的求取中位数struct BTreeNode{ K _keys[M]; //关键字的至多个数,多预留一个位置是可以更加方便的求取中位数 BTreeNode<K, M>* _subs[M + 1]; //孩子节点的最大数目 BTreeNode<K, M>* _parent; //指向父亲节点 size_t _size; //数组中存在的有效关键字的个数 BTreeNode() //构造B树节点 :_parent(NULL) , _size(0) { for (int i = 0; i <= M; ++i) { _subs[i] = NULL; } }};template <class K, class V> //需要返回两个参数,使用结构体struct Pair{ K _first; V _second; Pair(const K& key = K(), const V& value = V()) //缺省参数,会调用默认构造函数 :_first(key) , _second(value) { }};template <class K, int M = 3>class BTree{ typedef BTreeNode<K, M> Node;public: BTree() //无参构造 :_root(NULL) {} Pair<Node*, int> Find(const K& key) //查找 { Node* parent = NULL; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { int index = 0; while (index < cur->_size) //在一个节点中找相同的关键字 { if (key == cur->_keys[index]) { return Pair<Node*, int>(cur, index); } else if (key < cur->_keys[index]) { break; } else { index++; } } parent = cur; cur = cur->_subs[index]; } return Pair<Node*, int>(parent, -1); } bool Insert(const K& key) //插入节点 { //没有节点 if (_root == NULL) { _root = new Node; _root->_keys[0] = key; _root->_size++; return true; } //判断返回值 Pair<Node*, int> cur = Find(key); if (cur._second != -1) { return false; } //在节点cur中插入key和sub Node* str = cur._first; K InsertKey = key; Node* sub = NULL; while (1) { _InsertKey(str, InsertKey, sub); if (str->_size < M) //插入后,节点中的数据个数没有超过规定的 { return true; } //插入数据后,节点的数据个数大于规定的数据个数,需要将节点进行分裂 int mid = (str->_size - 1) / 2; int index = 0; Node* tmp = new Node; //先拷贝key for (int i = mid + 1; i < str->_size; i++) { tmp->_keys[index++] = str->_keys[i]; tmp->_size++; } //后拷贝sub for (int i = mid + 1; i < str->_size; i++) { tmp->_subs[index + 1] = str->_subs[i]; if (str->_subs[i]) { str->_subs[i]->_parent = tmp; } } str->_size = (str->_size - 1) / 2; //更改str的大小 if (str->_parent == NULL) { _root = new Node; _root->_keys[0] = tmp->_keys[mid]; _root->_subs[0] = str; _root->_subs[1] = tmp; _root->_size = 1; str->_parent = _root; tmp->_parent = _root; } else { InsertKey = str->_keys[mid]; sub = tmp; str = str->_parent; } } return true; } void _InsertKey(Node* cur, const K& key, Node* sub) //插入key值 { int index = cur->_size - 1; while (index >= 0 && cur->_keys[index] > key) //将后面的数据向后移一位 { cur->_keys[index + 1] = cur->_keys[index]; cur->_subs[index + 2] = cur->_subs[index + 1]; --index; } cur->_keys[index + 1] = key; //插入数据及其子节点 cur->_subs[index + 2] = sub; if (sub) sub->_parent = cur; cur->_size++; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); } void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) { return; } for (int i = 0; i < root->_size; i++) { cout << root->_keys[i] << " "; _InOrder(root->_subs[i]); } } protected: Node* _root;};void Test(){ int a[] = { 53, 75, 139, 49, 145, 36, 101 }; BTree<int, 1023> t; for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i) { t.Insert(a[i]); } t.InOrder();}本文出自 “无心的执着” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://10740590.blog.51cto.com/10730590/1827991
1 0
- 多路平衡树—BTree(B树)
- 平衡搜索树-BTree
- BTree(多路搜索树)
- B树 平衡多路查找树
- B树(平衡多路查找树)
- M路平衡B树
- B树(平衡多路查找树)B-tree树
- BTree树
- 【BTree、B-树】B树的C++实现
- B平衡树
- 动态查找---->B树(broad-tree 平衡多路查找树)
- 【Bzoj3196】2B平衡树
- btree-C二叉树
- 数据结构中的树(红黑树,平衡二叉树,B树,B+树,B*树)
- 二叉排序树、平衡二叉排序树、B-树、B+树、B*树
- 二叉排序树(B树)和平衡树(AVL树)
- 适用于外查找的平衡树——B树
- 数据结构(9)平衡查找树之B树
- 几种进程调度算法总结
- 数据结构--‘搜索二叉树’
- 复习php知识点十
- 平衡搜索树—AVLTree
- 二叉搜索树—RBTree(红黑树)
- 多路平衡树—BTree(B树)
- 图—并查集(解决朋友圈问题)
- 论‘进程’相关操作
- 再谈‘进程’
- ‘信号’基本概念总结
- 进程间通信—‘匿名管道’
- 系统调度—‘线程’
- JAVA 方法重载和构造函数重载---转载自阿朱
- ‘生产者-消费者’模型与‘读-写者’模型


