wifidog 源码初分析(1)
来源:互联网 发布:hdfs如何查看数据字段 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/01 10:00
wifidog 的核心还是依赖于 iptables 防火墙过滤规则来实现的,所以建议对 iptables 有了了解后再去阅读 wifidog 的源码。
在路由器上启动 wifidog 之后,wifidog 在启动时会初始化一堆的防火墙规则,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- /** Initialize the firewall rules
- */
- int iptables_fw_init(void)
- {
- … …
- /*
- *
- * Everything in the NAT table
- *
- */
- /* Create new chains */
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_OUTGOING);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_ROUTER);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_GLOBAL);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_AUTHSERVERS);
- /* Assign links and rules to these new chains */
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A PREROUTING -i %s -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_OUTGOING, config->gw_interface);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_OUTGOING " -d %s -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_ROUTER, config->gw_address);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_ROUTER " -j ACCEPT");
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_OUTGOING " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -m mark --mark 0x%u -j ACCEPT", FW_MARK_KNOWN);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -m mark --mark 0x%u -j ACCEPT", FW_MARK_PROBATION);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_AUTHSERVERS);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_GLOBAL);
- // 将 80 端口的访问重定向(REDIRECT)到 (本路由)网关web服务器的监听端口
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN " -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports %d", gw_port);
- /*
- *
- * Everything in the FILTER table
- *
- */
- /* Create new chains */
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_AUTHSERVERS);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_LOCKED);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_GLOBAL);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_VALIDATE);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_KNOWN);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -N " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN);
- /* Assign links and rules to these new chains */
- /* Insert at the beginning */
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -I FORWARD -i %s -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET, config->gw_interface);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -m state --state INVALID -j DROP");
- /* TCPMSS rule for PPPoE */
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -o %s -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -j TCPMSS --clamp-mss-to-pmtu", ext_interface);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_AUTHSERVERS);
- iptables_fw_set_authservers();
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -m mark --mark 0x%u -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_LOCKED, FW_MARK_LOCKED);
- iptables_load_ruleset("filter", "locked-users", TABLE_WIFIDOG_LOCKED);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_GLOBAL);
- iptables_load_ruleset("filter", "global", TABLE_WIFIDOG_GLOBAL);
- iptables_load_ruleset("nat", "global", TABLE_WIFIDOG_GLOBAL);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -m mark --mark 0x%u -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_VALIDATE, FW_MARK_PROBATION);
- iptables_load_ruleset("filter", "validating-users", TABLE_WIFIDOG_VALIDATE);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -m mark --mark 0x%u -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_KNOWN, FW_MARK_KNOWN);
- iptables_load_ruleset("filter", "known-users", TABLE_WIFIDOG_KNOWN);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_WIFI_TO_INTERNET " -j " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN);
- iptables_load_ruleset("filter", "unknown-users", TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN);
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN " -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable");
- UNLOCK_CONFIG();
- return 1;
- }
在该 防火墙规则的初始化过程中,会首先清除掉已有的防火墙规则,重新创建新的过滤链,另外,除了通过iptables_do_command("-t nat -A "TABLE_WIFIDOG_UNKNOWN " -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports %d",gw_port); 这个命令将 接入设备的 80 端口(HTTP)的访问重定向至网关自身的 HTTP 的端口之外,还通过iptables_fw_set_authservers(); 函数设置了 鉴权服务器(auth-server) 的防火墙规则:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- void iptables_fw_set_authservers(void)
- {
- const s_config *config;
- t_auth_serv *auth_server;
- config = config_get_config();
- for (auth_server = config->auth_servers; auth_server != NULL; auth_server = auth_server->next) {
- if (auth_server->last_ip && strcmp(auth_server->last_ip, "0.0.0.0") != 0) {
- iptables_do_command("-t filter -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_AUTHSERVERS " -d %s -j ACCEPT", auth_server->last_ip);
- iptables_do_command("-t nat -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_AUTHSERVERS " -d %s -j ACCEPT", auth_server->last_ip);
- }
- }
- }
首先从上面的代码可以看出 wifidog 支持多个 鉴权服务器,并且针对每一个鉴权服务器 设置了如下两条规则:
1)在filter表中追加一条[任何访问鉴权服务器都被接受]的WiFiDog_$ID$_AuthServers过滤链:
iptables -t filter -A WiFiDog_$ID$_AuthServers -d auth-server地址 -j ACCEPT
2)在nat表中追加一条[任何访问鉴权服务器都被接受]的WiFiDog_$ID$_AuthServers过滤链:
iptables -t nat -A WiFiDog_$ID$_AuthServers -d auth-server地址 -j ACCEPT
这样确保可以访问鉴权服务器,而不是拒绝所有的出口访问。
wifidog 源码初分析(2)
上一篇分析了接入设备的首次浏览器访问请求如何通过 防火墙过滤规则 重定向到 wifidog 的 HTTP 服务中,本篇主要分析了 wifidog 在接收到 接入设备的 HTTP 访问请求后,如何将此 HTTP 请求重定向到 认证服务器(auth-server) 上。
通过上面的防火墙规则,会将通过上面的防火墙规则,会将HTTP请求的外部IP地址和端口通过NAT方式重定向至本地wifidog内嵌HTTP服务器的地址和端口上,并由内嵌HTTP服务器进行服务,而内嵌HTTP服务器的路径和回调处理如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- if ((webserver = httpdCreate(config->gw_address, config->gw_port)) == NULL) {
- debug(LOG_ERR, "Could not create web server: %s", strerror(errno));
- exit(1);
- }
- debug(LOG_DEBUG, "Assigning callbacks to web server");
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/", "wifidog", 0, NULL, http_callback_wifidog);
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "", 0, NULL, http_callback_wifidog);
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "about", 0, NULL, http_callback_about);
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "status", 0, NULL, http_callback_status);
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "auth", 0, NULL, http_callback_auth);
- httpdAddC404Content(webserver, http_callback_404);
客户端首次访问时回调客户端首次访问时回调http_callback_404函数,在该函数中根据获取的客户端信息来配置重定向的URL fragment,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- void
- http_callback_404(httpd *webserver, request *r)
- {
- char tmp_url[MAX_BUF],
- *url,
- *mac;
- s_config *config = config_get_config();
- t_auth_serv *auth_server = get_auth_server();
- memset(tmp_url, 0, sizeof(tmp_url));
- /*
- * XXX Note the code below assumes that the client's request is a plain
- * http request to a standard port. At any rate, this handler is called only
- * if the internet/auth server is down so it's not a huge loss, but still.
- */ /* 用户需要访问的URL */
- snprintf(tmp_url, (sizeof(tmp_url) - 1), "http://%s%s%s%s",
- r->request.host,
- r->request.path,
- r->request.query[0] ? "?" : "",
- r->request.query);
- url = httpdUrlEncode(tmp_url);
- if (!is_online()) {
- /* 路由器都接入不到 internet */
- char * buf;
- send_http_page(r, "Uh oh! Internet access unavailable!", buf);
- free(buf);
- }
- else if (!is_auth_online()) {
- /* auth server 挂起 */
- char * buf;
- send_http_page(r, "Uh oh! Login screen unavailable!", buf);
- free(buf);
- }
- else {
- /* 配置重定向到 auth server 的 url 参数 */
- char *urlFragment;
- if (!(mac = arp_get(r->clientAddr))) {
- /* We could not get their MAC address */
- debug(LOG_INFO, "Failed to retrieve MAC address for ip %s, so not putting in the login request", r->clientAddr);
- safe_asprintf(&urlFragment, "%sgw_address=%s&gw_port=%d&gw_id=%s&url=%s",
- auth_server->authserv_login_script_path_fragment,
- config->gw_address,
- config->gw_port,
- config->gw_id,
- url);
- } else {
- debug(LOG_INFO, "Got client MAC address for ip %s: %s", r->clientAddr, mac);
- safe_asprintf(&urlFragment, "%sgw_address=%s&gw_port=%d&gw_id=%s&mac=%s&url=%s",
- auth_server->authserv_login_script_path_fragment,
- config->gw_address,
- config->gw_port,
- config->gw_id,
- mac,
- url);
- }
- /* 调用该函数将用户请求重定向到 auth server 的登录页面 */
- http_send_redirect_to_auth(r, urlFragment, "Redirect to login page");
- free(urlFragment);
- }
- free(url);
- }
上面代码基本不用解释,具体重定向至auth server的消息在下面的 http_send_redirect_to_auth 函数中实现:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- void http_send_redirect_to_auth(request *r, char *urlFragment, char *text)
- {
- char *protocol = NULL;
- int port = 80;
- t_auth_serv *auth_server = get_auth_server();
- if (auth_server->authserv_use_ssl) {
- protocol = "https";
- port = auth_server->authserv_ssl_port;
- } else {
- protocol = "http";
- port = auth_server->authserv_http_port;
- }
- char *url = NULL;
- safe_asprintf(&url, "%s://%s:%d%s%s",
- protocol,
- auth_server->authserv_hostname,
- port,
- auth_server->authserv_path,
- urlFragment
- );
- http_send_redirect(r, url, text);
- free(url);
- }
具体的重定向URL给个实例:
POST /login/?gw_address=192.168.1.1&gw_port=2060&gw_id=default&mac=44:94:fc:ef:28:40&url=http%3A//www.baidu.com/ HTTP/1.1
可以看到这里有这几个参数信息:
2gw_address,路由器的LAN地址
2gw_port:为wifidog的监听端口
2gw_id:路由器的标识名
2mac:客户端设备的MAC地址
2url:为客户端访问的原URL(以便于重定向)
wifidog 源码初分析(3)
上一篇分析了 接入设备 在接入路由器,并发起首次 HTTP/80 请求到路由器上时,wifidog 是如何将此 HTTP 请求重定向至 auth-server 的流程。
之后 接入设备 的浏览器接收到 wifidog 返回的 302 重定向请求后,会将页面重定向至 auth-server 的 /login 页面,并且在此 URL 中会携带一些 路由器/网关 参数,以及 接入设备的 MAC 地址 和 客户端访问的源URL(如示例中的 baidu.com)。
下面几个步骤就是 接入设备 到 auth-server 上的认证过程,因本系列主要分析 wifidog 源码,这里只截取了 接入设备 与 auth-server 之间的通信报文:
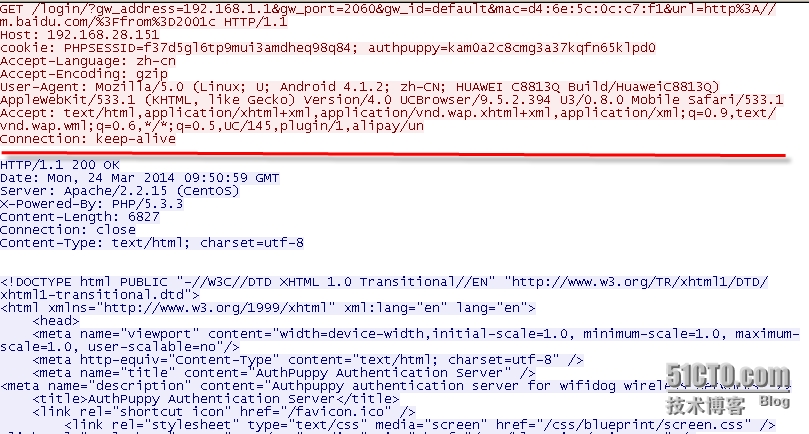
本示例对应的 auth-server 是使用 authpuppy 搭建的认证服务器,且使用了 localUser 插件,该插件是需要用户输入用户名/密码的方式来认证的,下图即为输入正确的用户名/密码后,auth-server 返回重定向到 wifidog 的响应(注:同时携带了为此接入设备的用户分配了 token):
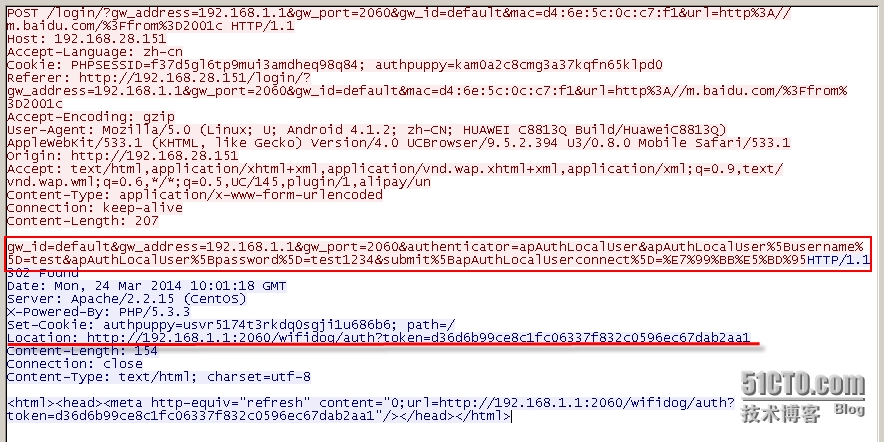
同样的,接入设备的浏览器会继续重定向到 路由器的 wifidog 的 /wifidog/auth 服务上。
+
下一篇会继续分析 wifidog 如何进一步对 客户端 进行鉴权,并为此接入设备开启防火墙。
wifidog 源码初分析(4)
在上一篇《wifidog 源码处分析(3)》的流程结束后,接入设备的浏览器重定向至 路由器 上 wifidog 的 http 服务(端口 2060) /wifidog/auth 上(且携带了 认证服务器 为此接入设备分配的 token),本篇就是从 wifidog 接收到 /wifidog/auth 的访问后的 校验流程。
-
根据《wifidog 源码初分析(2)》中描述的,在 wifidog 启动 http 服务前,注册了一个针对访问路径 /wifidog/auth 的回调,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "about", 0, NULL, http_callback_about);
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "status", 0, NULL, http_callback_status);
- // 注册了针对 /wifidog/auth 的访问回调 http_callback_auth
- httpdAddCContent(webserver, "/wifidog", "auth", 0, NULL, http_callback_auth);
这样对于 接入设备(or 客户端) 重定向过来的 /wifidog/auth 就进入了 http_callback_auth 函数中,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- http_callback_auth(httpd *webserver, request *r)
- {
- t_client *client;
- httpVar * token;
- char *mac;
- // 1, 获取条件参数中的 logout 值
- httpVar *logout = httpdGetVariableByName(r, "logout");
- // 2, 获取条件参数中的 token 值
- if ((token = httpdGetVariableByName(r, "token"))) {
- /* They supplied variable "token" */
- // 3, 可以看到, 这里要求必须能够通过 ARP 协议获取到 接入设备 的 MAC 地址
- if (!(mac = arp_get(r->clientAddr))) {
- /* We could not get their MAC address */
- debug(LOG_ERR, "Failed to retrieve MAC address for ip %s", r->clientAddr);
- send_http_page(r, "WiFiDog Error", "Failed to retrieve your MAC address");
- } else {
- /* We have their MAC address */
- LOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- // 4, 检查该客户端(接入设备)是否已经在 wifidog 维护的接入客户端列表中
- if ((client = client_list_find(r->clientAddr, mac)) == NULL) {
- debug(LOG_DEBUG, "New client for %s", r->clientAddr);
- client_list_append(r->clientAddr, mac, token->value);
- } else if (logout) {
- // 5, 退出处理
- t_authresponse authresponse;
- s_config *config = config_get_config();
- unsigned long long incoming = client->counters.incoming;
- unsigned long long outgoing = client->counters.outgoing;
- char *ip = safe_strdup(client->ip);
- char *urlFragment = NULL;
- t_auth_serv *auth_server = get_auth_server();
- fw_deny(client->ip, client->mac, client->fw_connection_state);
- client_list_delete(client);
- debug(LOG_DEBUG, "Got logout from %s", client->ip);
- /* Advertise the logout if we have an auth server */
- if (config->auth_servers != NULL) {
- UNLOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- auth_server_request(&authresponse, REQUEST_TYPE_LOGOUT, ip, mac, token->value,
- incoming, outgoing);
- LOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- /* Re-direct them to auth server */
- debug(LOG_INFO, "Got manual logout from client ip %s, mac %s, token %s"
- "- redirecting them to logout message", client->ip, client->mac, client->token);
- safe_asprintf(&urlFragment, "%smessage=%s",
- auth_server->authserv_msg_script_path_fragment,
- GATEWAY_MESSAGE_ACCOUNT_LOGGED_OUT
- );
- http_send_redirect_to_auth(r, urlFragment, "Redirect to logout message");
- free(urlFragment);
- }
- free(ip);
- }
- else {
- // 6, 已经登录校验通过
- debug(LOG_DEBUG, "Client for %s is already in the client list", client->ip);
- }
- UNLOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- if (!logout) {
- // 7, 到 auth server 上进一步校验 token
- authenticate_client(r);
- }
- free(mac);
- }
- } else {
- /* They did not supply variable "token" */
- // 8, 未携带 token, 直接拒绝
- send_http_page(r, "WiFiDog error", "Invalid token");
- }
- }
在该函数中主要处理了 客户端退出,非法校验,以及 客户端校验等流程,下面分别描述注释中的各个步骤:
-
1,对于客户端退出,则会携带 logout 参数信息,并走到第 5 步(当然,如果连 token 参数都没有的话,会直接走到第 8 步,也就是拒绝);
2,按照正常的认证流程,会携带由认证服务器分配的 token 参数;
3,正如注释说明的,这里要求必须能够通过 ARP 协议获取到 接入设备 的 MAC 地址;(其实通过查看 arg_get 的实现,可以看到是直接解析 /proc/net/arp 文件 -- ARP cache -- 来获取对应客户端 IP 地址的 MAC 信息的),类似如下:
[steven@sasd ~]$ more /proc/net/arp
IP address HW type Flags HW address Mask Device
192.168.1.203 0x1 0x2 18:03:73:d5:1b:a2 * eth0
192.168.1.1 0x1 0x2 00:21:27:63:c0:ce * eth0
[steven@sasd ~]$
4,在能够获取到该客户端的 MAC 地址后,根据客户端的 IP 和 MAC 地址检查该客户端是否已经在 wifidog 维护的接入设备(or客户端)列表中,如果不在,则追加到此列表中(关于此列表的数据结构在后面再详细描述);
5,如果该客户端已经存在,且本次访问是要求 logout 退出的,则进入此退出处理的流程,该流程主要包括几个步骤:关闭该客户端 ip/mac 的出口(outgoing)规则 --> 从客户端列表中删除该客户端记录 --> 通知 认证服务器 该客户端退出(且携带该客户端的token, 上下行流量等信息) --> 返回重定向至 认证服务器 的 #define DEFAULT_AUTHSERVMSGPATHFRAGMENT "gw_message.php?" 访问路径(携带一个已退出的 message);
6,如果该客户端已经登录校验过,且本次访问非 logout 退出,则直接跳转到第 7 步;
7,这一步就是 token 校验的过程,具体实现在 authenticate_client 函数中:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- authenticate_client(request *r)
- {
- t_client *client;
- t_authresponse auth_response;
- char *mac,
- *token;
- char *urlFragment = NULL;
- s_config *config = NULL;
- t_auth_serv *auth_server = NULL;
- LOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- // 根据 IP 地址获取 客户端的 MAC 地址以及本次会话分配的 token
- // 主要用于 token 校验过程
- client = client_list_find_by_ip(r->clientAddr);
- if (client == NULL) {
- debug(LOG_ERR, "authenticate_client(): Could not find client for %s", r->clientAddr);
- UNLOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- return;
- }
- mac = safe_strdup(client->mac);
- token = safe_strdup(client->token);
- UNLOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- /*
- * At this point we've released the lock while we do an HTTP request since it could
- * take multiple seconds to do and the gateway would effectively be frozen if we
- * kept the lock.
- */
- // 通过 "login" 到 认证服务器 上进行客户端的 token 校验
- auth_server_request(&auth_response, REQUEST_TYPE_LOGIN, r->clientAddr, mac, token, 0, 0);
- LOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- /* can't trust the client to still exist after n seconds have passed */
- // 这里主要防止在到 认证服务器 上进行 token 校验的过程中
- // 该客户端已经退出的情形, 此时就不需要再进行处理
- client = client_list_find(r->clientAddr, mac);
- if (client == NULL) {
- debug(LOG_ERR, "authenticate_client(): Could not find client node for %s (%s)", r->clientAddr, mac);
- UNLOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- free(token);
- free(mac);
- return;
- }
- free(token);
- free(mac);
- /* Prepare some variables we'll need below */
- config = config_get_config();
- auth_server = get_auth_server();
- // 根据返回的校验结果做不同的处理
- switch(auth_response.authcode) {
- case AUTH_ERROR:
- case AUTH_DENIED:
- case AUTH_VALIDATION:
- case AUTH_VALIDATION_FAILED:
- ... ...
- break;
- case AUTH_ALLOWED:
- /* Logged in successfully as a regular account */
- debug(LOG_INFO, "Got ALLOWED from central server authenticating token %s from %s at %s - "
- "adding to firewall and redirecting them to portal", client->token, client->ip, client->mac);
- client->fw_connection_state = FW_MARK_KNOWN;
- fw_allow(client->ip, client->mac, FW_MARK_KNOWN);
- served_this_session++;
- safe_asprintf(&urlFragment, "%sgw_id=%s",
- auth_server->authserv_portal_script_path_fragment,
- config->gw_id
- );
- http_send_redirect_to_auth(r, urlFragment, "Redirect to portal");
- free(urlFragment);
- break;
- }
- UNLOCK_CLIENT_LIST();
- return;
- }
这里主要是两大步骤:
-
1,通过调用 auth_server_request(&auth_response, REQUEST_TYPE_LOGIN, r->clientAddr, mac, token, 0, 0); 让 认证服务器 对该客户端的 token 进行校验;
2,根据 认证服务器 返回的 token 校验结果进行不同的处理(主要是对该客户端的防火墙过滤规则进行不同的设置),这里主要以 AUTH_ALLOWED 校验结果进行分析,这里主要是两个动作:
2.1,通过 fw_allow 函数调用对此客户端"放行";
2.2,返回重定向至 认证服务器的 portal 路径访问的响应;
-
这里就简要分析一下 fw_allow 函数的实现,查看fw_allow的实现可以看到真正设置allow客户端通过防火墙的动作是在iptables_fw_access中实现的,如下:
[cpp] view plaincopy![]()
- /** Set if a specific client has access through the firewall */
- // 针对上面的流程,这里的输入参数
- // type 为 FW_ACCESS_ALLOW,tag 为 FW_MARK_KNOWN
- int iptables_fw_access(fw_access_t type, const char *ip, const char *mac, int tag)
- {
- int rc;
- fw_quiet = 0;
- switch(type) {
- case FW_ACCESS_ALLOW:
- iptables_do_command("-t mangle -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_OUTGOING " -s %s -m mac --mac-source %s -j MARK --set-mark %d", ip, mac, tag);
- rc = iptables_do_command("-t mangle -A " TABLE_WIFIDOG_INCOMING " -d %s -j ACCEPT", ip);
- break;
- case FW_ACCESS_DENY:
- iptables_do_command("-t mangle -D " TABLE_WIFIDOG_OUTGOING " -s %s -m mac --mac-source %s -j MARK --set-mark %d", ip, mac, tag);
- rc = iptables_do_command("-t mangle -D " TABLE_WIFIDOG_INCOMING " -d %s -j ACCEPT", ip);
- break;
- default:
- rc = -1;
- break;
- }
- return rc;
- }
同样的,我们这里主要分析一下ALLOW时的iptables的防火墙设置规则,对执行的两个iptables命令展开来就是下面两个步骤:
-
1) 在mangle表中追加WiFiDog_$ID$_Outgoing外出过滤链,该链的规则如下几条:
a) IP 地址为该客户端的IP地址;
b) MAC地址为该客户端的MAC地址;
c) 设置MARK为FW_MARK_KNOWN;
-
iptables –t mangle –AWiFiDog_$ID$_Outgoing -s 客户端IP地址 -m mac --mac-source 客户端MAC地址 -j MARK --set-markFW_MARK_KNOWN
-
2)在mangle表中追加一条[接受所有目的地址为此客户端IP地址的] WifiDog_$ID$_Incoming输入过滤链;
-
iptables -t mangle -AWiFiDog_$ID$_Incoming -d 客户端IP地址 -j ACCEPT
-
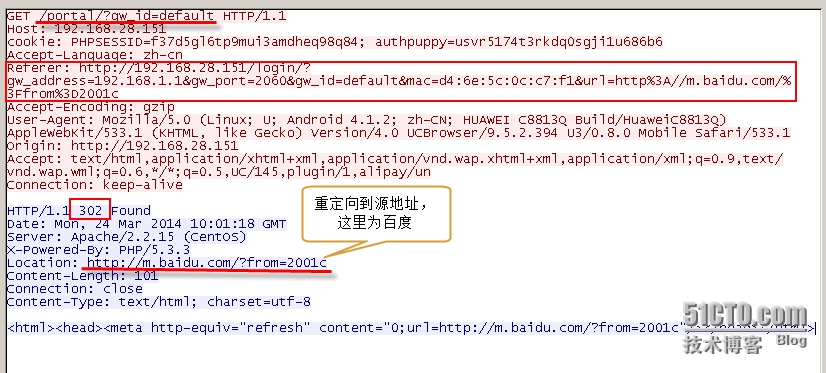
最后,看一下 wifidog 返回的重定向请求到 认证服务器 的请求报文 以及 认证服务器 返回给 客户端的(重定向到原始访问 baidu.com 的)响应报文:
- wifidog 源码初分析(1)
- wifidog 源码初分析(1)
- wifidog 源码初分析(1)
- wifidog 源码初分析(1)
- wifidog 源码初分析
- wifidog 源码初分析-1-转
- wifidog 源码初分析(2)
- wifidog 源码初分析(3)
- wifidog 源码初分析(4)
- wifidog 源码初分析(一)
- wifidog 源码初分析(二)
- wifidog 源码初分析(三)
- wifidog 源码初分析(2)
- wifidog 源码初分析(3)
- wifidog 源码初分析(4)
- wifidog 源码初分析(4)
- wifidog 源码初分析(3)
- wifidog 源码初分析(2)
- config.mk
- JDBC编程要点
- ORA-12560: TNS: 协议适配器错误的解决方法
- Callable与Future的介绍
- Android Gallery用法(自定义边框+底部小圆点)
- wifidog 源码初分析(1)
- iOS运行时(runtime)探究三:消息转发
- java基础学习——final,static,const在使用上有什么区别
- 线段树初识
- LUA中table的排序问题
- java常量池的理解
- OpenGL多线程
- c++派生类的构造函数和析构函数
- c++ string类的内部实现


