HDU5531 Rebuild 【几何+数学】
来源:互联网 发布:手机导航电子狗软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/28 18:31
Rebuild
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2008 Accepted Submission(s): 431
Problem Description
Archaeologists find ruins of Ancient ACM Civilization, and they want to rebuild it.
The ruins form a closed path on an x-y plane, which hasn endpoints. The endpoints locate on (x1,y1) , (x2,y2) , …,(xn,yn) respectively. Endpoint i and endpoint i−1 are adjacent for 1<i≤n , also endpoint 1 and endpoint n are adjacent. Distances between any two adjacent endpoints are positive integers.
To rebuild, they need to build one cylindrical pillar at each endpoint, the radius of the pillar of endpointi is ri . All the pillars perpendicular to the x-y plane, and the corresponding endpoint is on the centerline of it. We call two pillars are adjacent if and only if two corresponding endpoints are adjacent. For any two adjacent pillars, one must be tangent externally to another, otherwise it will violate the aesthetics of Ancient ACM Civilization. If two pillars are not adjacent, then there are no constraints, even if they overlap each other.
Note thatri must not be less than 0 since we cannot build a pillar with negative radius and pillars with zero radius are acceptable since those kind of pillars still exist in their neighbors.
You are given the coordinates ofn endpoints. Your task is to find r1,r2,…,rn which makes sum of base area of all pillars as minimum as possible.
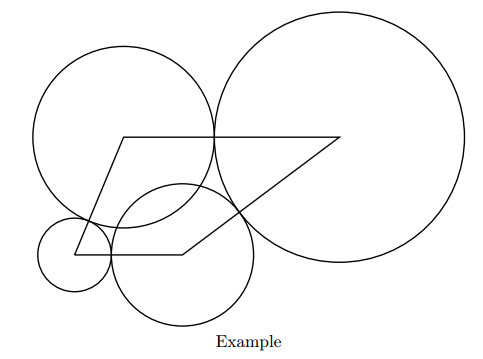
For example, if the endpoints are at(0,0) , (11,0) , (27,12) , (5,12) , we can choose (r1 , r2 , r3 , r4 )= (3.75 , 7.25 , 12.75 , 9.25 ). The sum of base area equals to 3.752π+ 7.252π+12.752π+9.252π=988.816… . Note that we count the area of the overlapping parts multiple times.
If there are several possible to produce the minimum sum of base area, you may output any of them.
The ruins form a closed path on an x-y plane, which has
To rebuild, they need to build one cylindrical pillar at each endpoint, the radius of the pillar of endpoint
Note that
You are given the coordinates of

For example, if the endpoints are at
If there are several possible to produce the minimum sum of base area, you may output any of them.
Input
The first line contains an integer t indicating the total number of test cases. The following lines describe a test case.
The first line of each case contains one positive integern , the size of the closed path. Next n lines, each line consists of two integers (xi,yi) indicate the coordinate of the i -th endpoint.
1≤t≤100
3≤n≤104
|xi|,|yi|≤104
Distances between any two adjacent endpoints are positive integers.
The first line of each case contains one positive integer
Distances between any two adjacent endpoints are positive integers.
Output
If such answer doesn't exist, then print on a single line "IMPOSSIBLE" (without the quotes). Otherwise, in the first line print the minimum sum of base area, and then print n lines, the i -th of them should contain a number ri , rounded to 2 digits after the decimal point.
If there are several possible ways to produce the minimum sum of base area, you may output any of them.
If there are several possible ways to produce the minimum sum of base area, you may output any of them.
Sample Input
340 011 027 125 1250 07 07 33 60 650 01 06 123 160 12
Sample Output
988.823.757.2512.759.25157.086.001.002.003.000.00IMPOSSIBLE
Source
2015ACM/ICPC亚洲区长春站-重现赛(感谢东北师大)
---------------------------------------------------
当n%2==1
假如n=3
r1+r2=L1
r2+r3=L2
r3+r1=L3
L1-L2+L3=2*r1
所以r1有唯一解:r1=(L1-L2+L3)/2.0
r2=L1-r1
r3=L2-r2
.....
依次检查r1到r2是否<0
当n%2==0
假如n=4
r1+r2=L1
r2+r3=L2
r3+r4=L3
r4+r1=L4
L1-L2+L3-L4=0
只有满足L1+L3=L2+L4时才可能有解
不难发现 对任意ri都可以表示为ri=x+k*r1
r1=r1
r2=L1-r1
r3=L2-L1+r1
.....
而总的面积S=PI*(r1^2+r2^2+r3^2+.....)
于是得到一个关于r1的一元二次方程:S=a*r1^2+b*r1+c
当ri=x+r1 --> ri>=0 --> x+r1>=0 --> r1>=-x
当ri=x-r1 --> ri>=0 --> x-r1>=0 --> r1<=x
通过以上约束 , 求得r1的范围[L,R]
然后可以使用三分法求解使得S最小的r1
或者 使用一元二次方程性质 ax^2+bx+c=0时 ,当x=-b/(2a)时,取得最值
再判断每边是否<0即可
#include<iostream>#include<cstdlib>#include<cstdio>#include<string>#include<vector>#include<deque>#include<queue>#include<algorithm>#include<set>#include<map>#include<stack>#include<ctime>#include<string.h>#include<math.h>#include<list>using namespace std;#define ll long long#define pii pair<int,int>const int inf = 1e9 + 7;const double EPS=1e-6;const double PI=4.0*atan(1.0);const int N = 1e4+5;pii p[N];int dis[N];double r[N];int distance(const pii&a,const pii&b){ return sqrt((a.first-b.first)*(a.first-b.first)+(a.second-b.second)*(a.second-b.second));}double getAns(double r0,int n){ r[0]=r0; double ans=r0*r0; for(int i=1;i<n;++i){ r[i]=dis[i-1]-r[i-1]; ans+=r[i]*r[i]; if(r[i]<-EPS){ return -1; } } return ans*PI;}double slove(int n){ p[n]=p[0]; ll sum=0; for(int i=0;i<=n-1;++i){ dis[i]=distance(p[i],p[i+1]); sum+=dis[i]*(i%2==0?1:-1); } double ans=0; if(n&1){ double r0=sum/2.0; if(r0<-EPS){ return -1; } ans=getAns(r0,n); } else{ if(sum!=0){ return -1; } ll a,b,c,t=0,L=0,R=inf; a=b=c=0; int k=1; for(int i=0;i<n;++i){ ++a; b+=2*k*t; c+=t*t; if(k==1){ L=max(L,-t); } else{ R=min(R,t); } k*=-1; t=dis[i]-t; } if(L>R){ return -1; } double mid=-b/(2.0*a); mid=max(mid,(double)L); mid=min((double)R,mid); ans=getAns(mid,n); } if(ans<-EPS){ return -1; } return ans;}int main(){ //freopen("/home/lu/Documents/r.txt","r",stdin); //freopen("/home/lu/Documents/w.txt","w",stdout); int T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=0;i<n;++i){ scanf("%d",&p[i].first); scanf("%d",&p[i].second); } double ans=slove(n); if(ans<-EPS){ puts("IMPOSSIBLE"); } else{ printf("%.2f\n",ans); for(int i=0;i<n;++i){ printf("%.2f\n",r[i]); } } } return 0;} 0 0
- HDU5531 Rebuild 【几何+数学】
- HDU5531-Rebuild(平面几何+数学)
- hdu5531 Rebuild
- hdu5531 Rebuild
- HDU 5531 Rebuild(几何)
- 数学-几何
- EOJ 1161 数学几何
- 数学几何算法
- [索引] 数学 - 几何
- 语言学、符号学、数学、几何
- 数学、半几何
- 【lightoj1043】几何数学
- Regular polygon 数学几何
- HDU 6097 数学几何
- 数学_几何模板
- HDU 5531 (ACM 2015 长春) Rebuild [计算几何]
- HDU 5531(2015长春 icpc E.Rebuild) 计算几何
- HDU5531(三分)
- javascript ---- UI
- Python3 cookiejar模块详解
- hdu 4611Balls Rearrangement
- Spring 缓存
- uva-1395
- HDU5531 Rebuild 【几何+数学】
- 俩孩有感
- 求第n个Fibonaccid的值 并取模
- snmp协议的学习。
- Android : hellocharts-android-master图表框架集成 及 新手花式教学(干货满满)------柱状图
- Drawable之ShapeDrawable
- 制作动态库与静态库的方法
- Mysql order by与limit混用陷阱
- python import上级路径文件


