Codeforces 821D Okabe and City【思维建图+Dij+优先队列优化】好题~好题~
来源:互联网 发布:软件视频会议排名 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/22 13:33
Okabe likes to be able to walk through his city on a path lit by street lamps. That way, he doesn't get beaten up by schoolchildren.
Okabe's city is represented by a 2D grid of cells. Rows are numbered from 1 to n from top to bottom, and columns are numbered1 to m from left to right. Exactlyk cells in the city are lit by a street lamp. It's guaranteed that the top-left cell is lit.
Okabe starts his walk from the top-left cell, and wants to reach the bottom-right cell. Of course, Okabe will only walk on lit cells, and he can only move to adjacent cells in the up, down, left, and right directions. However, Okabe can also temporarily light all the cells in any single row or column at a time if he pays 1 coin, allowing him to walk through some cells not lit initially.
Note that Okabe can only light a single row or column at a time, and has to pay a coin every time he lights a new row or column. To change the row or column that is temporarily lit, he must stand at a cell that is lit initially. Also, once he removes his temporary light from a row or column, all cells in that row/column not initially lit are now not lit.
Help Okabe find the minimum number of coins he needs to pay to complete his walk!
The first line of input contains three space-separated integers n, m, and k (2 ≤ n, m, k ≤ 104).
Each of the next k lines contains two space-separated integersri andci (1 ≤ ri ≤ n,1 ≤ ci ≤ m) — the row and the column of thei-th lit cell.
It is guaranteed that all k lit cells are distinct. It is guaranteed that the top-left cell is lit.
Print the minimum number of coins Okabe needs to pay to complete his walk, or -1 if it's not possible.
4 4 51 12 12 33 34 3
2
5 5 41 12 13 13 2
-1
2 2 41 11 22 12 2
0
5 5 41 12 23 34 4
3
In the first sample test, Okabe can take the path 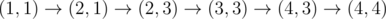 , paying only when moving to (2, 3) and (4, 4).
, paying only when moving to (2, 3) and (4, 4).
In the fourth sample, Okabe can take the path 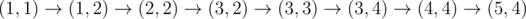
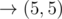 , paying when moving to(1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 4).
, paying when moving to(1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 4).
题目大意:
现在给你N*M的一个矩阵,现在上边一共有K个永恒亮着的点,主人公从左上角出发,走到的点必须有亮光才行。
但是现在不保证有亮光的点能够使得主人公到达右下角,所以他可以花费1单位金币去使得一行或者一列暂时性的亮着,如果他想再次使用魔法,那么之前暂时亮着的部分就必须灭掉了。
问他最少花费多少金币,能够从左上角走到有下角。
如果不能走到,输出-1.
思路:
和前一阵复赛的计蒜之道的那个题和这个题的套路是一毛一样的。
只不过这个题稍微隐秘一点说的没有那么直接。而且稍微相对复杂一些。
1、我们知道,如果暴力建图的方式不难想到:
①O(n*4)先建出权值为0的边。
②O(n^2)建出权值为1的边。但是显然内存不够大。
内存不够大就要优化内存。
我们知道,每一次点亮的要么是一行,要么是一列。
那么我们来讨论两行之间的建边关系:
如果所有点都集中于两行的话,一行5e3个点,那么暴力建图需要5e3*5e3条边,内存是不够用的,那么我们针对于两行进行空间优化:
①我们将一行中的所有点都连入一个替代点out中,权值为0.
②再将一个替代点in连入这一行中的所有点,权值为0.
③那么相关两行之间的建边我们只要将一行的out点连入另一行的in点即可。
④这样我们建边只需要4*5e3.达到了优化空间的目的。
2、那么建好图之后,直接跑Dij即可。注意建边的细节,注意起点终点最终的判定,以及起点和终点是否存在永恒亮光的区别。
注意好细节就没有其他问题了。
另外注意内存开取,我们这样做会多出来2*n+2*m个点,所以我们跑最短路的时候要用优先队列优化一下。
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<map>#include<algorithm>#include<queue>using namespace std;struct node{ int x,y;}a[150000];struct node3{ int d,u; bool operator <(const node3 rhs) const { return d > rhs.d; } node3(int uu,int dd):d(dd),u(uu) {}};struct node2{ int from,to,next,w;}e[15000000];int cont,tmpkk;int head[105000];int dist[105000];int vis[105000];map<int ,int >s[10500];int fx[4]={0,0,1,-1};int fy[4]={1,-1,0,0};int n,m,kk;void add(int from,int to,int w){ e[cont].to=to; e[cont].w=w; e[cont].next=head[from]; head[from]=cont++;}void Dij(){ memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); priority_queue<node3>s; for(int i=1;i<=kk;i++)dist[i]=0x3f3f3f3f; int ss=-1; for(int i=1;i<=kk;i++) { if(a[i].x==1&&a[i].y==1) { ss=i; break; } } if(ss==-1) { for(int i=1;i<=tmpkk;i++) { if(abs(a[i].x-1)<=1||abs(a[i].y-1)<=1) { dist[i]=1; s.push(node3(i,1)); } } } else { dist[ss]=0; vis[ss]=1; s.push(node3(ss,0)); for(int i=head[ss];i!=-1;i=e[i].next) { int v=e[i].to; int w=e[i].w; dist[v]=min(dist[v],w); s.push(node3(v,dist[v])); } } while(!s.empty()) { node3 x = s.top(); s.pop(); int u=x.u; if(vis[u])continue; vis[u] = 1; for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].next) { int v=e[i].to; int w=e[i].w; if(dist[v]>dist[u]+w) { dist[v]=dist[u]+w; s.push(node3(v,dist[v])); } } } int output=0x3f3f3f3f; for(int i=1;i<=tmpkk;i++) { if(a[i].x==n&&a[i].y==m) { output=min(output,dist[i]); } else { if(abs(n-a[i].x)<=1||abs(m-a[i].y)<=1) { output=min(output,dist[i]+1); } } } if(output==0x3f3f3f3f)printf("-1\n"); else printf("%d\n",output);}int main(){ while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&kk)) { memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); cont=0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(int i=1;i<=kk;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); s[a[i].x][a[i].y]=i; } for(int i=1;i<=kk;i++) { for(int j=0;j<4;j++) { int xx=a[i].x+fx[j]; int yy=a[i].y+fy[j]; if(s[xx][yy]>0) { add(i,s[xx][yy],0); add(s[xx][yy],i,0); } } } tmpkk=kk; kk+=2*n; kk+=2*m; for(int i=1;i<=tmpkk;i++) { add(i,tmpkk+a[i].x,0); add(tmpkk+n+a[i].x,i,0); add(i,tmpkk+2*n+a[i].y,0); add(tmpkk+2*n+a[i].y+m,i,0); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int len=-2;len<=2;len++) { int j=i+len; if(j>=1&&j<=n) { add(i+tmpkk,j+n+tmpkk,1); add(j+tmpkk,i+n+tmpkk,1); } } } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { for(int len=-2;len<=2;len++) { int j=i+len; if(j>=1&&j<=m) { add(i+tmpkk+2*n,2*n+j+m+tmpkk,1); add(j+tmpkk+2*n,2*n+i+m+tmpkk,1); } } } Dij(); return 0; }}- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City【思维建图+Dij+优先队列优化】好题~好题~
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City 思维建图+dij
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City (拆点+思维建图+spfa)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City 思维建图+spfa
- Codeforces 821 D. Okabe and City
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City 题解
- codeforces 821d Okabe and City
- Educational Codeforces Round 31-k叉哈夫曼&优先队列&好题-D. Boxes And Balls
- codeforces 754D Fedor and coupons【优先队列+贪心*好题】
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City
- Codeforces 821D Okabe And City 最短路
- D. Okabe and City codeforces 最短路
- Codeforces 586D Phillip and Trains【思维+Bfs】好题~!
- Codeforces821D Okabe and City(思维建图+最短路运用)
- Codeforces 353D Queue【思维】好题~
- Codeforces 669D Little Artem and Dance【思维】好题!好题!
- CF 821D Okabe and City
- Codeforces 557D Vitaly and Cycle【二分图染色+思维】好题~
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) C. Okabe and Boxes
- 高效能人士的七个习惯——习惯二以终为始
- C# SQLite通用读写操作方法
- csrf
- 浅谈mvp架构模式
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City【思维建图+Dij+优先队列优化】好题~好题~
- POJ 1064 Cable master【二分】
- 如何用 Android Studio 导入开源项目以及常见错误的解决办法
- Run-Time Check Failure #3
- 深入浅出看流媒体前世今生,分分钟二逼变牛逼
- Android中退出app的另类姿势
- [HPUOJ] 1152: 棋盘变换 [搜索]
- AndroidStudio 2.2.3:编译C++文件、生成so文件及so文件使用
- 解决NestScrollView嵌套RecyclerView,RecyclerView抢焦点导致页面会自己滑动



