codeforces 821d Okabe and City
来源:互联网 发布:周扬青 淘宝 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 03:21
Okabe likes to be able to walk through his city on a path lit by street lamps. That way, he doesn't get beaten up by schoolchildren.
Okabe's city is represented by a 2D grid of cells. Rows are numbered from 1 to n from top to bottom, and columns are numbered 1 to mfrom left to right. Exactly k cells in the city are lit by a street lamp. It's guaranteed that the top-left cell is lit.
Okabe starts his walk from the top-left cell, and wants to reach the bottom-right cell. Of course, Okabe will only walk on lit cells, and he can only move to adjacent cells in the up, down, left, and right directions. However, Okabe can also temporarily light all the cells in any single row or column at a time if he pays 1 coin, allowing him to walk through some cells not lit initially.
Note that Okabe can only light a single row or column at a time, and has to pay a coin every time he lights a new row or column. To change the row or column that is temporarily lit, he must stand at a cell that is lit initially. Also, once he removes his temporary light from a row or column, all cells in that row/column not initially lit are now not lit.
Help Okabe find the minimum number of coins he needs to pay to complete his walk!
The first line of input contains three space-separated integers n, m, and k (2 ≤ n, m, k ≤ 104).
Each of the next k lines contains two space-separated integers ri and ci (1 ≤ ri ≤ n, 1 ≤ ci ≤ m) — the row and the column of the i-th lit cell.
It is guaranteed that all k lit cells are distinct. It is guaranteed that the top-left cell is lit.
Print the minimum number of coins Okabe needs to pay to complete his walk, or -1 if it's not possible.
4 4 51 12 12 33 34 3
2
5 5 41 12 13 13 2
-1
2 2 41 11 22 12 2
0
5 5 41 12 23 34 4
3
In the first sample test, Okabe can take the path 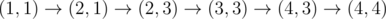 , paying only when moving to (2, 3) and (4, 4).
, paying only when moving to (2, 3) and (4, 4).
In the fourth sample, Okabe can take the path 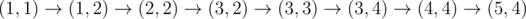
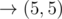 , paying when moving to (1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 4).
, paying when moving to (1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 4).
题意:有一个n*m地图,有k个位置是点亮的,有4个移动方向,每次可以移动到相邻的点亮位置,每次站在初始被点亮某个位置,暂时使某行或该某列全部点亮,花费为1,下一次使用时,上一次暂时点亮被熄灭。
思路:最短路: 以K个在初始就被点亮的点建图,如果有在四联通下相邻的灯则两点之间权为0,如果两点之间横/纵坐标相差不超过2,也就是说相隔一行/列,则两点之间权为1.
代码:
#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<algorithm>#include<cmath>#include<queue>using namespace std;const int maxn=10005;const int inf=1e9-1;int n,m,k;int u[maxn],v[maxn];int vis[maxn],d[maxn];int SPFA(int start){ memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++) d[i]=inf; queue<int>que; while(!que.empty()) que.pop(); que.push(start),d[start]=0; vis[start]=1; while(!que.empty()) { int x=que.front(); que.pop(); vis[x]=0; for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) { if(i==x) continue; int w=inf; int p=abs(u[i]-u[x]),q=abs(v[i]-v[x]); if(p+q==1) w=0; else if(p<=2||q<=2) w=1; if(d[i]>d[x]+w) { d[i]=d[x]+w; if(!vis[i]) { vis[i]=1; que.push(i); } } } } return d[k]>=inf?-1:d[k];}int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k); memset(u,0,sizeof(u)); memset(v,0,sizeof(v)); int flag=0; for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&u[i],&v[i]); if(u[i]==n&&v[i]==m) flag=1; } if(!flag) u[++k]=n+1,v[k]=m+1; int ans=SPFA(1); printf("%d\n",ans);}- Codeforces 821 D. Okabe and City
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City 题解
- codeforces 821d Okabe and City
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City
- Codeforces 821D Okabe And City 最短路
- D. Okabe and City codeforces 最短路
- CF 821D Okabe and City
- CF-Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)-D-Okabe and City
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City (拆点+思维建图+spfa)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City 思维建图+dij
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City 思维建图+spfa
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City【思维建图+Dij+优先队列优化】好题~好题~
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City (最短路)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City(最短路)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City 最短路
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City(最短路)
- Codeforces 821 B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces 821 C. Okabe and Boxes
- 【UOJ261 BZOJ 】天天爱跑步(线段树合并)
- leetcode -- 345. Reverse Vowels of a String 【双指针 + 逆序的变形】
- Mybatis:ReflectionException: There is no getter for property named 'productName' in 'class java.lang
- 搜索 棋盘问题
- 内存的几个小问题
- codeforces 821d Okabe and City
- 安装Python3-ipython
- NKOJ 3252 (CQOI 2015) 多项式(数学,高精度)
- 暑期集训之最大公约数问题
- jdbc 工具类的抽取
- 测试用例编写考虑的细节
- 最大公约数等几个算法
- Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
- Ubuntu和windows7双系统时间错误


