Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City(最短路)
来源:互联网 发布:php unpack 二进制 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 05:46
Okabe likes to be able to walk through his city on a path lit by street lamps. That way, he doesn't get beaten up by schoolchildren.
Okabe's city is represented by a 2D grid of cells. Rows are numbered from 1 to n from top to bottom, and columns are numbered 1 to mfrom left to right. Exactly k cells in the city are lit by a street lamp. It's guaranteed that the top-left cell is lit.
Okabe starts his walk from the top-left cell, and wants to reach the bottom-right cell. Of course, Okabe will only walk on lit cells, and he can only move to adjacent cells in the up, down, left, and right directions. However, Okabe can also temporarily light all the cells in any single row or column at a time if he pays 1 coin, allowing him to walk through some cells not lit initially.
Note that Okabe can only light a single row or column at a time, and has to pay a coin every time he lights a new row or column. To change the row or column that is temporarily lit, he must stand at a cell that is lit initially. Also, once he removes his temporary light from a row or column, all cells in that row/column not initially lit are now not lit.
Help Okabe find the minimum number of coins he needs to pay to complete his walk!
The first line of input contains three space-separated integers n, m, and k (2 ≤ n, m, k ≤ 104).
Each of the next k lines contains two space-separated integers ri and ci (1 ≤ ri ≤ n, 1 ≤ ci ≤ m) — the row and the column of the i-th lit cell.
It is guaranteed that all k lit cells are distinct. It is guaranteed that the top-left cell is lit.
Print the minimum number of coins Okabe needs to pay to complete his walk, or -1 if it's not possible.
4 4 51 12 12 33 34 3
2
5 5 41 12 13 13 2
-1
2 2 41 11 22 12 2
0
5 5 41 12 23 34 4
3
In the first sample test, Okabe can take the path 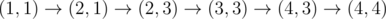 , paying only when moving to (2, 3) and (4, 4).
, paying only when moving to (2, 3) and (4, 4).
In the fourth sample, Okabe can take the path 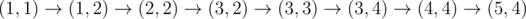
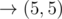 , paying when moving to (1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 4).、
, paying when moving to (1, 2), (3, 4), and (5, 4).、
题意:N*M的表格上已经有K个被点亮的格子,现在你像从(1,1)到(n,m),每步只能沿上下左右的方向走被点亮的格子,现在你可以在任意被点亮的格子上再点亮任意的一行或一列格子且花费为1,问你要走到(n,m)的最小花费是多少.
分析:我们考虑把每行每列都单独作为图中一个点,那么对于一个被点亮的格子x,y,将其向行x-1,x,x+1和列y-1,y,y+1连权值为1的边(因为向其他的行和列连边没有意义),再连两者之间的权值为0的反向边,然后相邻点之间再连边,最后跑一边最短路就可以了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>#define INF 1000000000using namespace std;typedef pair<int,int> pii;const int D[4][2] = {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};int n,m,x,y,k,ans,N,d[40005];bool done[40005];vector<pii> G[40005];map<pii,int> s;priority_queue< pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii> > q;int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k); for(int i = 1;i <= k;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); pii u = make_pair(x,y); s[u] = i; for(int t = 0;t < 4;t++) { int dx = x + D[t][0],dy = y + D[t][1]; pii v = make_pair(dx,dy); if(s.find(v) != s.end()) { G[i].push_back(make_pair(s[v],0)); G[s[v]].push_back(make_pair(i,0)); } } G[k+x].push_back(make_pair(i,0)); G[i].push_back(make_pair(k+x,1)); G[k+n+y].push_back(make_pair(i,0)); G[i].push_back(make_pair(k+n+y,1)); if(x != 1) G[k+x-1].push_back(make_pair(i,0)),G[i].push_back(make_pair(k+x-1,1)); if(x != n) G[k+x+1].push_back(make_pair(i,0)),G[i].push_back(make_pair(k+x+1,1)); if(y != 1) G[k+n+y-1].push_back(make_pair(i,0)),G[i].push_back(make_pair(k+n+y-1,1)); if(y != m) G[k+n+y+1].push_back(make_pair(i,0)),G[i].push_back(make_pair(k+n+y+1,1)); } N = k+n+m; for(int i = 0;i <= N;i++) d[i] = (i == 1 ? 0 : INF); memset(done,0,sizeof(done)); q.push(make_pair(d[1],1)); while(!q.empty()) { int u = q.top().second; q.pop(); if(done[u]) continue; done[u] = true; for(pii v : G[u]) { if(d[v.first] > d[u] + v.second) { d[v.first] = d[u] + v.second; q.push(make_pair(d[v.first],v.first)); } } } ans = INF; if(s.count(make_pair(n,m))) ans = min(ans,d[s[make_pair(n,m)]]); ans = min(ans,d[k+n]); ans = min(ans,d[k+n+m]); if(ans == INF) ans = -1; cout<<ans<<endl;}- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City (最短路)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City(最短路)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City 最短路
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City(最短路)
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City
- CF-Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)-D-Okabe and City
- D. Okabe and City codeforces 最短路
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City 思维建图+dij
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) 821D Okabe and City 思维建图+spfa
- Codeforces 821D Okabe And City 最短路
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) B. Okabe and Banana Trees
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) C. Okabe and Boxes
- CF-Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)-C-Okabe and Boxes
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) C. Okabe and Boxes 思维
- Codeforces 821 D. Okabe and City
- Codeforces 821D Okabe and City 题解
- codeforces 821d Okabe and City
- Codeforces Round #257 div.2 D or 450D Jzzhu and Cities【最短路】
- android(java) DES加密、解密详解
- 后缀数组详解
- 图片压缩
- matlab 2017a Linux 和Mac版本安装技巧
- 安装tesseract-ocr出错的解决策略
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) D. Okabe and City(最短路)
- 算法-->反序(插入)
- Centos中Qt编译问题(/usr/bin/ld: 找不到 -lpulse-mainloop-glib,/usr/bin/ld: 找不到 -lpulse...)
- POJ
- URG-PSH
- 51Nod 1135 原根
- Java中状态模式介绍
- Linux——文件系统中inode的工作
- Git版本控制工具和Github代码托管平台


