leetcode 70. Climbing Stairs
来源:互联网 发布:bf2怎么修改大炮数据 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 02:25
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
这道题我一开始用的排列组合的思想,知道了1步台阶的个数 a 和2步台阶的个数 b,那么可以得到总个数c=a+b。然后这种情况就是组合题,c个台阶去取b(或者c个台阶去取a),即C(c,b)。但是这种方法不行!!因为求C(n/k)的时候会有精度问题,如C(5,3),如果令result为double类型,那么(5/3)*(4/2)*(3/1)由于是double*double*double,在double数量足够多时,会出现精度不准的问题,这个无法避免。而如果先求出被除数5*4*3,再求出除数3*2*1,最后再用被除数/除数,则会出现被除数太大而溢出的情况,即使把被除数换成long类型,当n为44时,依旧发生溢出。心累!只好换其他方法了。
public int climbStairs(int n) {if(n == 1 || n == 2){return n;}int[] dp=new int[n+1];dp[1]=1;dp[2]=2;for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){//相当于在dp[i-1]的每个情况上加上1步//和在dp[i-2]的每个情况上加上2步dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];}return dp[n];}这道题有solutions:https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs/solution/
Solution
Approach #1 Brute Force [Time Limit Exceeded]
Algorithm
In this brute force approach we take all possible step combinations i.e. 1 and 2, at every step. At every step we are calling the function climbStairs for step 1and 2, and return the sum of returned values of both functions.
climbStairs(i,n)=(i+1,n)+climbStairs(i+2,n), where i defines the current step and n defines the destination step.
Java
public class Solution { public int climbStairs(int n) { climb_Stairs(0, n); } public int climb_Stairs(int i, int n) { if (i > n) { return 0; } if (i == n) { return 1; } return climb_Stairs(i + 1, n) + climb_Stairs(i + 2, n); }}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(2n). Size of recursion tree will be 2n.
Recursion tree for n=5 would be like this:
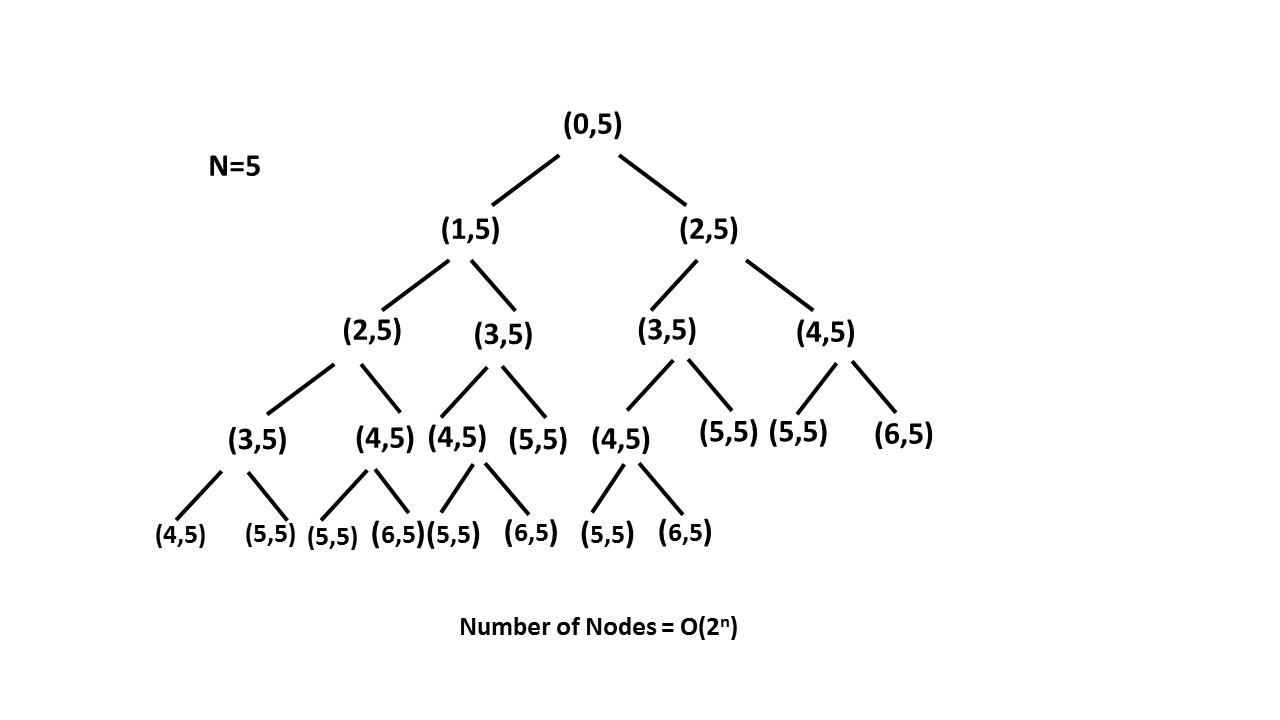
Space complexity : O(n). The depth of the recursion tree can go upto n.
Approach #2 Recursion with memorization [Accepted]
Java
public class Solution { public int climbStairs(int n) { int memo[] = new int[n + 1]; return climb_Stairs(0, n, memo); } public int climb_Stairs(int i, int n, int memo[]) { if (i > n) { return 0; } if (i == n) { return 1; } if (memo[i] > 0) { return memo[i]; } memo[i] = climb_Stairs(i + 1, n, memo) + climb_Stairs(i + 2, n, memo); return memo[i]; }}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(n). Size of recursion tree can go upto n.
Space complexity : O(n). The depth of recursion tree can go upto n.
Approach #3 Dynamic Programming [Accepted]
Algorithm
One can reach ith step in one of the two ways:
Taking a single step from (i−1)th step.
Taking a step of 2 from (i−2)th step.
dp[i]=dp[i−1]+dp[i−2]
Java
public class Solution { public int climbStairs(int n) { if (n == 1) { return 1; } int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; dp[1] = 1; dp[2] = 2; for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]; } return dp[n]; }}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(n). Single loop upto n.
Space complexity : O(n). dp array of size n is used.
Approach #4 Fibonacci Number [Accepted]:
Algorithm
In the above approach we have used dp array where dp[i]=dp[i−1]+dp[i−2]. It can be easily analysed that dp[i] is nothing but ith fibonacci number.
Fib(n)=Fib(n−1)+Fib(n−2)
Now we just have to find nth number of the fibonacci series having 1 and 2 their first and second term respectively i.e. Fib(1)=1 and Fib(2)=2.
Java
public class Solution { public int climbStairs(int n) { if (n == 1) { return 1; } int first = 1; int second = 2; for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { int third = first + second; first = second; second = third; } return second; }}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(n). Single loop upto n is required to calculate nth fibonacci number.
Space complexity : O(1). Constant space is used.
Approach #6 Fibonacci Formula [Accepted]:
Algorithm
We can find nth fibonacci number using this formula:
Fn=1/√5[(21+√5)n−(21−√5)n]
For the given problem, the Fibonacci sequence is defined by F0=1, F1=1, F1=2, Fn+2=Fn+1+Fn. A standard method of trying to solve such recursion formulas is assume Fn of the form Fn=an. Then, of course, Fn+1=an+1 and Fn+2=an+2 so the equation becomes an+2=an+1+an. If we divide the entire equation by an we arrive at a2=a+1 or the quadratic equation
a2−a−1=0.
Solving this by the quadratic formula, we get:
a=1/√5((21±√5)).
The general solution, thus takes the form:
Fn=A(21+√5)n+B(21−√5)n
For n=0, we get A+B=1
For n=1, we get A(21+√5)+B(21−√5)=1
Solving the above equations, we get:
A=(2√51+√5),B=(2√51−√5)
Putting these values of A and B in the above general solution equation, we get:
Fn=1/√5((21+√5)n+1−(21−√5)n+1)
Java
public class Solution { public int climbStairs(int n) { double sqrt5=Math.sqrt(5); double fibn=Math.pow((1+sqrt5)/2,n+1)-Math.pow((1-sqrt5)/2,n+1); return (int)(fibn/sqrt5); }}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(log(n)). pow method takes log(n) time.
Space complexity : O(1). Constant space is used.
- [LeetCode]70.Climbing Stairs
- LeetCode --- 70. Climbing Stairs
- [Leetcode] 70. Climbing Stairs
- [leetcode] 70.Climbing Stairs
- [leetCode]70. Climbing Stairs
- 70. Climbing Stairs LeetCode
- [LeetCode]70. Climbing Stairs
- 【LeetCode】70. Climbing Stairs
- leetcode 70. Climbing Stairs
- leetcode 70. Climbing Stairs
- LeetCode *** 70. Climbing Stairs
- 【LeetCode】70. Climbing Stairs
- LeetCode 70. Climbing Stairs
- leetcode 70. Climbing Stairs
- [LeetCode]70. Climbing Stairs
- 【LeetCode】70. Climbing Stairs
- LeetCode 70. Climbing Stairs
- #leetcode#70.Climbing Stairs
- SpringBoot 表单验证
- 解决合并css文件后spring MVC下glyphicons-halflings-regular文件无法加载问题
- 关于modelsim仿真时出现Missing instance name in instantiation of 'xx'.
- Spring的事务管理
- UESTC1716 京电的会议室(排列组合)
- leetcode 70. Climbing Stairs
- 异常总结
- SpringBoot的RabbitMQ消息队列: 六、第五模式"Topics"
- Photoshop CS6最新官方正式中文破解版(32位、64位)
- Android ShareSDk三方登录笔记
- 4385: [POI2015]Wilcze doły
- 用Supervisord管理进程
- Javadoc-有用的注解
- 接口的外部调用的单元测试思路介绍


