codeforces D. Merge Sort 分治
来源:互联网 发布:java 1.7.0 64 bit 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/02 02:01
Merge sort is a well-known sorting algorithm. The main function that sorts the elements of array a with indices from [l, r) can be implemented as follows:
- If the segment [l, r) is already sorted in non-descending order (that is, for any i such that l ≤ i < r - 1 a[i] ≤ a[i + 1]), then end the function call;
- Let
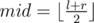 ;
; - Call mergesort(a, l, mid);
- Call mergesort(a, mid, r);
- Merge segments [l, mid) and [mid, r), making the segment [l, r) sorted in non-descending order. The merge algorithm doesn't call any other functions.
The array in this problem is 0-indexed, so to sort the whole array, you need to call mergesort(a, 0, n).
The number of calls of function mergesort is very important, so Ivan has decided to calculate it while sorting the array. For example, if a = {1, 2, 3, 4}, then there will be 1 call of mergesort — mergesort(0, 4), which will check that the array is sorted and then end. If a = {2, 1, 3}, then the number of calls is 3: first of all, you call mergesort(0, 3), which then sets mid = 1 and calls mergesort(0, 1) and mergesort(1, 3), which do not perform any recursive calls because segments (0, 1) and (1, 3) are sorted.
Ivan has implemented the program that counts the number of mergesort calls, but now he needs to test it. To do this, he needs to find an array a such that a is a permutation of size n (that is, the number of elements in a is n, and every integer number from [1, n] can be found in this array), and the number of mergesort calls when sorting the array is exactly k.
Help Ivan to find an array he wants!
The first line contains two numbers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 100000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 200000) — the size of a desired permutation and the number of mergesort calls required to sort it.
If a permutation of size n such that there will be exactly k calls of mergesort while sorting it doesn't exist, output - 1. Otherwise output ninteger numbers a[0], a[1], ..., a[n - 1] — the elements of a permutation that would meet the required conditions. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
3 3
2 1 3
4 1
1 2 3 4
5 6
-1
题解:
构造
初始化一个数组a[0]=1,a[1]=2,a[2]=3...a[n-1]=n;
函数dfs(l,r,x)表示的是把区间[l,r)变成需要x次call才能排好序的一个功能。
其中call的次数是一棵满二叉树的形式,所以call的次数x一定是奇数。
因此,如果x是偶数的话一点是不可能的。
这样的话dfs(l,r,x)里面应该是
x--;(表示该call)
然后x剩下的次数应由左右两部分完成。
即
dfs(l,mid,t1);dfs(mid,r,t2);(其中t1+t2=x)
然后把a[l,mid)放在右面a[mid,r)放在左边
注意!这里mid = (l+r+1)/2;为什么呢,因为在调用归并排序的时候左边略小一点,所以我们在构造的时候左边要略大一点。
如果x/2刚好是奇数,那么t1 =t2 =x/2;此时t1,t2都为奇数
因为dfs(,,x)中x只能接收为奇数的情况。
否则的话t1要比t2大2.(因为如果左右区间不能平分的话,左边要比右边略大一点)
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int n,k;const int maxn = 100011;int a[maxn];int tmp[maxn];bool dfs(int l,int r,int x){if(r - l <= 1) return x == 1;x--;if(x == 0) return true;int mid = (l+r+1)/2;if(x%2) return false;int t1,t2;if((x/2)%2 == 0){t1 = x/2+1;t2 = x/2-1;}else t1 = t2 = x/2;bool s = dfs(l,mid,t1) && dfs(mid,r,t2);if(!s) return s;int p = l;for(int i = mid;i < r;++i) tmp[p++] = a[i];for(int i = l;i < mid;++i) tmp[p++] = a[i];for(int i = l;i < r;++i) a[i] = tmp[i];return s;}int main(){cin>>n>>k;for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) a[i] = i+1;bool s = dfs(0,n,k);if(!s) cout<<-1;else{for(int i = 0;i < n;++i){printf("%d ",a[i]);}}return 0;}- codeforces D. Merge Sort 分治
- Codeforces 873D. Merge Sort 分治 + 构造
- Codeforces 873 D Merge Sort 【分治】
- Codeforces 873D Merge Sort
- Educational Codeforces Round 30 D. Merge Sort
- Educational Codeforces Round 30 D.Merge Sort
- codeforces 873D merge sort 构造
- 分治排序(MERGE-SORT)
- Codeforces 873 D Merge Sort(归并排序性质)
- Codeforces 847B Preparing for Merge Sort
- 【二分优化】Preparing for Merge Sort CodeForces
- Java练习:分治法之合并排序(merge Sort)
- 算法导论2.3MERGE-SORT(分治或者合并排序算法)
- merge-sort (归并排序)——分治算法
- codeforces 161D 树的点分治
- codeforces 868D 分治哈希
- Codeforces 875D High Cry rmq+分治
- CodeForces 340D - Bubble Sort Graph
- 实现二维数组排序
- LwIP之UDP协议实现
- 建模所使用的工具
- 初入职场---沟通的重要性
- 使用github desktop隐藏文件和文件夹
- codeforces D. Merge Sort 分治
- virsh edit查询虚拟机
- fragment简单使用
- [绍棠_Swift] Swift指纹验证解锁 touch事件
- 八大排序算法之(二)插入排序 希尔排序
- 广州本爱的郑舒匀老师挽救了我的婚姻,谁说她是骗子?!
- Java内部类的总结
- wxWidgets3.03的下载与安装
- 【cocos2d-x 源码解析】帧动画


