Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction
来源:互联网 发布:梯度的分水岭算法 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 08:43
During the programming classes Vasya was assigned a difficult problem. However, he doesn't know how to code and was unable to find the solution in the Internet, so he asks you to help.
You are given a sequence a, consisting ofn distinct integers, that is used to construct the binary search tree. Below is the formal description of the construction process.
- First element a1 becomes the root of the tree.
- Elements a2, a3, ..., an are added one by one. To add elementai one needs to traverse the tree starting from the root and using the following rules:
- The pointer to the current node is set to the root.
- If ai is greater than the value in the current node, then its right child becomes the current node. Otherwise, the left child of the current node becomes the new current node.
- If at some point there is no required child, the new node is created, it is assigned valueai and becomes the corresponding child of the current node.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the length of the sequencea.
The second line contains n distinct integersai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the sequencea itself.
Output n - 1 integers. For all i > 1 print the value written in the node that is the parent of the node with valueai in it.
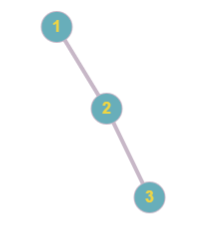
31 2 3
1 2
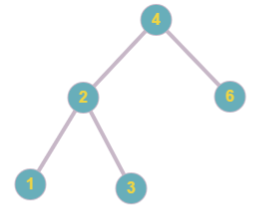
54 2 3 1 6
4 2 2 4
Picture below represents the tree obtained in the first sample.
Picture below represents the tree obtained in the second sample.
题意:给你一个数列,让你以此构造一个排序二叉树,输出每个点的父亲。
分析:再次被智商压制,排序二叉树中一个点向左找到的第一个点(左下或左上)一定是之前序列中出现的最后一个小于等于当前节点权值得数,右边同理。
#include <set> #include <cstdio>#include <iostream>#include <unordered_map>using namespace std;set <int> f;unordered_map <int,int> l,r;int n,a[100005];int main(){cin.sync_with_stdio(false);cin>>n;for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){cin>>a[i];if(i == 1) f.insert(a[i]);else {auto it = f.lower_bound(a[i]);if(it == f.end()) r[*--it] = a[i];else {if(!l[*it]) l[*it] = a[i];else r[*--it] = a[i];}cout<<*it<<" ";f.insert(a[i]);}}}- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2)D. Tree Construction
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction (BST)
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction __ Binary Search Tree
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction (二叉搜索树+set)
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction (构造二叉搜索树)
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction (BST询问父亲节点)
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D. Tree Requests
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D. Tree Requests dfs_clock,二分
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D Tree Requests
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D. Tree Requests
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D. Tree Requests (DFS序)
- Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2) D. Happy Tree Party
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2)D. Tree Requests
- Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D. Tree Requests
- 善用stl。。。。。。。。Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) D - Tree Requests
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- 一句话概括C# . NET VS 关系
- Hadoop-2.6.1伪分布式集群环境搭建
- char码值对应列表大全
- Linux_bug收集_linux忘记root密码解决方法
- android中的context是起什么作用?
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) D. Tree Construction
- IOS 使用QLPreviewController浏览PDF WORD等文件
- 大型网站系统架构的演化
- main中的运行时(runtime)
- equals()方法的重写
- 算法复杂度
- ViewPager+Fragment 延迟加载
- NYOJ - 擅长排列的小明
- POJ 3254 Corn Fields(状态压缩DP)


