CF 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers(组合数学)
来源:互联网 发布:5250设置端口trunk 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/08 20:17
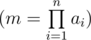 . Your task is to find the number of distinct decompositions of numberm into the product ofn ordered positive integers.
. Your task is to find the number of distinct decompositions of numberm into the product ofn ordered positive integers.Decomposition into n products, given in the input, must also be considered in the answer. As the answer can be very large, print it modulo1000000007(109 + 7).
The first line contains positive integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500). The second line contains space-separated integersa1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
In a single line print a single number k — the number of distinct decompositions of numberm inton ordered multipliers modulo1000000007(109 + 7).
115
1
31 1 2
3
25 7
4
In the second sample, the get a decomposition of number 2, you need any one number out of three to equal 2, and the rest to equal 1.
In the third sample, the possible ways of decomposing into ordered multipliers are [7,5], [5,7], [1,35], [35,1].
A decomposition of positive integer m inton ordered multipliers is a cortege of positive integersb = {b1, b2, ...bn} such that 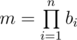 . Two decompositionsb and c are considered different, if there exists indexi such that bi ≠ ci.
. Two decompositionsb and c are considered different, if there exists indexi such that bi ≠ ci.
题意:有n个数,把这n个数分为a1到an个数连乘。(比方说n为2,这两个数为3,5,则可以有1,35; 5,7; 7,5;35,1;)
分析:可以将这n个数全部分解为素因子,然后将每种素因子(设为k个)分别放到n个位置。用隔板法求得为每种总数为c(n+m-1,n-1)。
#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<iostream>#include<map>#define LL long long#define N 37000const int MOD=1e9+7;using namespace std;map<int,int> mp;bool is[N+10];LL prime[N],k,n;LL jc[N+10],fjc[N+10];void addm(int x){ for(int i=1;prime[i]*prime[i]<=x;i++) { while(x%prime[i]==0) { mp[prime[i]]++; x/=prime[i]; } if(x==1)break; } if(x>1)mp[x]++;}LL quickmi(LL x,LL m) //快速幂{ LL ans=1; while(m>0) { if(m&1) ans=(ans*x)%MOD; x=x*x%MOD; m/=2; } return ans;}LL CC(int n,int m){ if(m==0)return 1; //cout<<jc[n]<<" "<<fjc[m]<<endl; return jc[n]*fjc[m]%MOD*fjc[n-m]%MOD;}int main(){ k=0; memset(is,true,sizeof(is)); is[0]=is[1]=0; for(int i=2;i<=N;i++) { if(is[i]) { prime[++k]=i; for(int j=i*i;j<=N;j+=i)is[j]=false; } } jc[0]=1; for(int i=1;i<=N;i++) { jc[i]=jc[i-1]*i%MOD; fjc[i]=quickmi(jc[i],MOD-2); //阶乘的逆模元,费马小定理 //if(i<20) //cout<<jc[i]<<" "<<fjc[i]<<endl; } int x; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { mp.clear(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d",&x); addm(x); } LL ans=1; map<int,int>::iterator it; for(it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++) { x=it->second; //printf("%d\n",x); ans=ans*CC(n+x-1,n-1)%MOD; } printf("%I64d\n",ans); } return 0;}- CF 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers(组合数学)
- CF 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers
- CF 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers
- codeforces 396A A. On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers(组合数学+数论)
- Codeforces 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers(组合数学)
- CF 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers 解题报告(质因数分解+组合数计算)
- CodeForce 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers
- Codeforces-396A - On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers-组合计数
- 解题报告: Codeforces 396A. On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers 组合
- CodeForces 397C On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers(组合数学)
- 396AOn Number of Decompositions into Multipliers 组合
- codeforces#232_div2_C On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers 数论 组合计数
- Codeforces Round #232 (Div. 2) C. On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers 之我为何如此菜
- cf 553A dp+组合数学
- Codeforces 615D Multipliers 【组合数学】
- Paths on a Grid(组合数学)
- POJ_1942_Paths on a Grid 组合数学
- Paths on a Grid(简单组合数学)
- 设计模式-观察者模式
- OpenCV读入图像及通道详解
- matlab入门教程一 ----- 初识matlab
- (转)史上最全人工智能产品清单(1/3)
- 打开网页就运行js方法
- CF 396A On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers(组合数学)
- java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: @EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected
- 玩转树莓派3 -- 串口问题的解决
- 周志華《機器學習》答案搜集
- myeclipse10 tomcat :the source attachment does not contain the source for the file URLClassPath.clas
- jzoj P2152【2017.7.7普及】终极数
- Python探索记(16)——Python的可变类型与不可变类型
- Vector & ArrayList 的主要区别
- 用dfs搜索特殊数


