树形dp--computer
来源:互联网 发布:cinebench数据库 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 17:53
Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5383 Accepted Submission(s): 2697
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
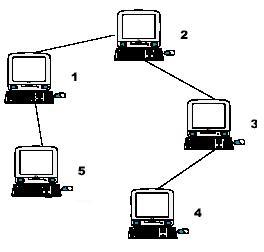
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.

Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
51 12 13 11 1
Sample Output
32344
中文题目:
给你一棵由n个节点构成的树,树中每条边都有一定的长度值。 对于树中的每个节点,请你找出树中离它最远的点,并输出它们的距离。
1<=n<=10000
1<=n<=10000
边的长度<=100000000
分析:
状态:
dp[i][0]:从点i往上经过父亲节点,能到达的最长距离。
dp[i][1]:从点i往下到叶子节点,能到达的最长距离。
dp[i][2]:从点i往下到叶子节点,能到达的次长距离。
为什么要记录次长距离?
dp[i][1]可能和dp[son[i]][0]重合
方程:
dp[i][1]=max{ dp[j][1]+Len[i][j] } j是i的儿子
dp[i][2]=max{ dp[j][1]+Len[i][j] } j是i的儿子 并且 j不是BestSon[i] BestSon[i]记录i往下最长距离来自哪个儿子所在子树
dp[i][0]=max{ dp[fa][1] , dp[fa][0] }+Len[fa][i] fa是i的父亲 并且 i!=BestSon[fa]
dp[i][0]=max{ dp[fa][2] , dp[fa][0] }+Len[fa][i] fa是i的父亲 并且 i==BestSon[fa]
答案:ans[i]=max{ dp[i][1] , dp[i][0] } 1<=i<=n
#include<cstdio>#include<iostream>#include<algorithm>#include<cstring>using namespace std;struct line{long long from,to,len;};line edge[100005];long long last[10005],_next[100005];long long n,m=0;long long f[10005][5];long long bestson[10005]; void add_edge(long long x,long long y,long long len){m++;_next[m]=last[x];last[x]=m;edge[m].from=x;edge[m].to=y;edge[m].len=len;}void dp_down(long long x,long long fa){long long i,j,k;for(j=last[x];j;j=_next[j]){i=edge[j].to;if(i==fa)continue;dp_down(i,x);if(f[x][1]<f[i][1]+edge[j].len){f[x][1]=f[i][1]+edge[j].len;bestson[x]=i;}}for(j=last[x];j;j=_next[j]){i=edge[j].to;if(i==fa||i==bestson[x])continue;if(f[x][2]<f[i][1]+edge[j].len){f[x][2]=f[i][1]+edge[j].len;}}}void dp_up(long long x,long long fa){long long i,j,k;for(j=last[x];j;j=_next[j]){i=edge[j].to;if(i==fa)continue;if(i==bestson[x])f[i][0]=max(f[i][0],max(f[x][2],f[x][0])+edge[j].len);else f[i][0]=max(f[i][0],max(f[x][1],f[x][0])+edge[j].len);dp_up(i,x);}}int main(){long long i,j,k;while(cin>>n){m=0;memset(edge,0,sizeof(edge));memset(last,0,sizeof(last));memset(_next,0,sizeof(_next));memset(bestson,0,sizeof(bestson));memset(f,0,sizeof(f));for(i=2;i<=n;i++){long long x,l;scanf("%I64d%I64d",&x,&l);add_edge(i,x,l);add_edge(x,i,l);}dp_down(1,0);dp_up(1,0);for(i=1;i<=n;i++){printf("%I64d\n",max(f[i][0],f[i][1]));}}}/*f[i][0]向上经过父亲f[i][1]向下的最长路f[i][2]为向下的次长路 */方法二(树的直径):
定义树的直径如下:
树上最长的两点间距离称为树的直径,这两点称为树的直径端点。
引理: 到树上任一点距离最远的点一定是直径端点之一。
有了这条引理,问题就简单了:先求出树的直径端点A、B,以及这两点到其他点的距离a[i],b[i]。所求的最远距离
就是max(a[i],b[i])。
代码如下:
#include<cstdio>#include<iostream>#include<cstdlib>#include<cmath>#include<cstring>#include<queue>#include<vector>#include<algorithm>#define LL long longusing namespace std;const LL maxn=20000+5,inf=1e9;LL n,m,a[maxn],b[maxn],dist[maxn],A,B;LL last[maxn],Next[maxn],to[maxn],w[maxn];inline void _read(LL &x){ char ch=getchar(); bool mark=false; for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())if(ch=='-')mark=true; for(x=0;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())x=x*10+ch-'0'; if(mark)x=-x; } void add_edge(LL From,LL To,LL dist){to[++m]=To;Next[m]=last[From];last[From]=m;w[m]=dist;} void DFS(LL v,LL *dis){ //深搜求出到每一点的距离,存在dis数组中 int i;for(i=last[v];i;i=Next[i]){if(dis[v]+w[i]<dis[to[i]]){dis[to[i]]=dis[v]+w[i];DFS(to[i],dis);}} }int main(){LL i,x,y,z;_read(n);for(i=1;i<n;i++){_read(x);_read(y);_read(z);add_edge(x,y,z);add_edge(y,x,z);}for(i=1;i<=n;i++) dist[i]=a[i]=b[i]=inf;dist[1]=0; DFS(1,dist); //随便从一点开始搜,找到其中一个直径端点。 for(i=1;i<=n;i++)if(dist[i]>dist[A])A=i;a[A]=0;DFS(A,a); //找到另一个直径端点,并求出a[i]。 for(i=1;i<=n;i++)if(a[i]>a[B])B=i;b[B]=0;DFS(B,b); //求出b[i]。 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d\n",max(a[i],b[i]));return 0;} 0 0
- 树形dp hdu Computer
- 【树形DP】 hdu2196 Computer
- HDU2196:Computer(树形DP)
- HDU2196 - Computer (树形DP)
- HDU2196 Computer(树形DP)
- 树形dp--computer
- hdu2196 Computer 【树形dp】
- hdu2196 Computer【树形DP】
- Computer (树形dp)
- 树形DP-Computer
- hdoj 2196Computer 树形DP
- HDU 2196 Computer(树形dp)
- computer hdoj 2196树形dp
- 【树形DP】 HDU 2196 Computer
- HDU 2196 Computer(树形DP)
- Hdu 2196 Computer(树形dp)
- Computer - HDU 2196 树形dp
- Hdu 2196 Computer (树形dp)
- 函数指针与指针函数区别
- 使用ViewPager实现左右循环滑动及轮播效果
- winform 自定义安装CustomActionData多个参数传递属性值写法
- php测试程序运行速度
- Spring注解详解
- 树形dp--computer
- Activity 启动模式个人见解
- caffe 源码细节
- django正续或者倒序查库
- c primer plus第7章总结:分支跳转
- Duplicate Symbol链接错的原因总结和解决方法
- 屏幕密度 ---像素/尺寸
- 一个不错的问答论坛
- java中==和equals的区别


