D. An overnight dance in discotheque
来源:互联网 发布:php gzip 解压缩 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/18 12:37
The crowdedness of the discotheque would never stop our friends from having fun, but a bit more spaciousness won't hurt, will it?
The discotheque can be seen as an infinite xy-plane, in which there are a total of n dancers. Once someone starts moving around, they will move only inside their own movement range, which is a circular area Ci described by a center (xi, yi) and a radius ri. No two ranges' borders have more than one common point, that is for every pair (i, j) (1 ≤ i < j ≤ n) either ranges Ci and Cj are disjoint, or one of them is a subset of the other. Note that it's possible that two ranges' borders share a single common point, but no two dancers have exactly the same ranges.
Tsukihi, being one of them, defines the spaciousness to be the area covered by an odd number of movement ranges of dancers who are moving. An example is shown below, with shaded regions representing the spaciousness if everyone moves at the same time.
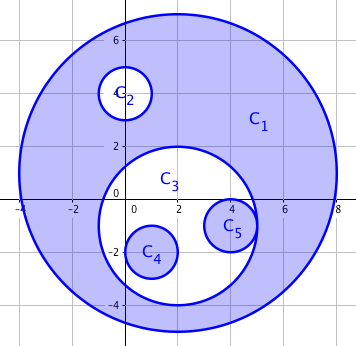
But no one keeps moving for the whole night after all, so the whole night's time is divided into two halves — before midnight and after midnight. Every dancer moves around in one half, while sitting down with friends in the other. The spaciousness of two halves are calculated separately and their sum should, of course, be as large as possible. The following figure shows an optimal solution to the example above.
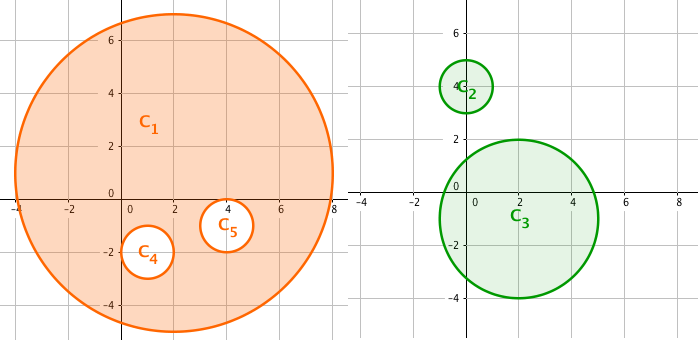
By different plans of who dances in the first half and who does in the other, different sums of spaciousness over two halves are achieved. You are to find the largest achievable value of this sum.
The first line of input contains a positive integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000) — the number of dancers.
The following n lines each describes a dancer: the i-th line among them contains three space-separated integers xi, yi and ri( - 106 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 106, 1 ≤ ri ≤ 106), describing a circular movement range centered at (xi, yi) with radius ri.
Output one decimal number — the largest achievable sum of spaciousness over two halves of the night.
The output is considered correct if it has a relative or absolute error of at most 10 - 9. Formally, let your answer be a, and the jury's answer be b. Your answer is considered correct if 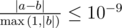 .
.
52 1 60 4 12 -1 31 -2 14 -1 1
138.23007676
80 0 10 0 20 0 30 0 40 0 50 0 60 0 70 0 8
289.02652413
思维题,让你计算覆盖奇数次的圆的面积和的最大值。你可以把一个圆移动到另外一个坐标系中。
其实我们可以画图想一下,首先就是没有圆包含的圆,我们记为树根,层数为0。很明显这个圆的面积必定是要加的。
然后我们看第一层的那些圆,要么移动,要么不移动。移动的话就是加上第一层的那些圆的面积,然后第二层的面积必定是要减得。而不移动的话这第一层的面积就需要减掉。但是第二层的面积就可以选择加上了。很明显这样是不划算的,因为层数越向上(小)面积越大的。所以我们把第二层的放到另外一个坐标系去就可以了。
画一画图会发现,第一层移动不移动改变的是第一层和第二层的加减号。
说白了,如果不存在第二个坐标系,按照层数应该是+-+-+-+-......
然后存在第二个坐标系后你可以把其中一个减号变成加号像这样+-......++-+-+-....。
然后其实就是-(a-b)和+(a-b)的区别因为a-b必定大于0,所以,我们应该第一次就变号。
所以最优的就是把第一层也加上。然后后面层数判断奇偶性就可以了奇加偶减就可以了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int MAXN = 1e3+7;const int inf = 1e9;const double pi = acos(-1);int n,m;struct node{ double x,y,r; int num = 0;}p[MAXN];bool check(int i,int j){ double d = hypot(p[i].x-p[j].x,p[i].y-p[j].y); if(p[j].r - p[i].r >= d)return 1; return 0;}int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i) { scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y,&p[i].r); } for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i) { for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++j)if(i!=j) { if(check(i,j))p[i].num++; } }// for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i)cout << p[i].num << " ";// puts(""); double sum = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i) { if(!p[i].num || p[i].num == 1)sum += pi*p[i].r*p[i].r; else if(p[i].num % 2)sum += pi*p[i].r*p[i].r; else sum -= pi*p[i].r*p[i].r; } printf("%.8f\n",sum); return 0;}- D. An overnight dance in discotheque
- codeforces D. An overnight dance in discotheque
- codeforces 814D An overnight dance in discotheque
- codeforces 814D An overnight dance in discotheque(思维)
- Codeforces 814D An overnight dance in discotheque DP(树形)
- Codeforces 814D-An overnight dance in discotheque
- Codeforces 814D An overnight dance in discotheque【思维】
- coderforces 814 D. An overnight dance in discotheque(贪心)
- codeforces 814 D An overnight dance in discotheque
- CF#418 Div2 D. An overnight dance in discotheque
- codeforces 814D An overnight dance in discotheque(贪心)
- Codeforces 814D-An overnight dance in discotheque 贪心
- Codeforces-814D An overnight dance in discotheque(贪心)
- [Codeforces 814D] An overnight dance in discotheque 树形dp,贪心
- codeforces 814D An overnight dance in discotheque(几何思维)
- Codeforces Round #418 (Div. 2) D. An overnight dance in discotheque(思维 贪心)
- Codeforces Round #418 (Div. 2) D. An overnight dance in discotheque
- Codeforces Round #418 (Div. 2) D. An overnight dance in discotheque 贪心
- MySQL 数据类型
- bzoj 2761 [JLOI2011]不重复数字
- 安装单机版zookeeper
- 欢迎使用CSDN-markdown编辑器
- Ubuntu14.04用户配置Python与tensorflow
- D. An overnight dance in discotheque
- RecyclerView封装--添加下拉刷新和上拉加载更多
- 设计模式六大原则(1):单一职责原则
- windbg 计算堆大小
- SICP 2.54 符号列表equal?
- 有客远来
- 搭建个人博客-hexo+github
- Java NIO 之阻塞与非阻塞
- PAT (Advanced Level) Practise 1109 Group Photo (25)


