【HDU2865】构造矩阵+Burnside定理+欧拉函数类似poj2888
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝上开店在哪里进货 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/17 23:17
Birthday Toy
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 466 Accepted Submission(s): 238
Problem Description
AekdyCoin loves toys. It is AekdyCoin’s Birthday today and he gets a special “Toy”.
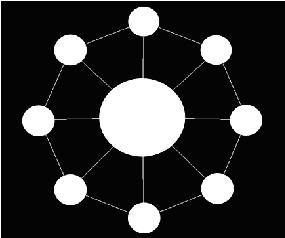
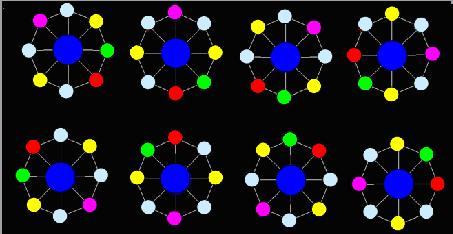
The “Toy” is in bulk and AekdyCoin has to make one by him. Let’s assume that the “Toy” has N small white beads and one Big bead .If someone want to make a “Toy”, he (or she) must always puts the Big bead in center, and then connect the other N small beads around it by using N sticks with equal length, and then the N small beads must be connected by N sticks with equal length, and it could be seen as a regular polygon. Figure 1 shows a “Toy” with 8 small white beads and one big white bead.
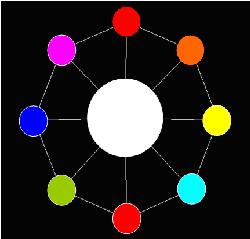
Now AekdyCoin has C kinds of available color, say blue, green, yellow, pink …etc. He wants to color these beads, but he thinks that must be too boring and stupid. So he colors these beads with one role: any adjacent beads couldn’t have same color. Figure 2 shows a legal situation, and Figure 3 shows an illegal situation.
It seems that the “Toy” becomes more interesting for AekdyCoin right now; however, he wants to color the big bead in center. Of course, he should follow the role above.
Now AekdyCoin begins to play with the “Toy”, he always colors the big beads and then the other small beads. He should color under the rule above. After several minutes, AekdyCoin finally makes a perfect “Toy”. Figure 4 shows a situation that is under the color rule.
AekdyCoin now want to know the different method to color the “Toy” whit at most K color. (“Toy” contains N small beads and one big bead.)
But, no, the problem is not so easy .The repetitions that are produced by rotation around the center of the circular necklace are all neglected. Figure 5 shows 8 “Toy”, they are regard as one method.
Now AekdyCoin will give you N and K, he wants you to help him calculate the number of different methods, because the number of method is so huge, so AekdyCoin just want you to tell him the remainder when divided by M.
In this problem, M = 1,000,000,007.
The “Toy” is in bulk and AekdyCoin has to make one by him. Let’s assume that the “Toy” has N small white beads and one Big bead .If someone want to make a “Toy”, he (or she) must always puts the Big bead in center, and then connect the other N small beads around it by using N sticks with equal length, and then the N small beads must be connected by N sticks with equal length, and it could be seen as a regular polygon. Figure 1 shows a “Toy” with 8 small white beads and one big white bead.

Now AekdyCoin has C kinds of available color, say blue, green, yellow, pink …etc. He wants to color these beads, but he thinks that must be too boring and stupid. So he colors these beads with one role: any adjacent beads couldn’t have same color. Figure 2 shows a legal situation, and Figure 3 shows an illegal situation.


It seems that the “Toy” becomes more interesting for AekdyCoin right now; however, he wants to color the big bead in center. Of course, he should follow the role above.
Now AekdyCoin begins to play with the “Toy”, he always colors the big beads and then the other small beads. He should color under the rule above. After several minutes, AekdyCoin finally makes a perfect “Toy”. Figure 4 shows a situation that is under the color rule.

AekdyCoin now want to know the different method to color the “Toy” whit at most K color. (“Toy” contains N small beads and one big bead.)
But, no, the problem is not so easy .The repetitions that are produced by rotation around the center of the circular necklace are all neglected. Figure 5 shows 8 “Toy”, they are regard as one method.

Now AekdyCoin will give you N and K, he wants you to help him calculate the number of different methods, because the number of method is so huge, so AekdyCoin just want you to tell him the remainder when divided by M.
In this problem, M = 1,000,000,007.
Input
The input consists of several test cases.(at least 1000)
Every case has only two integers indicating N, K
(3<=N<=10^9, 4<=K<=10^9)
Every case has only two integers indicating N, K
(3<=N<=10^9, 4<=K<=10^9)
Output
For each case, you should output a single line indicates the remainder of number of different methods after divided by M.
Sample Input
3 43 53 17162 78923
Sample Output
8401904019469065
Source
2009 Multi-University Training Contest 7 - Host by FZU
鸣谢:http://www.cnblogs.com/DrunBee/archive/2012/09/14/2684935.html
题意:n个小圆组成的正n边形,中间有一个大圆。有木棍相连的两个圆不能有相同的颜色,旋转后相同视为相同的方案,求着色方案数。

设有n个小圆,k种颜色(3<=N<=10^9, 4<=K<=10^9)。
首先,很容易想到从k种选一种给大圆,然后用k-1种颜色对小圆着色。
若不存在相邻圆颜色不同这个限制,则直接Burnside定理。
若存在限制,但是颜色种数很少,可以构造矩阵然后快速幂,得到一个置换使着色不变的着色方案数。
现在颜色种数很多,但是颜色限制较简单,可以考虑公式之类的。
考虑将n个圆的环,等分成t部分,每部分有m个圆。F表示m个圆满足限制的着色方案数。
若m=1,则F=0
若m=2,则F=k*(k-1)
若m=3,则F=k*(k-1)*(k-2)
若m=4,则F=k*(k-1)*[(k-1)+(k-2)*(k-2)]
……
观察到F[n]=F[n-1]*(k-2)+F[n-2]*(k-1)。
那么就可以对该递推式构造矩阵快速幂得到每种分法的方案数。
剩下的同【POJ】2888 Magic Bracelet。
#define DeBUG#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <cmath>#include <cstdlib>#include <algorithm>#include <vector>#include <stack>#include <queue>#include <string>#include <set>#include <sstream>#include <map>#include <list>#include <bitset>using namespace std ;#define zero {0}#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f#define EPS 1e-6#define TRUE true#define FALSE falsetypedef long long LL;const double PI = acos(-1.0);//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")inline int sgn(double x){ return fabs(x) < EPS ? 0 : (x < 0 ? -1 : 1);}#define N 100005#define mod 1000000007const int MAXN = 2;struct Matrix{ long long mat[MAXN][MAXN]; void Zero() { memset(mat, 0, sizeof(mat)); } void Unit() { memset(mat, 0, sizeof(mat)); for (int i = 0; i < MAXN; i++) mat[i][i] = 1; } void Build(long long k) { Zero(); mat[0][1] = 1; mat[0][0] = k - 2; mat[1][0] = k - 1; } void output() { for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++) { for(int j=0;j<MAXN;j++) { printf("%d ", mat[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } }};Matrix operator*(Matrix &a, Matrix &b){ Matrix tmp; tmp.Zero(); for (int k = 0; k < MAXN; k++) { for (int i = 0; i < MAXN; i++) { if (!a.mat[i][k]) continue; for (int j = 0; j < MAXN; j++) { tmp.mat[i][j] += a.mat[i][k] * b.mat[k][j]%mod; if( tmp.mat[i][j]>=mod) tmp.mat[i][j]-=mod; } } } return tmp;}Matrix operator ^(Matrix a, int k){ Matrix tmp; tmp.Unit(); for (; k; k >>= 1) { if (k & 1) tmp = tmp * a; a = a * a; } return tmp;}std::vector<int> prime;const int MAXPR = 320000;bool vispr[MAXPR];void Init(){ prime.clear(); memset(vispr, 1, sizeof(vispr)); int sqrtnum = (int)(sqrt((double)MAXPR) + EPS); for (int i = 2; i < sqrtnum; i++) { if (vispr[i]) for (int j = i * i; j < MAXN; j += i) vispr[j] = false; } for (int i = 2; i < MAXPR; i++) { if (vispr[i]) prime.push_back(i); }}LL Ext_gcd(LL a, LL b, LL &x, LL &y){ if (b == 0) { x = 1, y = 0; return a; } LL ret = Ext_gcd(b, a % b, y, x); y -= a / b * x; return ret;}LL Inv(LL a, LL m) ///求逆元a相对于m{ LL d, x, y, t = m; d = Ext_gcd(a, t, x, y); if (d == 1) return (x % t + t) % t; return -1;}//复杂度根号xstd::vector<int> factor;void Factor(int n){ factor.clear(); int i; for (i = 1; i * i < n; i++) { if (n % i == 0) { factor.push_back(i); factor.push_back(n / i); } } if (i * i == n) factor.push_back(i);}long long F(int n, int k){ long long res; if (n == 1) res = 0; else if (n == 2) res = (long long)k * (k - 1); else if (n == 3) res = (long long)k * (k - 1) % mod * (k - 2); else { Matrix g; g.Build(k); g = g ^ (n - 3); // g.output(); res = g.mat[0][0] * k % mod * (k - 1) % mod * (k - 2); res += g.mat[1][0] * k % mod * (k - 1); } return (res) % mod;}int eular(int n){ int i, res = 1; for (i = 2; i * i <= n; ++i) { if (n % i == 0) { n /= i; res *= i - 1; while (n % i == 0) { n /= i; res *= i; } } } if (n > 1) res *= n - 1; return res;}int eularbyPR(int x){ int res, i; res = x; for (i = 0; prime[i] * prime[i] <= x; i++) { if (x % prime[i] == 0) { res -= res / prime[i]; while (x % prime[i] == 0) x /= prime[i]; } } if (x > 1) res -= res / x; return res;}long long Burnside(int n, int k){ long long ans=0; int i; Factor(n); for (i = 0; i < factor.size(); i++) { ans += F(factor[i], k) * eular(n / factor[i]) % mod; if (ans >= mod) ans -= mod; } return (ans * Inv(n, mod) + mod) % mod;}int main(){#ifdef DeBUGs freopen("C:\\Users\\Sky\\Desktop\\1.in", "r", stdin);#endif int n, k; Init(); while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &k) + 1) { printf("%I64d\n", (Burnside(n, k - 1)*k + mod) % mod); } return 0;} 0 0
- 【HDU2865】构造矩阵+Burnside定理+欧拉函数类似poj2888
- Burnside引理、Polya定理和欧拉函数
- 【HDU2865】Birthday Toy-Burnside引理+数论+DP矩阵优化
- 【POJ2888】Magic Bracelet-Burnside引理+数论+DP矩阵优化
- POJ2154 以欧拉函数优化的BurnSide定理(有部分详细证明)
- Poj 2888 & Hoj 2722 Magic Bracelet (有限制的Burnside 矩阵性质 欧拉函数)
- hdu 5868 矩阵快速幂+burnside引理 +欧拉函数+乘法逆元
- POJ 2888 Magic Bracelet(Burnside引理+欧拉函数+矩阵快速幂+逆元)
- 欧拉函数及定理
- 欧拉定理与函数
- 欧拉函数与欧拉定理
- 欧拉函数与欧拉定理
- 欧拉函数&&欧拉定理
- 欧拉定理,欧拉函数
- 欧拉函数与欧拉定理
- 欧拉函数/欧拉定理
- 欧拉函数和欧拉定理
- 欧拉函数,欧拉定理模板
- redis缓存集群及集群负载均衡方案设计
- POJ 1651 Multiplication Puzzle (区间dp)
- Centos安装nginx服务
- Gdb调试多进程程序
- IOS中http请求使用cookie
- 【HDU2865】构造矩阵+Burnside定理+欧拉函数类似poj2888
- Qt中的信号与槽机制
- Scala数组操作
- HDU 2104 hide handkerchief
- 【第一篇章-android平台buffer播放探索】Steaming Source Player
- java对象序列化与反序列化
- jQuery 点击tr选中checkbox,并点击checkbox本身也正常,表格练习完工
- 数据结构复习之【图】二
- cocos2d-x封装一个转码的工具解决中文乱码可以直接拖过去用通用跨平台


